-
Notes from Broadband Video Leadership Breakfast
Yesterday, I hosted and moderated the inaugural Broadband Video Leadership Breakfast, in association with the CTAM New England and New York chapters, here in Boston (a few pics are here). We taped the session and I'll post the link when the video is available. Here are a few of key takeaways.
My opening question to frame the discussion centered on broadband's eventual impact on the cable business model: does it ultimately upend the traditional affiliate fee-driven approach by enabling a raft of "over-the-top" competitors (e.g. Hulu, Netflix, Apple, YouTube, etc.) OR does it complement the model by creating new value and choice? As I said in my initial remarks, I believe that how this question is ultimately resolved will be the key determinant of success for many of the companies involved in today's broadband ecosystem and video industry.
I posed the question first to Peter Stern, who's in the middle of the action as Chief Strategy Officer of Time Warner Cable, the second largest cable company in the U.S. I thought his answer was intriguing: he said that it is cable networks themselves who will determine the sustainability of the model, depending on whether they choose to put their full-length programs online for free or not.
Later in the session, he put a finer point on his argument, saying that "a move to online distribution by cable networks would directly undermine the affiliate fees that are critical to creating great content" and that finding ways to offer these programs only to paying broadband Internet access subscribers was a far better model for today's cable networks and operators to pursue (for more see Todd Spangler's coverage at Multichannel News).
Peter's point echoes my recent "Cord-Cutters" post: to the extent that cable networks - which now attract over 50% of prime-time viewership, and derive a third or more of their total revenues from affiliate fees - withhold their most popular programs from online distribution, they provide a powerful firewall against cord-cutting. Speaking for myself for example, the prospect of missing AMC's "Mad Men" (not available online anywhere, at least not yet...) would be a powerful disincentive for me to yank out my Comcast boxes.
These thoughts were amplified by the other panelists, Deanna Brown, President of SN Digital, David Eun, VP of Content Partnerships for Google/YouTube, Roy Price, Director of Digital Video for Amazon and Fred Seibert, Creative Director and Co-founder of Next New Networks, who held fast to a highly consistent message that broadband should be thought of as expanding the pie, thereby creating a new medium for new kinds of video content. David, in particular cited the massive amount of user-uploaded and consumed video at YouTube (amazingly, about 13 hours of video uploaded every minute of every day) as strong evidence of the community and context that broadband fosters.
Still, our audience Q&A segment revealed some very basic cracks in the panelists' assertions that the transition to the broadband era can be orderly and managed (not to mention that afterwards, I was privately barraged by skeptical attendees). First and foremost these individuals argued the idea that the cable industry can maintain the value of its subscription service by using the control-oriented approach typified by the traditional windowing process flies in the face of valuable lessons learned by the music industry.
Of course most of us know that sorry story well by now: an assortment of entrenched, head-in-the-sand record labels forcing a margin rich, but speciously valued product (namely the full album or CD) on digitally empowered audiences, who decided to take matters into their own hands by stealing every song they could click their mouses on. Consequently, a white knight savior (Apple) offering a legitimate and consumer-friendly purchase alternative (iPod + iTunes), which would grew to be so popular that it has made the record labels beholden to it, while simultaneously hollowing out the last vestiges of the original album-oriented business model.
Does history repeat itself? Are Peter and the other brightest lights of the cable industry deluding themselves into thinking that a closed, high-margin, windowed platform like cable can ever possibly morph itself into a flexible, must-have service for today's YouTube/Facebook generation?
I've been a believer for a while that by virtue of their massive base of broadband-connected homes, high-ARPU customer relationships and programming ties, cable operators have enormous incumbent advantages to win in the broadband era. But incumbency alone does not guarantee success. Instead, what wins the day now is staying in tune with and adapting to drastically changed consumer expectations, and then executing well, day after day. One look at the now gasping-for-breadth behemoth that was once proud General Motors hammers this point home all too well.
As Fred succinctly wrapped things up, "The reason I love capitalism is that it forces all of us to keep doing things better and better." To be sure, broadband and digital delivery are unleashing the most powerful capitalistic forces the video industry has yet seen. What impact these forces ultimately have on today's market participants is a question that only time will answer.
What do you think? Post a comment now!
Categories: Aggregators, Broadband ISPs, Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators, Indie Video
Topics: Amazon, CTAM, Google, Next New Networks, Scripps, SN Digital, Time Warner Cable, YouTube
-
October '08 VideoNuze Recap - 3 Key Themes
Welcome to November. October was a particularly crazy month with the unfolding financial crisis. Here are 3 key themes.
1. Financial crisis hurts all industries; broadband is no exception
In October the financial crisis was omnipresent. During the month I addressed its probable effects on the broadband industry here and here so I'm not going to spend much more time on it today. Suffice to say, for the foreseeable future, the key industry metrics are financing, staffing and customer spending. Conserving cash and getting to breakeven are paramount for all.
In particular, in "Thinking in Terms of a 'GOTI' Objective" I tried to provide some food for thought about why focus is so important right now. Industry CEOs' jobs have gotten a whole lot harder in the wake of the meltdown; those with the best strategic and financial skills will come through the storm, others will encounter significant challenges.
2. Broadband video is still in very early stages of development
I'm constantly trying to gauge just how developed the broadband video industry actually is. All kinds of indicators continue to suggest to me that we're still in the very early days. For example, in one post this month comparing iTunes and Hulu, it was evident that iTunes is currently far outpacing Hulu in TV episode-related revenues. Remember that Hulu is the undisputed premium ad-supported aggregator. And that the ad-supported business model itself is predicted by most to eventually be far larger than the paid model. That iTunes is so far ahead for now shows how young Hulu really is (in fact, just celebrating its first anniversary) and how much more development the ad-supported model still has ahead of it.
I think another relevant indicator of progress is how well the broadband medium is distinguishing itself from alternatives by capitalizing on its key strengths. In "Broadband Video Needs to Become More Engaging," I noted that while there have recently been positive signs of progress, overall, much of broadband's engagement potential is still untapped. That's why I'm always encouraged by compelling UGV contests like the one Fox and Metacafe unveiled this month or by technology like EveryZing's new MetaPlayer that drives more granular interactivity. To truly succeed, broadband must become more than just an online video-on-demand medium.
3. Cable operators are central to broadband video's development
As ISPs, cable operators account for the lion's share of broadband Internet access. Further, their ongoing efforts to increase bandwidth widens the universe of addressable homes for high-quality content delivery. Still, their multichannel subscription-based business model is increasingly threatened by broadband's on-demand, a la carte nature. As delivery quality escalates and consumer spending remains pinched, the notion of dropping cable in favor of online-only access become more alluring.
Yet in "Cutting the Cord on Cable: For Most of Us It's Not Happening Any Time Soon," I explained why restricted access to popular cable network programs and an inability to easily view broadband video on the TV will keep cable operators in a healthy position for some time to come. Still, it's a confusing landscape; this month I noticed Time Warner Cable itself helped foster cable bypass, when in the midst of its retransmission standoff with LIN TV, it offered an instructive video for how to watch most broadcast network programming online. Comcast also got into the act, unveiling "Premiere Week" on its Fancast portal. These kinds of initiatives remind consumers there's a lot of good stuff available for free online; all you need is a broadband connection.
Lots more to come in November, stay tuned.
Categories: Broadband ISPs, Broadcasters, Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators, Technology, UGC
Topics: Comcast, EveryZing, FOX, Hulu, iTunes, LIN TV, MetaCafe, Time Warner Cable
-
Cutting the Cord on Cable: For Most of Us It's Not Happening Any Time Soon
Two questions I like to ask when I speak to industry groups are, "Raise your hand if you'd be interested in 'cutting the cord' on your cable TV/satellite/telco video service and instead get your TV via broadband only?" and then, "Do you intend to actually cut your cord any time soon?" Invariably, lots of hands go up to the first question and virtually none to the second. (As an experiment, ask yourself these two questions.)
I thought of these questions over the weekend when I was catching up on some news items recently posted to VideoNuze. One, from the WSJ, "Turn On, Tune Out, Click Here" from Oct 3rd, offered a couple examples of individuals who have indeed cut the cord on cable and how their TV viewing has changed. My guess is that it wasn't easy to find actual cord-cutters to be profiled.
There are 2 key reasons for this. First it's very difficult to watch broadband video on your TV. There are special purpose boxes (e.g. AppleTV, Vudu, Roku, etc.), but these mainly give access to walled gardens of pre-selected content, that is always for pay. Other devices like Internet-enabled TVs, Xbox 360s and others offer more selection, but are not really mass adoption solutions. Some day most of us will have broadband to the TV; there are just too many companies, with far too much incentive, working on this. But in the short term, this number will remain small.
The second reason is programming availability. Potential cord-cutters must explicitly know that if they cut their cord they'll still be able to easily access their favorite programs. Broadcasters have wholeheartedly embraced online distribution, giving online access to nearly all their prime-time programs. While that's a positive step, the real issue is that cord-cutters would get only a smattering of their favorite cable programs. Since cable viewing is now at least 50% of all TV viewing (and becoming higher quality all the time, as evidenced by cable's recent Emmy success), this is a real problem.
To be sure, many of the biggest ad-supported cable networks (MTV, USA, Lifetime, Discovery) are now making full episodes of some of their programs available on their own web sites. But these sites are often a hodgepodge of programming, and there's no explanation offered for why some programs are available while others are not. For example, if you cut the cord and could no longer get Discovery Channel via cable/satellite/telco, you'd only find one program, "Smash Lab" available at Discovery.com. Not an appealing prospect for Discovery fans.
Then there's the problem of navigation and ease of access. Cutting the cord doesn't mean viewers don't want some type of aggregator to bring their favorite programming together in an easy-to-use experience. Yet full streaming episodes are almost never licensed to today's broadband aggregators. Cable networks are rightfully being cautious about offering full episodes online to aggregators not willing to pay standard carriage fees.
For example, even at Hulu, arguably the best aggregator of premium programming around, you can find Comedy Central's "The Daily Show" and "Colbert Report." But aside from a few current episodes from FX, SciFi and Fuel plus a couple delayed episodes from USA like "Monk" and "Psych," there's no top cable programming to be found.
As another data point, I checked the last few weeks of Nielsen's 20 top-rated cable programs and little of this programming is available online either. A key gap for cord-cutters would be sports. At a minimum, they'd be saying goodbye to the baseball playoffs (on TBS) and Monday Night football (on ESPN). In reality, sports is the strongest long-term firewall against broadband-only viewing as the economics of big league coverage all but mandate carriage fees from today's distributors to make sense.
Add it all up and while many may think it's attractive to go broadband only, I see this as a viable option for only a small percentage of mainstream viewers. Only when open broadband to the TV happens big time and if/when cable networks offer more selection will this change.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Aggregators, Broadcasters, Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators, Devices, Telcos
Topics: AppleTV, Comedy Central, Discovery, ESPN, FX, Hulu, Lifetime, Roku, SciFi, TBS, USA, VUDU, Xbox360
-
Inside the Netflix-Starz Play Licensing Deal
This past Wednesday, Starz, the Liberty Media-owned premium cable network, licensed its "Starz Play" broadband service to Netflix. The three year deal makes all of Starz's 2,500 movies, TV shows and concerts available to Netflix subscribers using its Watch Instantly streaming video feature. Very coincidentally I happened to be at Starz yesterday for an unrelated Liberty meeting, and had a chance to speak to Starz CEO Bob Clasen, who I've known for a while, to learn more.
On the surface the deal is an eye-opener as it gives a non-cable/telco/satellite operator access to Starz's
 trove of prime content. As I've written in the past, cable channels, which rely on their traditional distributors for monthly service fees, have been super-sensitive to not antagonizing their best customers when trying to take advantage of new distribution platforms. This deal, which uses broadband-only distribution to reach into the home, no doubt triggers "over-the-top" or "cable bypass" alarm bells with incumbent distributors.
trove of prime content. As I've written in the past, cable channels, which rely on their traditional distributors for monthly service fees, have been super-sensitive to not antagonizing their best customers when trying to take advantage of new distribution platforms. This deal, which uses broadband-only distribution to reach into the home, no doubt triggers "over-the-top" or "cable bypass" alarm bells with incumbent distributors. Then there is the value-add/no extra cost nature of Netflix's Watch Instantly feature. That there is no extra charge to subscribers for Starz's premium content (as there typically is when subscribing to Starz through cable for example) raises the question of whether Starz might have given better pricing to Netflix to get this deal done than it has to its other distributors.
But Bob is quick to point out that in reality, the Netflix deal is a continuation of Starz's ongoing push into broadband delivery begun several years ago with its original RealNetworks deal and continued recently with Vongo. To Starz, Netflix is another "affiliate" or distributor, which, given its tiny current online footprint does not pose meaningful competition to incumbent distributors. With only about 17 million out of a total 100 million+ U.S. homes subscribing to Starz, broadband partnerships are seen as a sizable growth opportunity by the company.
Further, Starz has been aggressively pitching online deals to cable operators and telcos for a while now, though only the latter has bit so far (Verizon's FiOS is an announced customer). Cable operators seem interested in the online rights, but have been reluctant to pay extra for them as Starz requires.
Bob also noted that Starz's wholesale pricing was protected in its Netflix deal, and that for obvious reasons of not hurting its own profitability, Starz has strong incentives to preserve incumbent deal terms in all of its new platform deals.
To me, all of this adds up to at least a few things. First is that Netflix must be paying up in a big way to
 license Starz Play. I assume this is an obvious recognition by Netflix that it needed more content to make Watch Instantly more compelling (see also Netflix's recent Disney Channel and CBS deals). Since it's not charging subscribers extra, Netflix is making a bet that over time - and aided by its Roku and other broadband-to-the-TV devices - Watch Instantly will succeed and as a result, will drive down its costs by reducing the number of DVDs the company needs to buy and ship. That seems like a smart long-term bet as the broadband era unfolds.
license Starz Play. I assume this is an obvious recognition by Netflix that it needed more content to make Watch Instantly more compelling (see also Netflix's recent Disney Channel and CBS deals). Since it's not charging subscribers extra, Netflix is making a bet that over time - and aided by its Roku and other broadband-to-the-TV devices - Watch Instantly will succeed and as a result, will drive down its costs by reducing the number of DVDs the company needs to buy and ship. That seems like a smart long-term bet as the broadband era unfolds.And while I agree that Starz Play on Netflix doesn't represent real competition to cable, telco and satellite outlets today, it's hard not to see it as a signal that traditional distributors are losing their hegemony in premium video distribution. (for another example of this, see Comedy Central's licensing of Daily Show and Colbert to Hulu). As I've said for a while, over the long term, the inevitability of broadband all the way to the TV portends significant disruption to current distribution models. I see Netflix at the forefront of this disruptive process.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Aggregators, Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators, Devices, Telcos
Topics: CBS, Comedy Central, Disney, Liberty Media, Netflix, Starz, Verizon
-
Key Takeaways from Yesterday's MTV - Visible Measures Deal
Yesterday brought news that MTV Networks has signed a deal with Visible Measures, a third-party analytics firm, to measure broadband video activity across over 340 of its sites. This is by far the biggest deal that Visible Measures has landed to date. And in the torrent of broadband deals and partnerships that hit my inbox each day, I believe this one is noteworthy for 3 reasons:
1. More evidence of syndication's growing importance to major media companies
A number of recent announcements have underscored the broadband market's shift to the "syndicated
 video economy," but this move by MTV demonstrates how the SVE concept is starting to infiltrate major media companies' thinking. To date many of these companies have taken a somewhat informal approach to syndication, giving users embed code or passing clips on to YouTube for promotion, but not diligently measuring the activity or benefits.
video economy," but this move by MTV demonstrates how the SVE concept is starting to infiltrate major media companies' thinking. To date many of these companies have taken a somewhat informal approach to syndication, giving users embed code or passing clips on to YouTube for promotion, but not diligently measuring the activity or benefits. MTV's deal shows serious intent to measure its syndication activity and use the resulting data to help shape its broadband video efforts. As a leader in broadband video, MTV's Visible Measures deal is certain to prompt other major media companies to up their commitment to syndication as well. This would synch with a comment a CEO of a broadband technology vendor told me yesterday: "...every content company we deal with has now prioritized syndication and they are actively addressing the technical, business and political issues."
2. Programming business changing to be more data-centric
You can be sure that when armed with a trove of new Visible Measures-generated data about how its users watch and engage with its video, MTV's programming decisions will be influenced accordingly. As I wrote in my initial post about Visible Measures last June, that's one of the beauties of broadband consumption vs. TV - all user behavior can be tracked and assessed. By knowing - down to the frame - things like when viewers dropped out, what scenes they rewound/viewed repeatedly and what clips they most shared, MTV's programming decisions should become ever smarter.
 Stalwart creatives may decry this research-intensive approach to program development, but in media businesses challenged to reduce costs and increase profitability, anything that helps predict what users will watch (and therefore help drive a higher ROI per program) is invaluable. This is especially true for TV networks trying to rationalize the pilot process. Gauging real-life user reactions to various videos online can only make the pilot process more effective.
Stalwart creatives may decry this research-intensive approach to program development, but in media businesses challenged to reduce costs and increase profitability, anything that helps predict what users will watch (and therefore help drive a higher ROI per program) is invaluable. This is especially true for TV networks trying to rationalize the pilot process. Gauging real-life user reactions to various videos online can only make the pilot process more effective.3. Ad model becomes even more important, and more refined
Though there's wide consensus that advertising will drive the broadband business for the foreseeable future, there is acute anxiety about how advertising will ultimately work (formats, insertion frequency, etc.) and how much revenue it will produce. While there's been plenty of testing to date, there's also been much guesswork involved. MTV for one will now have a bird's-eye view into its users' reactions to various ad implementations so it can continually refine its approach.
Optimizing the broadband ad model is a key issue for all players in the market. Recently I asserted that Hulu is leaving a lot of money on the table with its current ad approach, and is also pressuring parent company NBC's own ad business. I suggested Hulu could insert more ads, but without hard data, it's impossible to say how much more. Here's another example: all those viral SNL clips of Tina Fey doing Sarah Palin could mean real money for NBC, yet without proper tracking and ad implementations their real value is being underoptimized. The list of examples goes on. More data on video usage can really help the ad model.
In sum, MTV's deal with Visible Measures is both a positive step in the ongoing maturation of broadband video, syndication and advertising and a harbinger of more deals to come.
(Note: if you'd like to learn more about MTV's and others' syndication strategies, please join me for a panel I'll be moderating next Tuesday, October 7th at Contentonomics in LA. Joining me are MTV's Greg Clayman, Revision3's Damon Berger, ClipBlast's Gary Baker and EgoTV's Jimmy Hutcheson. Information and registration is here.)
What do you think? Post a comment.Categories: Analytics, Cable Networks
Topics: MTV, Visible Measures
-
Presidential Debate Video on NYTimes.com is Classic Broadband Disruption
Here's a classic example of how broadband is causing traditionally distinct worlds to collide: on Friday night the NYTimes.com opened up a dedicated streaming video window on their home page, where the presidential debate played for the full hour and a half. I watched the first half of the debate there, before switching on the TV and watching it on CNN HD. While HD was obviously superior, the NYTimes.com's video was more than adequate (though disappointing there was no full screen option).
Saturday morning and NYTimes.com is offering the video on demand, with an accompanying full written transcript. You can search (try typing "wrong" to see), to get how many times each candidate used that term, and then jump to the points in the video when it was used (alas, it would be great if the Times gave the ability to clip that specific segment and virally distribute it). The Times does offer a "check point" feature, where it fact checks the candidate's assertions. Note that other sites like ABCNews.com and CNN.com have the debate on demand today as well, but not the interactive features that NYTimes.com has.
Stop and consider how significant all of this is - a print publisher using broadband to offer a clear alternative to broadcasters and cable networks in carrying high-quality video. It's a great value proposition just for people without access to TVs at the moment of the live event, but more important, it provides a glimpse of some very interesting additional opportunities for NYTimes.com.
For example, the site could host its own post-debate punditry show, assembling its all-star lineup of daily Times columnists. Dedicated Times readers would no doubt love to see a roundtable with Frank Rich, Tom Friedman, William Kristol, Maureen Dowd and others dissect the candidates' performances, rather than waiting for their thoughts to come in columns over the next several days. Also think about how this type of show would scoop Sunday talk shows like NBC's "Meet the Press" or ABC's "This Week with George S." in bringing serious punditry to political junkies who can't wait.
In fact, the NYTimes.com could even offer viewers the ability to interact with their columnists, building on the wildly popular commenting feature already available with each daily piece in the paper itself. This type of immediacy and interactivity would be very compelling. The site could also offer the live debate video stream with a companion chat area that would enable viewer engagement during the debate itself (see Paltalk for an example of how this could work).
And last but not least, NYTimes.com could offer a single premium sponsorship slot to underwrite its whole debate coverage. Think Mercedes, Four Seasons, Cartier or other upscale brands might be interested?
As I've said many times, broadband blurs previously siloed worlds, bringing more competition to traditional players like broadcast and cable networks. They now need to deliver more to stay competitive. For video entrants like NYTimes, broadband creates enormous new opportunities to both leverage core assets/talent and pioneer new and different ways to create value. Another reminder why broadband is so disruptive for so many.
What do you think? Post a comment.
Categories: Broadcasters, Cable Networks, Newspapers, Politics
Topics: ABC News, CNN, NYTimes.com, Paltalk
-
CNN is Undermining Its Own Advertisers with New AC360 "Live Webcasts"
Here's an example of how convoluted broadband's use can be.
On CNN's AC360 program last night, Anderson Cooper was promoting "live webcasts" with news anchor Erica Hill, which would run during on-air commercial breaks. As explained here, the idea is that CNN viewers can go "behind the scenes" to continue their AC360 experience by watching the live stream on their computers. I dutifully did this and watched Hill and Cooper somewhat mindlessly chatting/flirting for several minutes.
But wait: if CNN is urging on-air viewers to turn their attention to these "webcasts" during commercial breaks, then that means that CNN is diverting attention from its own on-air advertisers. That undermines CNN's all-important advertiser value proposition. That of course begs the question: is CNN's ad sales team on board with these webcasts? And if so, what are they thinking??
I guess the argument could be made that CNN believes anyone who would jump online would be multi-tasking, so they'd still have their TV on. Yet at a minimum they'll mute their TV's audio (as I did) to hear the webcast's audio. That means the users' eyes and ears are now focused online instead of on-air.
CNN has been laudably in the forefront of weaving online technology into their on-air programs. Tune in to anchor Rick Sanchez's show some time and you'll him juggling an orgy of on-air Twittering, Facebook emailing and YouTube video sharing. Cooper too has been relentlessly flogging his AC360.com web site since its recent relaunch.
That all works, in my opinion. But the "live webcasts" do not. They might work after or before the on air program, but not during. At a time when advertiser relationships are more tenuous than ever due to the rise of DVRs, VOD and broadband, the last thing a network should be doing is undermining their value proposition any further. Someone at CNN no doubt thought, "hey these will be really cool." That may be, but in my opinion, they're not smart business. Broadband should complement existing franchises not undermine them.
What do you think? Post a comment.
Categories: Cable Networks
Topics: CNN
-
CNN Gets UGC Foothold with "iReport" Feature
Give CNN credit: their 4 month-old "iReport" feature seems to making steady progress, demonstrating how a traditional news organization can effectively incorporate user-generated content.
If you haven't been following iReport, it is essentially a user generated content feature on CNN.com that
 incents CNN viewers to upload their own photos and videos to the site. Sometimes these uploads are in response to "assignments" CNN has created such as "Midwest flooding," "Celebrity look-alikes" or "Is Jesse Jackson relevant?" Other times it's just users uploading content they find compelling. As an extra inducement, CNN will periodically show these iReport segments on-air (as an "AC 360" viewer, I notice them several times per week).
incents CNN viewers to upload their own photos and videos to the site. Sometimes these uploads are in response to "assignments" CNN has created such as "Midwest flooding," "Celebrity look-alikes" or "Is Jesse Jackson relevant?" Other times it's just users uploading content they find compelling. As an extra inducement, CNN will periodically show these iReport segments on-air (as an "AC 360" viewer, I notice them several times per week). CNN benefits from the iReport content in several ways. First and most obvious, CNN is creating a virtual extension of its news gathering operation, providing it access to free content that is often as good or better in terms of its immediacy and relevance that what CNN itself could produce. In this era of belt-tightening by all news organizations, CNN is able to do more with less.
Second, iReport generates a powerful "citizen journalist" engagement opportunity for both ardent newshounds and amateurs alike to help shape the news, not just passively watch it. This helps CNN position itself as more relevant and in-touch, giving it a competitive advantage vs. its peers.
Last, iReport gives CNN an ongoing stream of promotional opportunities, keeping the brand fresh and in-touch with audiences. Last night, Campbell Brown (who was sitting in for Anderson Cooper as anchor on
 AC360) provided another great example: a new iReport Film Contest, which challenges users to produce short films from the campaign trail. So rather than the perpetual pundit talking heads, this contest will provide a fresh look at the current election. (I must note regrettably though, that currently clicking on the AC360 site's link to learn more about the contest's details yields a "Page Not Found" error. Ugh.)
AC360) provided another great example: a new iReport Film Contest, which challenges users to produce short films from the campaign trail. So rather than the perpetual pundit talking heads, this contest will provide a fresh look at the current election. (I must note regrettably though, that currently clicking on the AC360 site's link to learn more about the contest's details yields a "Page Not Found" error. Ugh.)Broadband poses particular challenges for broadcast and cable news organizations, not only because it shifts consumption away from linear-scheduled newscasts to pure on-demand, but also because it enables news to be covered and made by amateurs outside the traditional boundaries of bureaus and assignment desks. Figuring out to responds to and shape these new forces is a key challenge for all news organizations. With the iReport feature, CNN seems to off to a good start.
What do you think? Post a comment now!
Categories: Cable Networks, UGC
-
Viacom - Google/YouTube Litigation Moves Into Slippery Territory
If you were off the grid last week celebrating the July 4th holiday, there were some important fireworks in the ongoing Viacom - Google/YouTube litigation well worth paying attention to.
Judge Louis Stanton of the US District Court in New York, who is presiding over the litigation, handed down an opinion that granted and denied some of what each party was requesting. The opinion is here. I have read it and below is my synopsis (remember I'm not a lawyer):
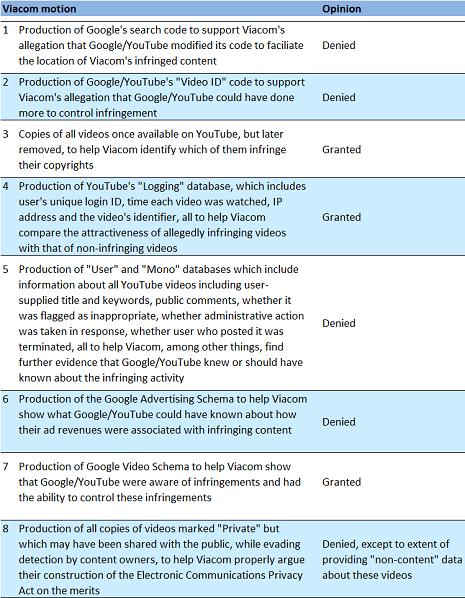
The fourth item is the one that has gained the most attention and controversy. Privacy advocates are ballistic that this is a violation of users' privacy rights. Specifically they have cited Judge Stanton's characterization of Google/YouTube's objection to this particular Viacom request on the basis of privacy concerns as "speculative." A cottage industry of ridicule has broken out across the blogosphere regarding whether the 80 year-old Judge Stanton is sufficiently tech literate to grasp online privacy concerns. Many believe Viacom will use the data to sue individual users for viewing pirated copies of Viacom's programs on YouTube.
Like everyone else, I'm concerned about privacy here as well and recognize that Judge Stanton has moved this case into some very slippery territory. Yet, at a higher level, I'm feeling some resentment toward Google and YouTube, especially given its famous "do no evil" mantra. There is no question that they knew pirated versions of key Viacom (and other) programs were showing up on YouTube, yet at the time months went by without them candidly addressing the issue and doing something sufficiently proactive about it. To many, including me, the standoff then was (and continues to be) a high-stakes battle between two multi-billion dollar companies jockeying for negotiating leverage.
When we use various web sites (whether for broadband or other uses), there is an implicit and explicit understanding that our privacy will not be trifled with. Sites have a right to defend their business practices based on their interpretation of the existing laws, but they need to be balanced by what impact their actions may ultimately have for their users. Each of us has our own interpretation of whether Google/YouTube should have done more to protect Viacom's and others' copyrights, but as Judge Stanton's decision shows, to what extent YouTube's users' privacy is protected is now entirely up to his interpretation.
What do you think? Post a comment and let everyone know!
Categories: Cable Networks, Video Sharing
Topics: Google, Viacom, YouTube
-
June '08 VideoNuze Recap - 3 Key Topics
Wrapping up a busy June, I'd like to quickly recap 3 key topics covered in VideoNuze:
1. Execution matters as much as strategy
I've been mindful since the launch of VideoNuze to not just focus on big strategic shifts in the industry, but also on the important role of execution. I'm not planning to get too far into the tactical weeds, but I do intend to show examples where possible of how successful execution can make a difference. This month, in 2 posts comparing and contrasting Hulu and Fancast (here and here) I tried to constructively show how a nimble upstart can get a toehold against an entrenched incumbent by getting things right.
While great execution is a key to successful online businesses, it may sometimes feel pretty mundane. For example, in "Jacob's Pillow Uses Video to Enhance Customer Experience" I shared an example of an arts organization has begun including video samples of upcoming performances on its web site, improving the user experience and no doubt enhancing ticket sales. A small touch with a big reward. And in this post about the analytics firm Visible Measures, I tried to explain how rigorous tracking can enhance programming and product decisions. I'll continue to find examples of where execution has had an impact, whether positive or negative.
2. Cable TV industry impacted by broadband
As many of you know, I believe the cable TV industry is a crucial element of the broadband video industry. Cable operators now provide tens of millions of consumer broadband connections. And cable networks have become active in delivering their programs and clips via broadband. Yet the broadband's relationships with operators and networks are complex, presenting a range of opportunities and challenges.
On the opportunities side, in "Cable's Subscriber Fees Matter, A Lot," I explained how the monthly sub fees that networks collect put them on a firm financial footing for weathering broadband's changes and an advantageous position compared to broadband content startups which must survive solely on ads. Further, syndication is offering new distribution opportunities, as evidenced by Scripps Networks syndication deal with AOL in May and Comedy Central's syndication of Daily Show and Colbert Report to Hulu and Adobe. Yet cable networks are challenged to exploit broadband's new opportunities while not antagonizing their traditional distributors.
For operators, though broadband access provides billions in monthly revenues, broadband is ultimately going to challenge their traditional video subscription business. In "Video Aggregators Have Raised $366+ Million to Date," I itemized the torrent of money that's flowed into the broadband aggregation space, with players ultimately vying for a piece of cable's aggregation revenue. These and other companies are working hard to change the video industry's value chain. There will be a lot more news from them yet to come.
3. Video publishing/management platforms continue to evolve
Lastly, I continued covering the all-important video content publishing/management platform space this month, with product updates from PermissionTV, Brightcove and Entriq/Dayport. Yesterday, in introducing Delve Networks, another new player, I included a chart of all the companies in this space. I put a significant emphasis on this area because it is a key building block to making the broadband video industry work.
These companies are jostling with each other to provide the tools that content providers need to deliver and optimize the broadband experience. The competitive dynamic between these companies is very blurry though, with each emphasizing different features and capabilities. Nonetheless, each seems to be winning a share of the expanding market. I'll continue covering this segment of the industry as it evolves.
That's it for June; I have lots more good stuff planned for July!
Categories: Aggregators, Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators, Technology
Topics: AOL, Brightcove, Comedy Central, Delve, Entriq, Fancast, Hulu, Jacobs Pillow, PermissionTV, Scripps, Visible Measures
-
Comcast/Fancast, Hulu and the Role of Great Execution, Part 2
A couple of weeks ago in "Hulu Out-Executing Comcast in On-Demand Programming?" I took Comcast's Fancast to task because Hulu was first to implement its deal with Comedy Central for full episodes of "The Daily Show" and "Colbert Report." It was a missed opportunity for Fancast, which had previously announced a deal with Comedy Central for these shows. Hulu gained a bonanza of favorable press attention, likely spiking its usage.
Well fair is fair and so I'm now happy to report that Fancast has also posted these programs. But at the risk of sounding like a Fancast scourge (which I'm really not trying to be) Hulu continues to distinguish itself with a superior user experience. For those looking to succeed in broadband video the execution differences between these two sites provide key lessons.
First, after searching for The Daily Show on Hulu, the site automatically displays the most recent episodes first (beginning with last night's episode). When starting the player, Hulu's quick 7 second "brand slate" runs and then the program starts. This emphasis on a quick payoff no doubt reflects lessons Hulu's CEO Jason Kilar learned from his years at Amazon, which, like all great e-commerce sites knows that a distraction-free checkout process results in more completed transactions.
Conversely, at Fancast, after doing a search for Daily Show, the results are "Sorted by air date Ascending | Descending." Ascending is pre-selected, and the first episode shown is from April 9th, with Lewis Black. Huh - why such an old episode being shown first by default? And is the average user really going to be familiar with these sorting terms? Why not just offer choices like "Newest" and "Oldest" with "Newest" as the default?
When I tried watching several episodes I encountered more distractions and inconsistency. I alternatively saw a 30 second pre-roll, a 15 second pre-roll and once I even got back-to-back 15 second pre-rolls (of the same A1 steak sauce ad no less). Contrast this with Hulu where each time I knew to expect the voiceover intoning "The following program is brought to you...." Hulu understands that positive online experiences emphasize usability and consistency.
Separately, Hulu offers the ability to send a link to the full episode to a friend or clip just a segment, which can also be posted easily to a number of social networking sites. The features worked flawlessly and when done the video resumed playing automatically. On the other hand, an envelope icon at Fancast reveals 2 sharing options, "Beginning of Video" or "Current Scene." Yet after clicking on both they seem to reveal the same screen. So what's the difference? Worse, after finishing up sharing, the video was frozen, forcing me to close the browser and start all over again. Ugh.
Just to be clear, I don't expect perfection and I do recognize that Fancast is still in beta. To put all this in some context and explain why I'm dragging you into the weeds with this part 2 post, I've long believed that broadband's openness will allow new aggregators to emerge, attempting to compete with incumbents like cable and satellite operators. Differentiating themselves is no small feat considering, as in this case, the underlying content they have will likely be similar to what's available elsewhere.
Hulu is differentiating itself through great execution - particularly noteworthy for such a young site. My
 guess is that execution and usability DNA run very deep within the Hulu team. On the other hand, Fancast has not yet demonstrated comparable execution mastery and as a result is leaving the competitive door ajar for its customers to give Hulu a try. Winning Hulu users back to Fancast will be tougher than winning them now.
guess is that execution and usability DNA run very deep within the Hulu team. On the other hand, Fancast has not yet demonstrated comparable execution mastery and as a result is leaving the competitive door ajar for its customers to give Hulu a try. Winning Hulu users back to Fancast will be tougher than winning them now. Broadband aggregation is going to be a battleground with big eventual payoffs. As a powerful incumbent, Comcast must do everything possible to preclude users from seeking out Hulu and other aggregators. (Truth be told, it is unlikely these broadband aggregators would have raised close to the $366+ million I recently reported in the first place had Comcast and other incumbents proactively seized the online aggregation space several years ago. But that's a story for another day.)
For all the time I spend talking about strategy at VideoNuze, I've always been a big believer that competition is mostly won in the trenches. That's especially true in online where great execution and usability separate winners from the rest. For Comcast, the competitive bar is far higher than it has ever been. To succeed, it must significantly improve its execution.
Categories: Aggregators, Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators
-
Scripps Networks Dips Into Syndication with AOL Video Deal
Scripps Networks, owner of the powerhouse cable brands HGTV and Food Network plus niche brands DIY, Fine Living and GAC, is joining the syndication fray, today announcing a deal with AOL Video for distribution of clips from at least 25 of its programs. The deal stops short of full program syndication along the lines of last week's Comedy Central-Hulu deal and others, but is still a meaningful step in extending these brands beyond the borders of their respective web sites.
I've been following Scripps Networks for a long while and recently got a briefing from Deanna Brown, who serves as president of the Interactive Group which handles all Internet-related activities at Scripps Networks. Brown joined the company a little over a year ago and is an online veteran, having served as an executive at both Yahoo and AOL previously.
Scripps was one of the early adopters of broadband video, initially seeding its site with program clips from HGTV and Food and more recently creating standalone broadband properties (e.g. HGTV KitchenDesign, HGTV BathDesign, others). Brown explained that Scripps views video as part of the overall user experience, not to be positioned as standalone. Contextualization drives more video consumption and page views. For the most recent 3 months Scripps averaged almost 10 million video views/month, up about 36% from the prior year's period. HGTV was a big part of that, doubling its video views year over year.
I've long thought that broadband is a huge win for Scripps because its lifestyle brands and programs are part information, part entertainment and presented in short segments. This is about as good a fit for online consumption as possible. In fact, over the years when content startups have sought my input, I've often referred to Scripps as an example of content having a highly actionable content model and a "natural base" of advertisers, a model for others to emulate in further product categories.
With Scripps, advertisers reach an audience that is both targeted and action-oriented. Given the massive size of the home and kitchen-related products markets, Scripps is in an enviable position. Yet once again reflecting the early state of the broadband video ad market, Brown explained that they're continuing to test what works in video advertising, particularly mid-rolls and overlays recently. Brown cited monetization flexibility as a key part of Scripps' recent decision to standardize on Maven Networks' platform. Note that in the AOL deal, Scripps will sell ads against its inventory.
Though Brown described herself as partnership-driven, most of Scripps broadband efforts have centered on building out its sites. She explained that they haven't felt pressure to do a lot of deals quickly, instead tending to be methodical about which distributors offer the best ROI potential. A key goal of its distribution deals is to reach younger audiences and video is seen as a way to speak to this audience. A slew of social networking initiatives are underway as well to tap this demo's online behavior.
With Scripps Networks poised to be separated on July 1st from the larger newspaper and broadcast businesses at E.W. Scripps, online will be a critical growth driver. That suggests we can expect plenty more video activity going forward.
Categories: Cable Networks
Topics: DIY, Fine Living, Food Network, GAC, HGTV, Scripps Networks
-
Hulu Out-Executing Comcast in On-Demand Programming?
The crew over at Hulu must be gleefully fist-bumping each other this week as Hulu scored a key strategic and public relations coup in adding to its lineup two of Comedy Central's most popular programs, "The Daily Show with Jon Stewart" and "The Colbert Report." Though officially positioned as a test, Hulu still deserves big-time kudos as the deal is an endorsement of its value proposition.
The deal and Hulu's execution illustrate a larger point that I've been making for a while: one of broadband's three key disruptions is that it enables new aggregators to gain an edge on larger incumbents by changing the dynamics of competition. To be more specific, in this case, I think that Hulu has out-executed Comcast, America's #1 cable operator by delivering new value to consumers and gaining important PR momentum. Here's why:
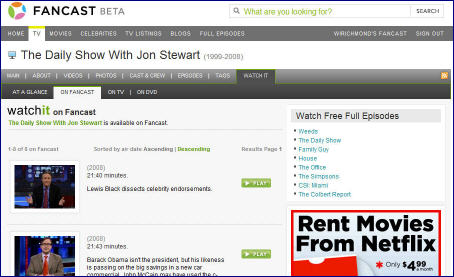
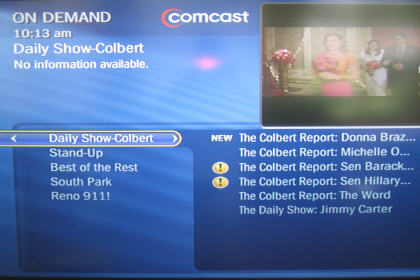
Fancast, which is Comcast's online portal (in beta), actually announced a deal with Comedy Central back on May 19th for access to these same programs and others. Yet go to Fancast and search for "Daily Show" and, as shown below, you won't find any Daily Show full episodes available, just an assortment of short clips and times when it's on TV. A Comcast spokesperson told me that Comcast's implementation is imminent, but its delay in getting the programs up and running is accentuated when you consider that Comedy Central must have done its distribution deal with Fancast BEFORE its deal with Hulu.
Second, and more concerning is that, as a Comcast digital subscriber, when I tried to find The Daily Show and Colbert in Comcast's VOD menu, all that is available are five older Colbert clips and 1 older Daily Show clip. My guess is these haven't been updated in a while. No full-length Daily Show or Colbert programs are available at all in VOD.
While the Comcast spokesperson told me that the company works closely with its programming partners like Viacom to figure out the optimal mix of programming to make available on VOD, I think an unavoidable conclusion here is that Comcast (and other cable operators) is constrained by its inability to monetize VOD programming with advertising (what this week's "Project Canoe" is meant to address) and to easily add new programming on the VOD menu. These programming gaps create opportunities for upstarts like Hulu to capitalize on.
It may be unfair to zero in so narrowly on Comcast's execution with Daily Show/Colbert, yet things weren't much different when I searched for MTV's popular "The Hills" on Hulu, Fancast and Comcast's VOD. While Hulu doesn't appear to have a deal for full episodes of "The Hills" it masks this cleverly by providing thumbail images and easy navigation back to MTV's site where the video lives, for over 50 episodes (this is tactic Hulu uses for ABC's shows as well). On the other hand, Fancast displays just 5 full episodes, 2 from this season and 3 from last. And on VOD there are also just 5 episodes, though all from this season.
I think it's pretty significant that Hulu, a site that only went live 3 months ago can not only gain access to hit Comedy Central programs like Daily Show/Colbert, but can execute quickly. Hulu is using its advantages - flexible technologies, interactive features (clipping, embedding, sharing), monetization capability, savvy PR and startup pluck to compete with far-larger incumbents like Comcast.
Of course Comcast racks up billions of VOD views each year and has vast resources, making it an important player in on-demand programming. Yet Hulu has managed to make Comcast's advantages look a little less intimidating. I asked the Comcast spokesperson about this. She acknowledged Hulu's progress, but maintained that Comcast believes its mulit-platform approach is stronger.
In the big picture that's true, but when it comes to winning consumers' hearts and minds, it's often execution, not broad strategy that carries the day. And don't forget, when Hulu is unshackled from the PC - with its content freely riding Comcast's broadband pipes all the way to the TV - execution will matter even more.
This week Hulu provided a textbook example of how broadband-only aggregators can gain a foothold against well-established incumbents. Comcast and other incumbents should be taking notice and getting their game on.
What do think? Post a comment and let everyone know!
Categories: Advertising, Aggregators, Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators
Topics: Comcast, Comedy Central, Fancast, Hulu, The Colbert Report, The Daily Show, Viacom
-
Cable's Sub Fees Matter, A Lot
In my recent post "Revisiting the Long Tail and Broadband" I explained how broadband is the next step in an evolution of video distribution systems and that now, after many years of growth, cable networks' niche, but collective audiences are exceeding those of the broadcasters.
Several readers emailed suggesting I append an important footnote to this analysis: there is a key business model difference between today's fledgling broadband video providers and cable networks. That difference is that cable networks benefit from monthly "sub fees" or "affiliate fees" that all distributors (cable TV and satellite operators, telcos, etc.) must pay to carry cable's programming. These fees are collected in addition to the advertising these networks sell. No such sub fees are available to broadband video providers (or broadcasters for that matter), at least not yet.
Having been in and around the cable industry for 20 years, I fully appreciate that sub fees matter a lot to cable networks. Since the beginning of the cable industry, they have served as a financial firewall for networks. Sub fees now range from pennies per month to over $3 for ESPN. Even on the low-end a "fully distributed" cable network (reaching approximately 80 million+ U.S. homes) reaps millions of sub fee dollars per month. And remember, that money comes in regardless of how well the network's ratings were that month. (btw, for an explanation of the genesis of sub fees, have a look at "Cable Cowboy," Mark Robichaux's biography of TCI's John Malone).
Cable networks' financial security continues to be translated into improved programming quality. Recently, in "Golden Age for TV? Yes, on Cable," the NY Times' David Carr lamented that broadcast TV seems to be on a degenerative slide to offer "all manner of contests and challenges," yet noted that cable is ascendant with Emmy and Oscar-winning talent dotting its innovative new dramas. No surprise to anyone, financial muscle translates into programming quality.
All this helps to explain why, whenever I moderate a panel including cable network executives, they fall all over themselves to declare their allegiance to their current, paying distributors. Cable networks are stepping gingerly into the broadband era, careful not to upset their enviable business model.
Conversely, broadband upstarts have no incumbent customers to consider. While this frees them to strike creative and wide-ranging distribution deals, as best I can tell, they're going to be totally dependent on advertising for a long time to come. This is why I continue urging that broadband video advertising must mature further, and fast.
While broadband upstarts scramble and broadcasters struggle, cable networks will keep chugging along, nicely fueled by their consistent sub fees.
Categories: Broadcasters, Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators, Indie Video
Topics: ESPN
-
Revisiting The Long Tail and Broadband Video
Way back in the dark ages of March, 2005, I wrote a newsletter entitled, "The Long Tail of Video is About to Get Longer - What Role Will Cable Play?" I thought of it yesterday when I read an article in Multichannel News "Cable Bests Broadcast - Basic Networks Steamroll Into Summer with Lion's Share of Audience." I continue to believe that cable TV provides a lot of lessons for those thinking about broadband video's future.
First, a quick refresher on the idea of The Long Tail. In October, 2004, Chris Anderson, editor of Wired
 magazine, wrote an article which later turned into a book, asserting that once physical limitations (e.g. manufacturing, distribution, inventory, etc.) are removed - thereby allowing all products with niche appeal to be readily available to consumers - it turns out that the aggregate sales of these niche products are greater than the few "mass" products which were always available in traditional distribution channels. When this effect is plotted on an XY graph, the line depicting the tiny sales per niche unit extends indefinitely, forming a "long tail."
magazine, wrote an article which later turned into a book, asserting that once physical limitations (e.g. manufacturing, distribution, inventory, etc.) are removed - thereby allowing all products with niche appeal to be readily available to consumers - it turns out that the aggregate sales of these niche products are greater than the few "mass" products which were always available in traditional distribution channels. When this effect is plotted on an XY graph, the line depicting the tiny sales per niche unit extends indefinitely, forming a "long tail."The Long Tail was an important contribution in understanding how the world of digital economics works. Anderson cited multiple examples where the Long Tail was evident (e.g. Amazon, Rhapsody, etc.). In my March '05 piece I explained that the Long Tail concept was familiar to anyone in the cable TV business: the traditional "head" content was the broadcasters, the long tail was the constellation of niche-oriented cable TV channels.
When I wrote the piece, as a group, basic cable TV's total audience had just nudged past the collective audience of the broadcasters for the first time (i.e. The Long Tail effect was becoming evident). While each cable channel's audience was small relative to each broadcaster's, cable's total audience was now greater. It had taken 30+ years for cable audience to reach this point.
Flash forward 3+ years to the Multichannel article revealing that in May sweeps period, cable's audience share had surged to 60%, compared with 40% for the broadcasters. And it's interesting to note that a key part of cable's May win is due to cable co-opting traditional broadcast programming: in May TNT's airing of NBA playoff games accounted for 12 of the month's top 20 most-watched programs.
What does all this have to do with broadband video? As I explained back in '05, in reality, broadband distribution is essentially extending the long tail of programming. Broadband allows startups and established players (including cable and broadcast networks!) to utilize newly available broadband infrastructure to reach their audiences. The result is a massive proliferation of new programming and new viewer behaviors, further fragmenting audiences to ever-smaller niches.
Today's cable channels will eventually be seen as the "mid-tail" with broadband as the hyper-niche long tail. Given their own first-hand experience of the last 30 years, cable operators, cable networks and broadcast networks should all have a pretty clear view of the challenges and opportunities that broadband creates. How well they respond will determine who will be the winners and losers of the next 30 years.
Categories: Broadcasters, Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators
Topics: The Long Tail
-
Akimbo, Vongo Expose Risks for Broadband Pioneers
The last few days' news about Akimbo and Starz's Vongo service, two of the earliest players in broadband video delivery, shows how risky the broadband video market can be for pioneers.
Akimbo - which has closed its doors after raising approximately $50 million since 2003 - demonstrates that
 misjudging the key characteristics of an early market can be devastating. Akimbo's faulty assumptions included:
misjudging the key characteristics of an early market can be devastating. Akimbo's faulty assumptions included:- Anticipating that consumers would be willing to buy a broadband-only set-top box, despite overwhelming research to the contrary.
- Expecting that consumers would be willing to pay yet another monthly subscription fee, although broadband's value proposition was still in its infancy and consumers were already complaining about the high cost of cable/satellite subscription services.
- Building its initial content strategy using a pure "Long Tail" approach of aggregating lots of niche programmers, not grasping that Long Tail models only succeed when "head" content - in this case from broadcasters and cable networks - is also included.
As these misjudgments became obvious, the box was dropped, select cable programming was added to the content lineup, pricing was changed and management was overhauled. Ultimately in February '08, the whole company strategy was blown up, as Akimbo unsuccessfully tried to get a toehold in the already over-crowded white-label content management/publishing business. But once a startup is in a deep hole, it's almost impossible to climb out.
Meanwhile, Starz's announcement yesterday with Verizon, of its first "wholesale deal" for broadband delivery of its programming, shows additional risks for early players. Yesterday I caught up with Bob Greene, EVP of Advanced Services at Starz, for whom I did some consulting work several years ago on Vongo's predecessor service, Starz Ticket.
 Starz launched Vongo in early '06 as a broadband-only subscription and download-to-own service, featuring programming it had under contract, plus other categories it later added. Vongo went to market direct-to-consumer and through device partners like HP, Samsung, Toshiba, Creative and Archos, but Vongo's growth has been modest as the broadband subscription category has yet to really take off.
Starz launched Vongo in early '06 as a broadband-only subscription and download-to-own service, featuring programming it had under contract, plus other categories it later added. Vongo went to market direct-to-consumer and through device partners like HP, Samsung, Toshiba, Creative and Archos, but Vongo's growth has been modest as the broadband subscription category has yet to really take off.Vongo's larger goal was getting deals done with existing service providers like cable, telco, and broadband ISPs. But this aspiration ran into the buzzsaw of incumbents' intransigence, illustrating that reliance on ecosystem partners, who often have divergent motivations, can be very risky. In this case, Vongo's would be distributors perceived Vongo as less as an opportunity to grow the market and tap new consumer behaviors, and more as a potential long-term end-run, with immediate threats to profit margins and cash flow contribution.
Cable operators have been saying "no thanks" to distributing Vongo, concluding it had more downside risk to existing Starz linear subscriptions and Video on Demand than it had upside broadband potential. The Verizon deal may reverse things; Bob says more deals are in the offing. Time will tell. In the meantime, with Vongo's direct marketing efforts set to be further de-emphasized, Starz's broadband fate is falling squarely into the hands of reluctant incumbent service providers.
Akimbo and Starz show that to succeed, it's essential to make correct fundamental assumptions about a market's early growth have a keen understanding of ecosystem partners' motivations and concerns. Missteps on any of these can have disastrous implications.
What do you think the lessons are from Akimbo and Starz's Vongo? Post a comment!
Categories: Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators, Devices, Startups, Telcos
Topics: Akimbo, Starz, Verizon
-
Online Movie Delivery Advances, Big Hurdles Still Loom
Online movie delivery is back in the news, but dramatic change is still well down the road in this space as usability, rights issues and incumbent business models/consumer behaviors pose formidable hurdles.
Yesterday Netflix announced a $99 appliance with Roku, enabling the company's "Watch Instantly" streaming service on TVs. That news follows Apple's deals with a number of big studios in early May obtaining "day-and-date" access to current titles. And today brings news that Bell Canada, that country's largest telco, is formally launching its Bell Video Store, also providing day-and-date delivery, of Paramount titles to start (and soon others), plus portable viewing on Archos devices.
Netflix, which I last wrote about here, took a shot across the bow of Apple TV and Vudu by introducing the
 Roku box, the lowest-priced broadband movies appliance yet. Apples-to-apples comparisons aren't fair as the stripped-down Netflix/Roku box doesn't have a hard-drive or equivalent processing. That inevitably means lower quality delivery vs. locally-stored content with the others, plus uncertainty about HD-delivery. Netflix/Roku's big advantage is that it's a value-add service for current Netflix subscribers, meaning no new fees as with the Apple TV/Vudu approaches.
Roku box, the lowest-priced broadband movies appliance yet. Apples-to-apples comparisons aren't fair as the stripped-down Netflix/Roku box doesn't have a hard-drive or equivalent processing. That inevitably means lower quality delivery vs. locally-stored content with the others, plus uncertainty about HD-delivery. Netflix/Roku's big advantage is that it's a value-add service for current Netflix subscribers, meaning no new fees as with the Apple TV/Vudu approaches.However, Watch Instantly has older titles and amounts to less than 10% of Netflix's total catalog. I don't see that changing much; Watch Instantly runs smack into studios' incumbent windowing approach and deals with HBO, Showtime and Starz for premium TV. Netflix's model is built on the home video window, so new online delivery rights must be obtained which will be a tough road. However, with Paramount, MGM, Lionsgate and others splintering from Showtime recently to set up their own premium channel, it's possible that some studios' rights may loosen up, but of course at a price.
Still, I don't see the Netflix/Roku box breaking 10% penetration of Netflix's sub base any time soon, barring a box giveaway. Enlarging the value proposition by licensing the Roku technology for inclusion in other devices (e.g. Blu-ray) could also help drive adoption.
Meanwhile, today Bell Canada is announcing the formal launch of its Bell Video Store. In beta since late '07,
 it offers 1,500 titles, now including day-and-date delivery from Paramount (and others soon according to Michael Freeman, Bell's director of product management who I spoke to yesterday). This is noteworthy, as it appears to be the first time a service provider has received day-and-date online access from any studio. If other providers follow suit we may finally witness some internal competition with sacrosanct-to-date Video on Demand initiatives.
it offers 1,500 titles, now including day-and-date delivery from Paramount (and others soon according to Michael Freeman, Bell's director of product management who I spoke to yesterday). This is noteworthy, as it appears to be the first time a service provider has received day-and-date online access from any studio. If other providers follow suit we may finally witness some internal competition with sacrosanct-to-date Video on Demand initiatives.By using ExtendMedia's platform, Bell is also enabling downloads-to-own directly to Archos portable devices. With a couple million satellite homes and fiber IPTV fiber-based deployments continuing, there are multiple three screen options looming for Bell. Yet for now these are limited. Michael confirmed Bell has no plans to offer a branded movie appliance a la Netflix/Roku, meaning it will dependent on XBoxes and other PC-TV bridge devices.
Renewed progress and experimentation are welcome in this space, but lots of hard work remains for online movie delivery to become mainstream.
What do you think of the online movie delivery space? Post a comment now!
Categories: Aggregators, Cable Networks, Devices, Downloads, FIlms, Studios
Topics: Apple, Bell Canada, HBO, Netflix, Paramount, Roku, Showtime, Starz, VUDU
-
HBO Wakes Up to Broadband
HBO's deal with Apple to include its programs in the iTunes store has received widespread coverage in the last couple of days, particularly because it includes differentiated pricing for the first time.
Indeed, while it's a big story that Apple's Steve Jobs has finally consented to deviate from his "one price for all" approach - which NBC couldn't attain last fall - there is another angle on this announcement: the possibility that, at long last, HBO has woken up to broadband video's potential.
HBO's absence from the broadband scene has been noticeable. As the most profitable and acclaimed TV
 network, I've long thought that HBO had significant upside in pursuing broadband initiatives. Instead it has badly lagged Showtime and Starz, its two principal rivals in the premium network space, as well as other networks.
network, I've long thought that HBO had significant upside in pursuing broadband initiatives. Instead it has badly lagged Showtime and Starz, its two principal rivals in the premium network space, as well as other networks. Showtime in particular has been quite innovative in both creating broadband-only extras for its programs, plus enticing user-involvement opportunities. For its part, Starz has been aggressive in pursuing Vongo, its broadband-subscription service, which continues to make inroads with numerous device partnerships.
Yet HBO has seemed contentedly disinterested in broadband. Between its hefty subscription fees and healthy DVD business, broadband has likely been seen as just a gnat buzzing about. HBO's lack of broadband interest is evident on its web site which has just a smattering of video clips and highlights, and it is fairly static, with little-to-nothing enticing for the broadband user.
In reality, broadband could have likely been adding real value to HBO's business. With the proper incentives, HBO's creative production partners could have easily come up with broadband extras that would have appealed to the diehard fans of its programs. In addition to their sheer programming value, these would have helped drive more fan loyalty and stickiness between seasons. That would help address HBO's churn rate during its off-season periods.
While HBO's iTunes relationship is a step forward, it's a small one. Contrast its approach to soon-to-be-corporate-sibling Bebo's programming model (which I wrote about yesterday), with its intense focus on community engagement and the different philosophies are evident. Of course HBO is a programming powerhouse and there's no arguing with its success. But for it to fully embrace broadband's opportunities, it would benefit from looking at what Bebo and others are currently doing.
Categories: Aggregators, Cable Networks, Indie Video, Video Sharing
Topics: Apple, HBO, iTunes, Showtime, Starz, Vongo
-
More Questions than Answers at Digital Hollywood Spring
I'm just back from a couple days at Digital Hollywood Spring, one of the broadband industry's leading conferences. A key takeaway for me is that there are still many more outstanding questions about the broadband video industry's future - and their implications for other players in related industries - than there are concrete answers.
Here are 3 big ones worth considering:
What role will current video distributors play in an increasingly broadband-centric world?
The subscription video business, dominated by cable and satellite operators, generates approximately $80 billion/year, depending on whose data you use. The model is well-understood, and is a huge part of funding the value chain of cable networks, rights-holders and TV program producers. Bundling ever more channels (50,70,100+) into digital tiers and charging ever-higher prices for them has been a core industry revenue driver.
Yet data continues to show that out of all those channels, the average household still only watches 5-10 at the most. Couple that with the migration to broadband, DVR and on-demand consumption and one is left with the feeling that there is a significant disconnect between the way video is packaged and priced today with growing consumer expectations and behaviors. Is the current approach sustainable long term or are new players (e.g. Sezmi) going to successfully disrupt the formula? Any major disruption would have significant ripple effects.
Is the ad-supported business model for broadband video going to deliver for all the content providers relying on it?
I've been a big supporter of the ad-supported approach for a while and believe in it strongly in the long-term. Yet as I see more and more content providers, aggregators, social networks and others look to it as their primary business model, I'm growing concerned that in the short-term there isn't going to be enough money to go around to support everyone. To be sure, current growth rates are strong, yet at DH many of advertising's big hurdles to reach long-term success were mulled over: achieving scale, standardizing formats, understanding performance metrics, converting media buyers, targeting, proving interactivity's value and so on.
The efficacy of the broadband ad model online is particularly pressing for broadcasters. Though some research indicates on-air viewership is benefited from online program availability, long-term there can be no question that a substitution effect will take place as viewers decide "do I watch on-air OR online?"
Jeff Zucker, NBCU's CEO tersely captured the threat this poses in his now often-repeated question "are we trading analog dollars for digital pennies?" In other words, if someone watching an NBC show like The Office on Hulu currently brings NBC far less revenue than if they were watching it on-air, is the migration to broadband viewership actually causing a permanent down-sizing of broadcasters' ad revenue per minute viewed? A scary thought to contemplate.
What does all this mean for Hollywood?
Surely less subscription or ad revenue eventually means less money for everyone including the whole Hollywood apparatus that has been funded out of the traditional models. But how, when and to what extent does this play out?
Further, is the very nature of what's expected of Hollywood changing? Herb Scannell, CEO/founder of Next New Networks asserted in his panel that the current generation of 'auteurs' - multi-skilled and motivated people who can write, direct, produce, act and promote implies a far different role for how Hollywood creates value for itself in the future. In fact, Herb believes that technology-empowered talent is the biggest disruptive force to the traditional Hollywood equation.
The point was brought home to me in a offsite function I attended in which Bebo, the massive youth-oriented social network (recently sold to AOL for $850 million), outlined its big push into original entertainment (e.g. "KateModern," "Sofia's Diary," etc.). Their expectations of what they, creators and users will be doing to create value are starkly different from the Hollywood model.
And the questions continue. There are ample reasons to be enthusiastic about broadband video, still, we are living through transformational times impacting every corner of the traditional video value chain. For now many questions loom. Hopefully more answers will be forthcoming soon.
Do you have any answers? Post a comment and let everyone know!
Categories: Broadcasters, Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators, Devices
Topics: Bebo, Digital Hollywood, Next New Networks
-
Sunday Morning Talk Shows Need Broadband Refresh
In the heat of the Democratic primary, the five major Sunday morning talk shows have recently taken on greater prominence. For political junkies like me, even after a week's worth of endless campaign coverage, it is great sport to watch the candidates and their surrogates put the best face on the week's events, while eagerly trying to tee up issues for the coming week's news cycle.
The Sunday shows are also perfect fodder for broadband video consumption. On-air they are neatly segmented by guests and topics, their archives offer a vivid research opportunity for both editorial and user-driven curation, and the audiences that tune in are upscale and appealing to advertisers.
With all this going for them, I decided to investigate the online presence of the five Sunday morning shows, ABC's "This Week with George Stephanopoulos," CBS's "Face the Nation with Bob Schieffer," FOX's "Fox News Sunday with Chris Wallace," NBC's "Meet the Press with Tim Russert" and CNN's "Late Edition with Wolf Blitzer."
Though all of the sites had their strengths, as a group I found them to be surprisingly average initiatives, especially in comparison to the superb efforts these same networks have mounted for their online entertainment programming. (Note that all I found for "Late Edition" was a brochure page)
"FTN" would have to rank at the top of my list, primarily because it segments the show by its guests and topics and displays them in the user-friendliest manner. This allows the user to quickly zero in on desired segments. "This Week" and "MTP" do some of this as well, though I found their presentation not as straightforward. What's missing from all are related clips across episodes curated in a meaningful way. Presentation is very episode-centric.
While all the sites rely heavily on pre-roll ads, "FTN" gets credit for using some frequency capping. "This Week," seems to ignore the best practices that ABC.com follows in presenting its shows with limited interruptions. Not only does it not frequency cap, it also ran the same 2 ads - one for Intel and one for Verizon Wireless - over and over. Needless to say this became tiresome after clicking to watch several segments.
Meanwhile, navigation and available content on these sites are all over the board. "MTP" offers a link to watch the whole program with limited interruptions, while "FNS" offers a text transcript of the most recent program, but not a video of the whole program. "This Week's" main text navigation has links to pure text stories, text stories with embedded video clips, and video clips alone, but no way to sort the list by media type. Search on each site also yields highly diverse results - some video, some not. One missed opportunity is that none offer any user editing features. Putting together your own highlights reel to be embedded on a blog or social networking site would likely be great fun for many hard-core viewers.
The Sunday talk shows offer dynamite content, highly leverageable for broadband consumption. Hopefully as the political season rolls on we'll see the networks recognize this and continue to invest in new features and improved usability.
What do you think? Post a comment and let us all know!
Categories: Broadcasters, Cable Networks
Topics: ABC, CBS, CNN, FOX, NBC