-
Google and Verizon Net Neutrality Proposal Comes With Big Loopholes
Responding to rampant rumors last week concerning a potential side-deal on net neutrality, Google and Verizon held a conference call this afternoon unveiling a "Legislative Framework Proposal" by their respective CEOs Eric Schmidt and Ivan Seidenberg. The proposal is meant to influence other net neutrality stakeholders, including the FCC. Google and Verizon insisted there's no companion business deal between them.
On positive side, the companies' proposal tries to break the Washington net neutrality logjam by endorsing an open Internet backed up with a sensible, transparent and non-discriminatory approach that mainly leaves it up to networks to act responsibly. However, the proposal comes with at least 2 big loopholes which until clarified, will no doubt undercut a lot of the proposal's credibility.
Categories: Broadband ISPs, Regulation, Telcos
-
5 News Items of Interest for the Week of Aug 2nd
In addition to producing daily original analyses focused on the evolution of the online/mobile video industry, another key element of VideoNuze is collecting and curating links to industry coverage from around the web. Each week there are typically 30-40 stories that VideoNuze aggregates in its exclusive news roundup. Many readers have come to depend on this curated news collection to ensure they're always up to speed.
Now, to take news curation up another level, on Fridays I'm going to test out highlighting 5-6 of the most intriguing news items of the week. In case you missed VideoNuze for a day or two during the week, you can check in on Friday to see the these top 5-6 industry stories of the week, some of which VideoNuze may have covered itself. Synopses and implications are noted. Enjoy and let me know your reactions!
Wired to Produce Short Films For iPad
The tech magazine recruits Will Ferrell for four short videos that lampoon inventions that failed to take off. Exclusively for its iPad app. More evidence of print pub capitalizing on video.
Motorola and Verizon team up for TV tablet
Enjoying success with its Droid smartphones, Motorola now looks to challenge the iPad, with its own tablet device, using Google's Android OS. A partnership with Verizon could mean new online video features for the phone giant's FiOS service. Another sign of evolution in the pay-TV business.
Bewkes: Rental Delays From Netflix, Redbox Is Paying Off For DVD Sales
The 28-day DVD delayed release window Warner Bros. struck with Netflix earlier this year is helping the studio gain better sales for films The Blind Side and Sherlock Holmes. The deal helps Netflix position itself as a valued partner in the midst of declining DVD sales.
Dish to stream live TV on iPad, other devices
Dish Network takes place-shifting to a new level with plans for an iPad app that would allow remote streaming, likely using its Sling technology. Subscription TV, mobile video viewing and cool devices converge.
FCC Calls Off Stakeholders Meetings
The FCC's private net neutrality negotiations are off the rails as a reported bilateral deal between Verizon and Google causes controversy. Next steps are unknown as the FCC's plan to keep Internet playing field level hits a major pothole.Categories: Devices, FIlms, Magazines, Regulation, Satellite, Telcos
Topics: DISH, FCC, iPad, Motorola, Netflix, Verizon, Warner Bros., Wired
-
With Google-Verizon Deal, Net Neutrality Uncertainty for Video Providers Rises
A possible private deal between Google and Verizon, for how the latter will handle traffic on its wired and wireless networks, means the prospect of the FCC brokering a net neutrality consensus among key stakeholders just got less certain. The inconsistency that could result isn't good news for online and mobile video content providers seeking assurance that delivery of their content won't be affected by network operators either technically or financially.
To put this possible deal in context, the FCC has been trying to forge a net neutrality agreement among key parties in the wake of a recent court decision that severely curtailed its regulatory authority. The talks have been conducted in secret and the parties have pledged not to disclose their progress. The policy goal is to ensure network owners don't bias for or against any kind of traffic, so that the Internet's longstanding openness will be perpetuated.
Categories: Broadband ISPs, Regulation, Telcos
-
Verizon is Now Using Clearleap for FiOS Content Management
Clearleap, a web-based TV technology provider, is announcing that Verizon has integrated its platform to manage content on its FiOS 1 local channel throughout all of its U.S. markets served. FiOS 1 offers local news, sports, traffic and weather. One particular use of Clearleap's technology will be to streamline the uploading and management of video by professional sports teams who offer extra coverage on FiOS VOD (one example of this is with my hometown New England Patriots).
traffic and weather. One particular use of Clearleap's technology will be to streamline the uploading and management of video by professional sports teams who offer extra coverage on FiOS VOD (one example of this is with my hometown New England Patriots).
For Clearleap, Verizon is the biggest telco launch to date, and it broadens the company's customer base beyond the cable operators it works with that cover 12M subscribers. I talked to Braxton Jarratt, Clearleap's CEO last week who said that it took Verizon just a few months to get up and running with the Clearleap technology. Unlike its cable deployments, in Verizon's case it didn't have to deploy any physical hardware in Verizon's data centers.
Categories: Technology, Telcos, Video On Demand
-
Verizon's Droid X Hits the Market Today
The smartphone market takes another important step forward today as the Droid X officially becomes available. Made by Motorola, powered by Google's Android OS and sold exclusively by Verizon, the device has received rave reviews from those who have tested it. The Droid X is particularly interesting to me because it sports a 4.3 inch high-resolution display that makes mobile video watching more satisfying than ever. In addition, the Droid X takes 720p HD video, making it a high impact pocket video camera as well.
reviews from those who have tested it. The Droid X is particularly interesting to me because it sports a 4.3 inch high-resolution display that makes mobile video watching more satisfying than ever. In addition, the Droid X takes 720p HD video, making it a high impact pocket video camera as well.
As I wrote last month when the Droid X was unveiled, watching video on the device itself is only half the pleasure. Because the Droid X has both a mini-HDMI output and is DLNA compliant, it offers the opportunity to connect to the big screen TV to watch videos and browse photos there, making it a "mobile set-top box." This is a very exciting prospect and yet again creates new video value.
I've been testing the HTC Evo from Sprint for the last month, which has a similar screen size to the Droid X and also has the HDMI output. It's very cool to be able to shoot HD video on the phone and then immediately be able to connect it to the TV and play it. My experience is that video stored locally on the Evo plays really nicely, but unfortunately when video is played over the network there's a fair amount of degradation, which may partly due to Sprint coverage at my house. I'm planning to get a Droid X and will be interested to see how they compare.
Regardless, it's still very early days in terms of the high-quality video features (both playback and record) for this new generation of smartphones and what we're seeing now is just a preview of things to come.
What do you think? Post a comment now (no sign-in required).Categories: Mobile Video
-
Best Buy's "Movie Mode" Mobile App is Part of New Promotional Trend
When I got home from my long holiday weekend I noticed a huge promotion on the cover of the Best Buy Sunday circular for its new "Movie Mode" app (see below). The app was featured with an offer to buy the new Sprint Evo, but it works on other Android devices as well as iPhones and certain BlackBerry models.
Categories: FIlms, Mobile Video
Topics: Best Buy, Droid X, Evo, Sprint, Verizon
-
Verizon Launches Droid X; Video is a Key Proposition in Battle with iPhone 4
Verizon officially unveiled its latest Droid smartphone this afternoon, the Droid X from Motorola, running Google's Android 2.1 mobile OS (with an upgrade to Android 2.2 planned for later this summer). I've been following
 coverage this afternoon, and aside from all of the other cool new features, what resounds most for me is how video-focused the device is, and how strongly Verizon will be promoting this.
coverage this afternoon, and aside from all of the other cool new features, what resounds most for me is how video-focused the device is, and how strongly Verizon will be promoting this. I've previously said that video would move to the forefront of the ferocious smartphone battle underway between Google (with Android) and Apple (with the iPhone). With the Droid X launch, and the recent HTC Evo from Sprint (which I've been testing and will report on next week), plus numerous others to follow, I'm convinced that we are now getting into the thick of things.
From what I've read about the Droid X, there are 3 dimensions of the video proposition, each of which stacks up differently with the iPhone 4: (1) shooting video, in 720p HD, (2) watching video on the device's 4.3 inch 854 x 480 resolution screen, and (3) connecting the device via DLNA over a home network or via an HDMI-out port to your widescreen TV.
Categories: Mobile Video
Topics: Android, Apple, Droid, Google, Motorola, Verizon
-
Verizon CEO: No Mobile Spectrum Shortage, FCC Should Butt Out
Were you as surprised as I was to read yesterday that Verizon CEO Ivan Seidenberg is questioning the need to reclaim broadcast spectrum for mobile data use? Instead he believes that ongoing advances in technology will address any potential bandwidth squeeze. His comments represent a weird reversal because Verizon has been (for obvious reasons) a key proponent of gaining access to this spectrum. As I wrote a few weeks ago, the bandwidth reclamation concept is one of the most contentious in the FCC's recently released National Broadband Plan.
I'm not clear on what's going on here. The iPad's release this past weekend is yet another reminder of the infinite mobile data uses ahead. Meanwhile recently-amped up rumors that Verizon will get getting the iPhone later this year means lots of data increases from Verizon itself. Throw in the coming proliferation of Android devices as yet more evidence of mobile data's rise. So why would Seidenberg now cast doubt on the spectrum reclamation effort? Beats me. Any ideas?
What do you think? Post a comment now (no sign-in required).Categories: Regulation, Telcos
-
Government to the Rescue in the Retransmission Consent Quagmire?
Earlier this week, in "Will Nasty Fee Fights Fuel Consumers' Cord-Cutting Interest," I conjectured that last weekend's WABC-Cablevision retransmission consent fee fight (the most recent of many fee fights) would ultimately sow consumers' interest "cutting the cord" in favor of free, online-only alternatives. Obviously that would be bad news for multichannel video programming distributors (MVPDs), but it would also be bad for the whole video ecosystem that depends on consumer payments for its economics to work.
In this context it's only mildly surprising that subsequently this week a group of MVPDs including Time Warner Cable, Cablevision, DirecTV, Verizon and others petitioned the FCC to intervene and revise the retransmission consent rules (for what it's worth, I can't remember the last time MVPDs asked the government for anything, except to stay out of their business). In a sure sign of who currently has the negotiating leverage, broadcasters sent their own letter saying the playing field was level and in no need of a review.
With broadcasters intent on getting paid for their signals, there are many chapters yet to be written in the retransmission consent story. The big risk here is that the parties' jousting will ultimately kill the proverbial golden goose, with consumers getting fed up and deciding they'll make do with whatever they can get through the combination of good old-fashioned antennas and a cheap convergence device that hooks their broadband connection to their TV. Cord-cutting has lacked a strong catalyst to date, but history shows that a wronged consumer is a motivated consumer. The TV industry as a whole needs to figure out the retransmission morass before consumers take things into their own hands.
What do you think? Post a comment now (no sign-in required)Categories: Broadcasters, Cable TV Operators, Satellite, Telcos
Topics: Cablevision, DirecTV, NAB, Time Warner Cable, Verizon
-
Sezmi is Slick; Marketing It Will Be the Big Challenge
While in LA this week, I caught up with Phil Wiser, Sezmi's president and co-founder and got another good look at the Sezmi service, which just officially launched in the entire LA market with Best Buy. I've been covering Sezmi for over 3 years, and from a technical and product standpoint, I continue to be impressed with what it has accomplished, especially for a 1.0 launch. Out-of-the box set up is very straightforward and a series of intuitive menus quickly creates a personalized user profile complete with recommended shows based on your interests and selections from linear and on-demand channels.
Sezmi gained my attention early on because unlike other broadband-only devices (e.g. Roku, Vudu, ZillionTV, AppleTV, gaming consoles, etc.), Sezmi's goal has always been to become a full replacement for existing multichannel video programming distributors ("MVPDs"). That "boil the ocean" strategy has
 required it to develop its own hybrid broadcast/broadband content delivery system, sign up local broadcasters for access to their bandwidth, ink carriage deals with cable networks and design the user experience from scratch, among other things. Having done much of that work (with a key exception being to still get the remaining cable channels from Disney/ESPN, Fox, Scripps and A&E into the line-up), Sezmi's next challenge is to actually market the service and add subscribers cost-effectively. This could well prove to be Sezmi's biggest challenge.
required it to develop its own hybrid broadcast/broadband content delivery system, sign up local broadcasters for access to their bandwidth, ink carriage deals with cable networks and design the user experience from scratch, among other things. Having done much of that work (with a key exception being to still get the remaining cable channels from Disney/ESPN, Fox, Scripps and A&E into the line-up), Sezmi's next challenge is to actually market the service and add subscribers cost-effectively. This could well prove to be Sezmi's biggest challenge.The market for multichannel video subscriptions has never been more competitive than it is today. Deep-pocketed cable operators, satellite operators and telcos (and in some places 3rd party "overbuilders" like RCN) are beating the hell out of each other in many U.S. geographies. For example, here in the Boston area we're bombarded daily with ads on radio, in newspapers, in direct mail, through door-hangers and other means, to switch providers. While there are a lot of noisy promotional offers, there are plenty of product and technology-based pitches as well - more HD channels, faster broadband speeds, better VOD and so on. The "triple play" bundle of video, voice and data is a significant marketing lever. I don't know what the marketing cost per acquired customer is for Comcast or Verizon these days, but I have no doubt it has never been higher.
This is battleground that Sezmi is now entering after nearly four years of development. Many people are skeptical about Sezmi's odds of success (read TDG president Michael Greeson's well-done piece from last week for a rundown of the issues), at least as Sezmi is currently configured. Some of these concerns are very valid, in particular Sezmi's $299 upfront equipment fee (which is pretty much unique in the industry), its currently incomplete channel lineup (note also that HBO, Showtime and Starz are also not available) and the $20/mo rate which is marginally better than alternatives (but is likely to increase anyway as more channels and especially expensive ones like ESPN are added).
No question, Sezmi faces a steep marketing challenge. Still, I believe there are reasons for optimism. First, as Sezmi has said many times, it is not a box company and Best Buy isn't its only route to market. It plans deals with telco and ISP partners who will not only bundle its pricing but also erase the upfront charge through a rental model. The rental could be very aggressive depending on the partner's goals, opening up more pricing competitiveness for Sezmi. Second, Sezmi's user interface and certain product features are very compelling differentiators. Granted, incumbent MVPDs are not standing still (see Cablevision's "Media Relay" announcement just yesterday), but the fact that Sezmi owns its whole system from end to end gives it more control and flexibility to enhance the product (for example in VOD it is not relying on traditional vendors).
Lastly, and I'll admit this is where things get fuzzy, but I do think there's a segment of existing MVPD customers who hunger for something new, better and lower cost than is currently available. I've made the analogy for Sezmi to what JetBlue has done in the airline industry and I think that still holds. Depending on how distinctive Sezmi's positioning and messaging is, I think it could really resonate with younger, urban, tech-savvy users. One Sezmi feature alone - access to all YouTube videos - is a totally new value proposition. Phil and I quickly searched YouTube yesterday for "Alec Baldwin Hulu Super Bowl Ad" and in seconds there it was. Can any other MVPD offer that today?
There are plenty of reasons to discount Sezmi's chances of success, but I think that's premature thinking, especially given how dynamic the video landscape is today. But even if Sezmi doesn't thread the needle and fully surmount the marketing challenges ahead, the company still has a lot of value in its technology and products. If Vudu fetched a reported $100 million from Wal-Mart, and Sling got $380 million from DISH as announced a couple years ago, then there should be a palatable financial exit in store for Sezmi as well, even with $75 million or so invested to date. Of course its investors and executives are hoping for far more than just a "palatable" final chapter. The real test of what's in store for Sezmi is just now beginning.
What do you think? Post a comment now (no sign-in required).
Categories: Cable TV Operators, Satellite, Telcos
Topics: Comast, SezMi, Sling, TDG, Verizon, VUDU
-
Google's Fiber-to-the-Home Experiment Could Cost $750 Million or More
I hope for Google's sake that it understands the cost to build its 1 gigabit/second ultra high-speed fiber network experiment announced today could be $750 million or more. Even for Google that's a very big number, especially considering the company has said it has no intention of actually pursuing this as a business. Of course, we don't know exactly what Google is forecasting its project costs to be, but using Verizon's FiOS numbers wouldn't be a bad starting point to do the math. So here goes.
Google said it would offer the gigabit service to between 50,000 and 500,000 people. Let's start at the high end of that range. Verizon has disclosed that it will spend $18 billion to pass approximately 18 million homes in its footprint with its FiOS fiber-to-the-home network. It's not fair to do a straight average and assume that Verizon is still paying $1,000/home passed given that its costs have no doubt declined over the years.
 However, in Google's case, since it has approximately zero experience laying fiber in neighborhoods, and won't get the same level of vendor discounts that Verizon enjoys, it is probably fair to assume Google will spend at least $1,000 per home passed. So if it goes all the way to 500,000 homes, that's $500 million in neighborhood build-out costs.
However, in Google's case, since it has approximately zero experience laying fiber in neighborhoods, and won't get the same level of vendor discounts that Verizon enjoys, it is probably fair to assume Google will spend at least $1,000 per home passed. So if it goes all the way to 500,000 homes, that's $500 million in neighborhood build-out costs. But that's only to wire the neighborhoods, then the service has to be deployed in the homes themselves. That means in-home wiring, on-premise equipment, labor, trucks, insurance, overhead, etc. Estimates for Verizon's per home cost vary, but $500 is in the range often cited. In Verizon's case they're also deploying a set-top box to deliver TV, which Google hasn't announced plans to do (more on that below), so that cost should be deducted. But on the flip side, once again, because Google has never wired a consumer's home (that I'm aware of anyway) it has a steep learning curve ahead of it, meaning its costs could be much higher than Verizon's.
But to make things easy, let's just use the $500 per installed home. So 500,000 homes at $500 apiece, another $250 million for the project. Add it to the $500 million for the neighborhood build-outs and the total is $750 million. This assumes Google decides to go all the way to 500,000. Obviously if it stopped at 50,000, the costs would be a lot lower.
However, there's another big caveat that could drive Google's costs far higher: passing 500,000 homes does not equal having 500,000 customers. It's impossible to predict what percentage of a community's residents would take the Google experimental service. One way of thinking about it is that around 65% of American homes currently subscribe to broadband Internet service. What percentage of those will Google lure? Say it's around 15%. So in a community with 100,000 residents for example, Google may get only get 9,750 people to take its gigabit service (100,000*.65*.15). That means Google may need to pass fiber by 10 homes for every one it gets as a participant in its experiment. Put another way, the $500 million homes passed budget could increase by a factor of 10x. (In case you're wondering, by comparison, Google's 2009 net income was $6.5 billion.) Each subscriber's home would have cost Google approximately $10,750 to connect.
Executives at cable operators and telcos - who build and operate residential networks for a living - are very familiar with modeling network deployment costs. But I wonder, how familiar do you think Google is? Does it know what it has bitten off here? And for what benefit exactly - to test next-generation apps? Hmm. Everyone knows video is the biggest bandwidth hog; an expensive experiment isn't going to change that. And also remember, Google only plans to sell broadband Internet access, not a full bundle with TV or voice. It says it will do this at competitive prices, which means around $50-$100/mo. At these revenue levels and with operating costs that I haven't even mentioned, it's inconceivable to me that there's a positive business case for Google's gigabit experiment.
I'm all for innovation and for pushing competitors along. But Google's experiment really has me scratching my head. No doubt the folks at Verizon, Comcast and other big broadband ISPs are wondering as well. It's one thing for Google to throw $2.5-$3 million at a 52-second Super Bowl ad, but quite another to be contemplating a $750 million experiment with ambiguous goals. What am I missing?
What do you think? Post a comment now (no sign-in required).
Categories: Broadband ISPs, Technology
Topics: Comcast, Google, Verizon
-
Scoring My 2009 Predictions
As 2009 winds down, in the spirit of accountability, it's time to take a look back at my 5 predictions for the year and see how they fared. As when I made them, they're listed below in the order of most likely to least likely to pan out.
1. The Syndicated Video Economy Accelerates
My least controversial prediction for 2009 was that video would continue to flow freely among content providers numerous third parties, in what I labeled the "Syndicated Video Economy" back in early 2008. The idea of the SVE is that "destination" sites for online audiences are waning; instead audiences are fragmenting to social networks, mobile devices, micro-blogging sites, etc. As a result, the SVE compels content providers to reach eyeballs wherever they may be, rather than trying to continue driving them to one particular site.
Video syndication continued to gain ground in '09, with a number of the critical building blocks firming up. Participants across the ecosystem such as FreeWheel, 5Min, RAMP, YouTube, Visible Measures, Magnify.net, Grab Networks, blip.TV, Hulu and others were all active in distributing, monetizing and measuring video across the SVE. I heard from many content executives during the year that syndication was now driving their businesses, and that they only expected that to increase in the future. So do I.
2. Mobile Video Takes Off, Finally
When the history of mobile video is written, 2009 will be identified as the year the medium achieved critical mass. I was bullish on mobile video at the end of 2008 primarily due to the iPhone's success and my expectation that other smartphones coming to market would challenge it with ever more innovation. The iPhone has continued its amazing run in '09, on track to sell 20 million+ units. Late in the year the Droid, which Verizon has relentlessly promoted, began making inroads. It also benefitted from Verizon highlighting AT&T's inadequate 3G network. Elsewhere, 4G carrier Clearwire continued its nationwide expansion.
While still behind online video in its development, mobile video is benefiting from comparable characteristics. Handsets are increasingly video capable, just as were computers. Mobile content is flowing freely, leaving the closed "on-deck" only model behind and emulating the open Internet. Carriers are making significant network investments, just as broadband ISPs did. A range of monetization companies have emerged. And so on. As I noted recently, the mobile video ecosystem is healthy and growing. The mobile video story is still in its earliest stages, we'll see much more action in 2010.
3. Net Neutrality Remains Dormant
Given all the problems the Obama administration was inheriting as it prepared to take office a year ago, I predicted that it would not expend energy and political capital trying to restart the net neutrality regulatory process. With broadband ISP misbehavior not factually proven, I also thought Obama's predilection for data in determining government action would prevail. However, I cautioned that politics is a tough business to predict, and so anything can happen.
And indeed, what turned out is that in September, new FCC Chairman Julius Genachowski launched a vigorous net neutrality initiative, despite the fact that there was still little data supporting it. With backwards logic, Genachowski said the FCC would be guided by data it would be collecting, though he was already determined to proceed. In "Why the FCC's Net Neutrality Plan Should Go Nowhere" I argued, among other things, that the FCC is way off the mark, and that in the midst of the gripping recession, to risk the unintended consequences that preemptive regulation carries, was foolhardy. Now, with Comcast set to acquire a controlling interest in NBCU, net neutrality advocates will say there's even more to be worried about. It looks like we can expect action in 2010.
4. Ad-Supported Premium Video Aggregators Shakeout
The well-funded category of ad-supported premium video aggregators was due for a shakeout in '09 and sure enough it happened. Players were challenged by little differentiation, hardly any exclusive content and difficulty attracting audiences. The year's biggest casualty was highflying Joost, which made a last ditch attempt to become a white label video platform before being quietly acquired by Adconion. Veoh, another heavily funded player, cut staff and changed its model. TidalTV barely dipped its toe in the aggregation waters before it became an ad network.
On the positive side, Hulu, YouTube and TV.com continued their growth in '09. Hulu benefited from Disney coming on board as both an investor and content partner, while YouTube improved its appeal to premium content partners and brought on Univision and PBS, among others. Aside from these, Fancast and nichier sites like Dailymotion and Babelgum, there isn't much left to the aggregator category. With TV Everywhere services starting to launch, the opportunity for aggregators to get access to cable programming is less likely than ever. And despite their massive traffic, Hulu and YouTube have significant unresolved business model issues.
5. Microsoft Will Acquire Netflix
This was my long ball prediction for '09, and unless something happens in the waning days of the year, I'll have to concede I got this one wrong. Netflix has remained independent and is charging along with its own streaming "Watch Instantly" feature, now used by over half its subscribers, according to recent research. Netflix has also broadened its penetration of 3rd party devices, adding PS3, Sony Bravia TVs and Blu-ray players, Insignia Blu-ray players this year, in addition to Roku, XBox and others. Netflix is quickly becoming the most sought-after content partner for "over-the-top" device makers.
But as I've previously pointed out, Netflix's number 1 challenge with Watch Instantly is growing its content selection. Though it has a deal with Starz, it is largely boxed out of distributing recent hit movies via Watch Instantly by the premium channels HBO, Showtime and Epix. My rationale for the Microsoft acquisition is that Netflix will need far deeper pockets than it has on its own to crack open the Hollywood-premium channel ecosystem to gain access to prime movies. For its part, Microsoft, locked in a pitched battle with Google and Apple on numerous fronts, could gain advantage with a Netflix deal, positioning it to be the leader in the convergence era. Meanwhile, others like Amazon and YouTube continue to circle this space.
The two big countervailing forces for how premium video gets distributed in the future are TV Everywhere, which seeks to maintain the traditional, closed ecosystem, and the over-the-top consumer device-led approach, which seeks to open it up. It's hard not to see both Netflix and Microsoft playing a major role.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Advertising, Aggregators, Broadband ISPs, Deals & Financings, Mobile Video, Regulation, Syndicated Video Economy
Topics: Apple, AT&T, Fancast, FCC, Hulu, iPhone, Joost, Microsoft, Netflix, Veoh, Verizon, YouTube
-
Mobile Video Advertising Market Shows Strength
Mobile video advertising is showing strength, benefiting from consumer adoption of the "mobile Internet," strong growth in video-capable smartphones and improving availability of high-quality content for mobile devices.
I gained further insight on the mobile video ad opportunity in a conversation yesterday with Ujjal Kohli, the CEO of Rhythm New Media, a firm focused on mobilizing and monetizing TV programming that has raised
 $27 million to date from a group of blue-chip of investors. Later this week Rhythm will formally unveil "RAMP," the Rhythm Advertising Media Platform, a mobile video ad network targeted to brands already advertising on TV who now also want to have a mobile presence.
$27 million to date from a group of blue-chip of investors. Later this week Rhythm will formally unveil "RAMP," the Rhythm Advertising Media Platform, a mobile video ad network targeted to brands already advertising on TV who now also want to have a mobile presence.Ujjal makes a strong case that mobile video is an ideal environment for brand building, and that it addresses many of the challenges that TV advertising itself is facing (clutter, distraction, fragmentation, inadequate frequency/targeting/measurability). Ujjal believes that the nature of mobile video consumption, with its relatively short duration, focused user sessions gives brands a renewed opportunity to engage their target audiences with hard-to-skip messages, not only in the prime-time window, but throughout the day as well.
Rhythm has been helping stoke the market for high-quality mobile video content by building video apps for clients like Discovery, E! Entertainment, TMZ, TV.com, Family Guy and others. App building has been a means to an end for the Rhythm, which is primarily focused developing its mobile video ad network. In Q4 the company has sold and run 20+ campaigns, for brands like MasterCard, Nikon, Toyota, Marriott, Anheuser-Busch and others. These are almost always 15 second spots repurposed from TV campaigns which is no surprise, as the mobile market is not yet big enough to warrant custom creative.
Ujjal explained that a key Rhythm differentiator is that its ads allow interactivity, or the ability for the user to click on an ad's call to action, as is common online. Rhythm has devised a way to incorporate interactivity in ads shown against videos viewed on iPhones, where the use of QuickTime doesn't enable linking. Ujjal said that click-through rates for its "interactive pre-roll" unit fall in the 2%-6% range, while a "full page" ad unit used for mobile photo viewing, (e.g. slide shows on TMZ.com) generate click-throughs up to 11%. Ujjal would not specify what volume of ads Rhythm is serving, except to say it's in the millions/month and that the CPMs are higher than in online video or TV itself.
I've been very bullish on mobile video for some time now, as I believe it is following a similar growth pattern as online video. The macro-trends supporting mobile video's growth are impressive: Nielsen believes that in Q4 '09, 40% of all phones sold will be smartphones and that by 2011 they'll be majority. By then Nielsen forecasts 90 million a month will be watching mobile video. According to its Q3 '09 A2/M2 report, almost 16 million are now watching mobile video/month, up 53% since Q3 '08. They are watching an average of 3 hours, 15 minutes/month. While this is inexplicably down a bit from a year ago, it's worth noting that the heaviest users, to nobody's surprise are age 12-17 (7 hours, 13 minutes) and 18-24 (4 hours, 20 minutes). As these segments age they'll no doubt carry along their mobile video expectations.
Another dynamic sure to have a positive impact on mobile video consumption is the intensifying competitive battle between carriers and between smartphone manufacturers themselves. The recent AT&T-Verizon ad war about their 3G availability is a glimpse of how these companies will use network capacity (key to a positive video experience) as a competitive lever. On the handset side, there is hyper activity: Motorola's Droid is off to a respectable start, a bevy of Google's Android-based smartphones are due in 2010, and, complicating things further, Google plans to release its own "unlocked" (i.e. carrier neutral) Nexus One smartphone next year. While the iPhone opened the smartphone floodgates, many others are now rushing to get a piece of the action.
The biggest uncertainty impacting mobile video's growth is the wireless networks' ability to keep up . All the snazzy smartphones in the world won't matter if users can't get 3G or better access to watch quality video. But, if broadband is any guide, wireless carriers will build out capacity to meet demand, driving up data plan subscriptions and their own ARPU. Broadband also illustrates that as the necessary building blocks fall into place, content providers will be motivated to take part, providing consumers with ever more choices. While it's still early days, taken together it looks as if big things lie ahead for mobile video and for those like Rhythm who can help monetize it.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Advertising, Mobile Video
Topics: AT&T, Google, Rhythm New Media, Verizon
-
4 Items Worth Noting for the Nov 16th Week (FCC's Open Access, Broadcast woes, Droid sales, AOL cuts)
Following are 4 items worth noting for the Nov 16th week:
1. FCC raises "Open Access" possibility, would further government's control of the Internet - As reported by the WSJ this week, the FCC is now considering an "Open Access" policy that would require broadband Internet providers to open up their networks for use by competitors. The move comes on top of FCC chairman Julius Genachowski's recent proposal for formalizing net neutrality, a plan that I vigorously oppose. Open Access gained steam recently due to a report released by Harvard's Berkman Center that characterized the U.S. as a "middle-of-the-pack" country along various broadband metrics. The report has been roundly dismissed by service providers as drawing incorrect conclusions due to reliance on incomplete data.
The FCC is in the midst of crafting a National Broadband Plan, as required by Congress, aimed at providing universal broadband service throughout the U.S. as well as faster broadband speeds. Improving broadband Internet access in rural areas of the U.S. is a worthy goal, but the FCC should be pursuing surgical approaches for accomplishing this, rather than turning the whole broadband industry upside down. As for increasing speeds, major ISPs are already pushing 50 and 100 mbps services, more than most consumers need right now anyway. Broadband connectivity is the lifeblood for online video providers and any government initiative that risks unintended consequences of slowing network infrastructure investments is unwise.
2. Broadcast TV executives waking up to online video's challenges - Reading the coverage of B&C/Multichannel News's panel earlier this week, "Free Streaming: Killing or Saving the Television Business" featuring Marc Graboff (NBCU), Bruce Rosenblum (Warner Bros.), Nancy Tellem (CBS) and John Wells (WGA), I kept wondering where were these sentiments when the Hulu business plan was being crafted?
Hulu is of course the poster child for providing free access to the networks' programs, with just a fraction of the ad load as on-air. While the panelists agreed that the industry should be dissuading consumers from cord-cutting, Hulu is (purposefully or not) the chief reason some people consider dropping cable/satellite/telco service. For VideoNuze readers, it's old news already that broadcast networks have been hurting themselves with their current online model. What was amazing to me in reading about the panel is that what now seems obvious should have been very apparent to industry executives from the start.
3. Motorola Droid sales off to a strong start - The mobile analytics firm Flurry released data suggesting that first week Verizon sales of the Motorola Droid smartphone were an estimated 250,000. Flurry tracks applications on smartphones to estimate sales volume of devices. While the Droid results are lower than the 1.6 million iPhone 3GS units sold in that device's first week, Flurry notes that the iPhone 3GS was available in 8 countries and also had an installed base of 25 million 1st generation iPhones to draft on.
The Droid's success is important for lots of reasons, but from my perspective the key is how it expands the universe of mobile video users. As I noted in "Mobile Video Continues to Gain Traction," a robust mobile ecosystem is developing, and getting more smartphones into users' hands is crucial. I was in my local Verizon store this week and saw the Droid for the first time - though it lacks some of the iPhone's sleekness, the video quality is even better.
4. AOL's downsizing suggests further pain ahead - AOL was back in the news this week, planning to cut one-third of its employees ahead of its spin-off from Time Warner on Dec. 9th. The cuts will bring the company's headcount to 4,500-5,000, down from its peak of 18,000 in 2001. As I explained recently, no company has been hurt more by the rise of broadband than AOL, whose dial-up subscribers have fled en masse to broadband ISPs. Now AOL is going all-in on the ad model, even as the ad business itself is getting hurt by the ongoing recession. New AOL CEO Tim Armstrong is clearly a guy who loves a challenge; righting the AOL ship is a real long shot bet. I once thought of AOL as being a real leader in online video. Now I'm hard-pressed to see how the AOL story is going to have a happy ending.
Enjoy your weekends!
Categories: Advertising, Aggregators, Broadband ISPs, Broadcasters, Mobile Video, Portals, Regulation
Topics: AOL, Droid, FCC, Hulu, iPhone, Motorola, Verizon
-
4 Items Worth Noting from the Week of August 24th
Following are 4 news items worth noting from the week of August 24th:
1. Time Warner Cable, Verizon launch TV Everywhere trials - Little surprise that Time Warner Cable announced its own TV Everywhere trial yesterday, given that former sister company Time Warner has been one of its biggest proponents. More interesting was Verizon launching a TV Everywhere initiative, which I regard as a pretty strong indicator that most or all service providers will eventually get on board. (The Hollywood Reporter has a story that DirecTV is in talks too for online distribution of TBS and TNT to start).
I have to give credit to Time Warner CEO Jeff Bewkes, TV Everwhere's key champion, who's clearly generated a groundswell of support. While some critics see TV Everywhere as being at odds with the "open Internet" ethos, I continue to think of it as a big win for consumers eager to get online access to their favorite cable programs. Assuming authentication is proven in during the trials I expect a speedy rollout.
2. Conde Nast distributes through boxee - I was intrigued by news that Conde Nast Digital will begin distributing video from its Wired.com and Style.com sites through boxee. boxee and others who connect broadband to TVs are valuable for magazines and other content providers who have long been shut out of the cable/satellite/telco distribution ecosystem, thereby unable to reach viewers' TVs. Years ago special interest magazines missed big opportunities to get into cable programming, allowing upstart cable networks to grow into far larger businesses (consider ESPN vs. Sports Illustrated, Food Network vs. Gourmet or CNBC vs. Forbes). Broadband gives magazines, belatedly, an opportunity to get back into the game.
3. Amazon announces 5 finalists in UGC ad contest - Have you seen the 5 finalists' ads in Amazon's "Your Amazon Ad" contest, announced this week? They're quite clever, with some amazing special effects. The contest is another great example of how brands are tapping users' talents, posing new competition to ad agencies. I haven't written about this in a while, but I continue to be impressed with how different brands are pursuing this path. Doritos has been the most visible and successful with its user-generated Super Bowl ads.
4. Microprojectors open up mobile video sharing opportunities - Maybe I've been living under a rock because I just read about "microprojectors" for the first time this week (I have a decent excuse since as I non-iPhone owner I wouldn't have a use for one, yet). As the name suggests, these are pocket-size projectors that allow you to output the video from your iPhone to project onto a large surface like a wall or ceiling. According to this NY Times review the quality is quite respectable, and is no doubt only going to improve. The mind boggles at what this could imply for sharing mobile video. Imagine bringing a kit - consisting of an iPhone, portable speakers and microprojector - to your friend's house, then plugging in and projecting either a live stream or an on-demand program for all to see.
Enjoy your weekend!
Categories: Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators, Commerce, Devices, Magazines, Telcos, UGC
Topics: Amazon, Comcast, Conde Nast, Time Warner Cable, Verizon
-
Made-for-Broadband Video and VOD are Looking Like Peanut Butter and Chocolate
Remember "two great tastes that taste great together," the slogan from the classic Reese's ads featuring the mixing of peanut butter and chocolate? Recent developments suggest that independently produced/made-for-broadband video and Video-on-Demand could be another Reese's-like combination, bringing together two disparate worlds that have attracted loyal audiences in an offering that could have significant consumer appeal.
Consider, last week Multichannel News reported that Verizon plans to bring over 7 million broadband video clips from providers like blip.tv, Veoh and Dailymotion to its FiOS service, which users can browse with their set-top boxes. Also last week, AnySource Media, a software company that powers broadband-connected TVs, announced content deals with TheStreet.com, Break.com, Revision3 and Next New Networks, creating hundreds of "virtual VOD channels." And yesterday, Clearleap, a startup technology platform I recently profiled, announced its own deals with blip.tv, Revision3 and Next New Networks, providing content that cable operators can meld with their VOD offerings.
This push among made-for-broadband producers, technology companies and incumbent video service providers is not coincidental. While they each have their own motivations, their alignment could signal a winning proposition for viewers.
For the indie content producers, on-demand access on TVs augments their viewing experience and access to their programming. Given how difficult the environment has become for independents (Daisy had a good piece on this topic yesterday) on-demand access is a real differentiator. For cable operators and telcos, popular indie video gives them a targeted pitch to the tech-savvy, younger audiences who have become loyal fans of indie content. Down the road this group is probably most up-for-grabs for alternative "over-the-top" services, so focusing on defending them is smart. And for technology providers, a big market opportunity looms trying to connect the previously disparate worlds of broadband and VOD.
In fact, in a conversation I had last week with Braxton Jarratt, CEO/founder of Clearleap, he explained that cable operators get all this. They're looking for quality "mid-tail" video from broadband producers, including clips and short-form programs. The company's technology is currently feeding broadband video to a couple hundred thousand cable VOD homes, with a backlog of "double digit" markets pending deployment. Braxton has a lot of content deals on Clearleap's docket, creating a menu for its cable customers to pick and choose from to incorporate into their VOD offerings. Clearleap also offers an ad insertion platform, so indie video can be monetized, not just offered as a value add.
Meanwhile, VOD has long proven itself popular with viewers. Comcast recently announced it has delivered 11B views since it launched VOD. It has continued to augment its library and add more HD titles. While VOD hasn't really been a money-maker itself, it has become a strong part of the digital value proposition and a defensive move against other viewing alternatives. By incorporating popular broadband video into its VOD choices, its appeal is only strengthened.
While the tectonic plates of "convergence" continue to shift, examples of broadband video making its way to the TV continue to happen. TiVo has been at this for a while with its "TiVoCast" service, along with technology providers like ActiveVideo Networks and others. The likelihood for independently-produced broadband video and VOD to get together seems poised to increase.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Cable TV Operators, Indie Video, Technology, Telcos
Topics: ActiveVideo Networks, AnySource Media, Clearleap, Comcast, TiVo, Verizon
-
2009 Prediction #2: Mobile Video Takes Off, Finally
As promised, each day this week I'm sharing one prediction for 2009, with each one getting progressively bolder as the week progresses (and yes, I'll concede - as a number of you privately pointed out to me - yesterday's forecast that the Syndicated Video Economy would grow in '09 was a pretty wimpy start). So moving out a little further on the limb, today's prediction #2 is that video delivered directly to mobile/wireless devices will take off in '09, finally.
For those of you who have been following mobile/wireless video delivery, this has been a market that's perpetually been "just around the corner." In fact, a little over a year ago when I was planning VideoNuze, several people suggested that I shouldn't just focus on broadband delivery (as I define it to mean high-speed wired delivery of video to a home or business), but also mobile/wireless video. But after doing some due diligence I concluded that the market wasn't there yet, and that the vast majority of new video activity would be focused on wired broadband. Indeed, I think that's how '07 and much of '08 have shaped up.
However, having tracked recent activity in the mobile video space, I think '09 is going to be a big year of growth and recognition for this new medium (in fact, an old friend gently chastised me over lunch last week for even drawing a distinction between wired and wireless delivery, saying, "come on, it's ALL broadband!" I think he makes a very fair point.)
What has traditionally held back mobile delivery are a lack of video-capable devices, voice and text-focused wireless networks and a closed "on-deck" paradigm, which is the wireless carrier's version of the cable and satellite industry's proverbial walled-garden.
These limitations have now been mostly addressed, or are in the process of being addressed. On the device side, the most notable video-capable device is of course the iPhone, which by my calculations has already sold over 13 million units and is on its way to almost 20 million by the end of the year. Everyone I know who has an iPhone - especially kids - are infatuated with the video feature (if you've never seen it, especially now using AT&T's 3G network, get thee to an Apple store immediately!). In '09, the iPhone is poised for even greater popularity as Wal-Mart begins stocking it, possibly for just $99. Recession or not, the iPhone is going to remain white hot.
Not to be lost in the iPhone's phenomenal wake are many other new video-capable phones. There's of course the new G1 from T-Mobile, powered by Android, Google's new mobile OS. I got my first look at one last week, and though not as sleek as the iPhone, I was able to watch excellent YouTube video. There are plenty of others to choose from as well, including the Samsung Propel, the LG Incite, the new BlackBerry Storm and the latest mother-of-all-phones, the Nokia N64, which comes with 16GB of internal memory (enough for 40 hours of video). Whereas many of us today carry phones incapable or barely capable of viewing video, in '09 the replacement process will be in full swing.
Of course, all the cool devices in the world don't matter unless you have a robust underlying network and the freedom to view what you want. On this front, the wireless carriers' push to build out their next generation 3G networks finally allows sufficient bandwidth to view high-quality video (though not HD yet). Next up is 4G, first from Clearwire, the SprintNextel-Intel-Google-cable industry consortium that's deploying its WiMax network with speeds of up to 6 Mbps downstream being promised. There's also MediaFLO, Qualcomm's mobile broadcasting platform that has steadily built out an ecosystem of technology, carrier and content partners.
Last but not least are the consumer-focused services and applications. Until recently, this market has mainly consisted of packaged subscription services like Verizon's VCast and MobiTV, which itself recently announced more than 5 million subscribers. The combination of new devices and networks promises to bring an increase in on-demand, web-based, ad-supported video consumption (plus paid downloads to be sure, courtesy of the iPhone mainly). Another interesting twist is the advent of live broadcasting from mobile devices, powered by providers like Qik, Kyte and Mogulus. These all supercharge the Twitter micro-blogging phenomenon.
All of this underscores why the distinction between wired and wireless broadband really becomes meaningless over time. The mobile experience is going to seem more and more like the one you have sitting at your computer, with the added benefit of portability. To throw a blue-sky variable into the mix, one wonders if at some point you'll simply plug your phone into your TV and watch streamed or downloaded video that way, rather than through a set-top box or a wired broadband connection. There's a convergence concept for you!
Years in the making, mobile/wireless video is finally upon us, and '09 is going to be a big year. That's good news for all of us as consumers, and it surely means I'll be working a lot harder to stay on top of things.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Previous, Prediction #1: Syndicated Video Economy Grows
Tomorrow, 2009 Prediction #3
Categories: Devices, Mobile Video
Topics: Android, Apple, AT&T, BlackBerry, Clearwire, Google, iPhone, LG, Medi, Nokia, Samsung, SprintNextel, T-Mobile, Verizon, Wal-Mart
-
Comcast: A Company Transformed
Three numbers in last week's third quarter Comcast earnings release underscored something I've believed for a while: Comcast is a company transformed, now reliant on business drivers that barely existed just ten short years ago. Comcast's transformation from a traditional, plain vanilla cable TV operator to a digital TV and broadband Internet access powerhouse is profound proof of how consumer behaviors' are changing and value is going to be created in the future.
The three numbers that caught my attention were the net additions of 382,000 broadband Internet subscribers and 417,000 digital subscribers, with the simultaneous net loss of 147,000 basic subscribers. The latter number is the largest basic sub loss the company has sustained and, based on the company's own earnings releases, the sixth straight quarter of basic sub contraction. In the pre-digital, pre-broadband days, when a key measure of cable operators' health was ever-expanding basic subscribers, this trend would have caused a DEFCON 1 situation at the company. (see graph below for 2 year performance of these three services)
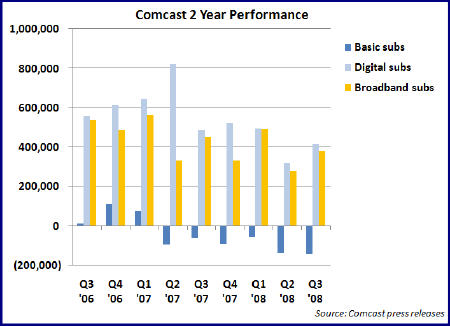
That it doesn't any longer owes to the company's ability to bolster video services revenue and cash flow through ever-higher penetration of digital services into its remaining sub base (at the end of Q3 it stood at 69% or 16.8 million subs). Years after Comcast and other cable operators introduced "digital tiers," stocked with ever-more specialized channels that consumers resisted adopting, the industry has hit upon a winning formula for driving digital boxes into Americans' homes: layering on advanced services like HD, VOD and DVR that are only accessible with digital set top boxes and then bundling them with voice and broadband Internet service into "triple play" packages. Comcast has in effect gone "up-market," targeting consumers willing and able to afford a $100-$200/month bundle in order to enjoy the modern digital lifestyle.
Still, in a sense the new advanced video services represent just the latest in a continuum of improved video services. Far more impressive to me is the broadband growth that both Comcast and other cable operators have experienced. Comcast's approximately 15 million YE '08 broadband subscribers will generate almost $8 billion in annual revenue for Comcast, up dramatically from its modest days as part of @Home 10 years ago. (It's also worth noting the company now also provides phone service to over 6 million homes today vs. zero 10 years ago)
The cable industry as a whole will end 2008 with approximately 37 million broadband subs, again up from single digit millions 10 years ago. And note that the 387,000 net new broadband subs Comcast added in Q3 '08 compares with just 277,000 net broadband subs that the two largest telcos, AT&T and Verizon added in quarter, combined. As someone who was involved in the initial trials of broadband service at Continental Cablevision less than 15 years ago, observing this growth is nothing short of astounding.
While broadband's financial contribution to Comcast is unmistakable, its real impact on the company is more
 keenly felt in its newfound importance in its customers' lives. Broadband Internet access has become a true utility for many, as essential in many homes as heat, water and electricity. A senior cable equipment executive told me recently that research done by cable companies themselves has shown that in broadband households, broadband service would be considered the last service to get cut back in these tough economic times. In these homes cable TV itself - long thought to be recession-resistant - would get cut ahead of broadband.
keenly felt in its newfound importance in its customers' lives. Broadband Internet access has become a true utility for many, as essential in many homes as heat, water and electricity. A senior cable equipment executive told me recently that research done by cable companies themselves has shown that in broadband households, broadband service would be considered the last service to get cut back in these tough economic times. In these homes cable TV itself - long thought to be recession-resistant - would get cut ahead of broadband.But Comcast and other cable operators must not rest on their laurels. Their next big challenge is to figure out how to take this massive base of broadband subs and start delivering profitable video services to it. If Comcast allows its broadband service to be turned into a dumb pipe, with "over the top," on demand video offerings from the likes of Hulu, YouTube, Neflix, Apple and others to ascend to dominance, that would be criminal. Not only would it devalue the broadband business, it would dampen interest in the company's advanced video services (VOD in particular) while making the company as a whole vulnerable in the coming era of alternative, high-quality wireless delivery.
Comcast is indeed a company transformed from what it was just 10 years ago. Technology, changing consumer behaviors and a little bit of "being in the right place at the right time" dumb luck have combined to allow Comcast to remake itself. Comcast itself must fully recognize these changes and aggressively build out Fancast and other initiatives to fully capitalize on its newfound opportunities.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Aggregators, Broadband ISPs, Cable TV Operators, Telcos
Topics: Apple, AT&T, Comcast, Netflix, Verizon, Verizon, YouTube
-
Inside the Netflix-Starz Play Licensing Deal
This past Wednesday, Starz, the Liberty Media-owned premium cable network, licensed its "Starz Play" broadband service to Netflix. The three year deal makes all of Starz's 2,500 movies, TV shows and concerts available to Netflix subscribers using its Watch Instantly streaming video feature. Very coincidentally I happened to be at Starz yesterday for an unrelated Liberty meeting, and had a chance to speak to Starz CEO Bob Clasen, who I've known for a while, to learn more.
On the surface the deal is an eye-opener as it gives a non-cable/telco/satellite operator access to Starz's
 trove of prime content. As I've written in the past, cable channels, which rely on their traditional distributors for monthly service fees, have been super-sensitive to not antagonizing their best customers when trying to take advantage of new distribution platforms. This deal, which uses broadband-only distribution to reach into the home, no doubt triggers "over-the-top" or "cable bypass" alarm bells with incumbent distributors.
trove of prime content. As I've written in the past, cable channels, which rely on their traditional distributors for monthly service fees, have been super-sensitive to not antagonizing their best customers when trying to take advantage of new distribution platforms. This deal, which uses broadband-only distribution to reach into the home, no doubt triggers "over-the-top" or "cable bypass" alarm bells with incumbent distributors. Then there is the value-add/no extra cost nature of Netflix's Watch Instantly feature. That there is no extra charge to subscribers for Starz's premium content (as there typically is when subscribing to Starz through cable for example) raises the question of whether Starz might have given better pricing to Netflix to get this deal done than it has to its other distributors.
But Bob is quick to point out that in reality, the Netflix deal is a continuation of Starz's ongoing push into broadband delivery begun several years ago with its original RealNetworks deal and continued recently with Vongo. To Starz, Netflix is another "affiliate" or distributor, which, given its tiny current online footprint does not pose meaningful competition to incumbent distributors. With only about 17 million out of a total 100 million+ U.S. homes subscribing to Starz, broadband partnerships are seen as a sizable growth opportunity by the company.
Further, Starz has been aggressively pitching online deals to cable operators and telcos for a while now, though only the latter has bit so far (Verizon's FiOS is an announced customer). Cable operators seem interested in the online rights, but have been reluctant to pay extra for them as Starz requires.
Bob also noted that Starz's wholesale pricing was protected in its Netflix deal, and that for obvious reasons of not hurting its own profitability, Starz has strong incentives to preserve incumbent deal terms in all of its new platform deals.
To me, all of this adds up to at least a few things. First is that Netflix must be paying up in a big way to
 license Starz Play. I assume this is an obvious recognition by Netflix that it needed more content to make Watch Instantly more compelling (see also Netflix's recent Disney Channel and CBS deals). Since it's not charging subscribers extra, Netflix is making a bet that over time - and aided by its Roku and other broadband-to-the-TV devices - Watch Instantly will succeed and as a result, will drive down its costs by reducing the number of DVDs the company needs to buy and ship. That seems like a smart long-term bet as the broadband era unfolds.
license Starz Play. I assume this is an obvious recognition by Netflix that it needed more content to make Watch Instantly more compelling (see also Netflix's recent Disney Channel and CBS deals). Since it's not charging subscribers extra, Netflix is making a bet that over time - and aided by its Roku and other broadband-to-the-TV devices - Watch Instantly will succeed and as a result, will drive down its costs by reducing the number of DVDs the company needs to buy and ship. That seems like a smart long-term bet as the broadband era unfolds.And while I agree that Starz Play on Netflix doesn't represent real competition to cable, telco and satellite outlets today, it's hard not to see it as a signal that traditional distributors are losing their hegemony in premium video distribution. (for another example of this, see Comedy Central's licensing of Daily Show and Colbert to Hulu). As I've said for a while, over the long term, the inevitability of broadband all the way to the TV portends significant disruption to current distribution models. I see Netflix at the forefront of this disruptive process.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Aggregators, Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators, Devices, Telcos
Topics: CBS, Comedy Central, Disney, Liberty Media, Netflix, Starz, Verizon


