-
VideoNuze Report Podcast #34 - October 2, 2009
Daisy Whitney and I are pleased to present the 34th edition of the VideoNuze Report podcast, for October 2, 2009.
This week Daisy and I first discuss my post "Break Media Gains Momentum with Branded Content in 2009" in which I describe how Break, a male-focused entertainment community, has used branded content to differentiate itself and increase revenues. Branded content is a relatively new media form where sponsors fund the production process and have significant creative input or outright control.
Break has been able to offer branded content projects as a value ad to sponsors' media buys on its sites by allocating a percentage of the client's media spend to the projects. I describe how Break does this, along with how branded content has helped it separate itself from competitors and grow revenue by a projected 18% this year.
Related, Daisy then talks about pricing trends in the online video advertising market, quoting ad network BrightRoll's CEO Tod Sacerdoti as saying that he's seen CPMs drop by an average of a dollar or more per quarter since launching in 2006. In his view prices have been inflated due to a "false equilibrium" about inventory scarcity. He sees prices continuing to fall into the low teens, a level at which more advertiser's budgets will flow into the online video medium - though not necessarily from TV. Learn more about Tod's predictions for the industry and Daisy's interpretations.
Click here to listen to the podcast (14 minutes, 12 seconds)
Click here for previous podcasts
The VideoNuze Report is available in iTunes...subscribe today!
Categories: Advertising, Branded Entertainment, Podcasts
Topics: Break Media, BrightRoll, Podcast
-
4 Items Worth Noting (Hulu, TiVo-Emmys, GAP-VMIX, Long Tail) for Sept 21st Week
Following are 4 news items worth noting from the week of Sept. 21st:
1. Bashing Hulu gains steam - what's going on here? - These days everyone seems to want bash Hulu and its pure ad-supported business model for premium content. Last week it was Soleil Securities releasing a report that Hulu costs its owners $920 per viewer in advertising when they shift their viewership. This week, it was a panel of industry executives turn. Then a leaked email from CBS's Quincy Smith showed his dissatisfaction with Hulu, and interest in trying to prove it is the cause of its parent networks' ratings declines.
What's happening here is that the world is waking up to the fact that although Hulu's user experience is world-class, its ad model implementation is simply too light to be sustainable. I wrote about this a year ago in "Broadcast Networks' Use of Broadband Video is Accelerating Demise of their Business Model," following up in May with "OK, Hulu Now Has ABC. But When Will it Prove Its Business Model?" Content executives are finally realizing that it is still too early to put long form premium quality video online for free. Doing so spoils viewers and reinforces their expectation that the Internet is a free-only medium. When TV Everywhere soon reasserts the superiority of hybrid pay/ad models, ad-only long-form sites are going to get squeezed. At VideoSchmooze on Oct 13th, we have Hulu's first CEO George Kliavkoff on our panel; it's going to be a great opportunity to understand Hulu's model and dig further into this whole issue.
2. TiVo data on ad-skipping for Emmy-winning programs should have TV industry alarmed - As if ad-skipping in general wasn't already a "hair-on-fire" problem for TV executives, research TiVo released this week on ad-skipping behavior specifically for Emmy-winning programs should have the industry on DEFCON 1 alert. Using data from its "Stop | Watch" ratings service, TiVo found that audiences for the winning programs in the 5 top Emmy categories - Outstanding Comedy Series, Drama Series, Animated Program, Reality-Competition and Variety/Music/Comedy Series - all show heavier than average (for their genre) time-shifting. The same pattern is true for ad-skipping; the only exception is "30 Rock" (winner of Outstanding Comedy Series) which performs slightly better than its genre average.
The numbers for AMC's "Mad Men" (winner of Outstanding Drama Series), are particularly eye-opening: 85% of the TiVo research panel's viewers time-shifted, and of those, 83% ad-skipped. (Note as an avid Mad Men viewer, I've been doing both since the show's premiere episode. It's unimaginable to me to watch the show at its appointed time, and with the ads.) The data means that even when TV execs produce a critical winner, their ability to effectively monetize it is under siege. How long will BMW sign up to be Mad Men's premier sponsor with research like this? TiVo's time-shifting data shows why network executives have to get the online ad model right. When TV Everywhere launches it will cater to massive latent interest in on-demand access by viewers; it is essential these views be better monetized than Hulu, for example, is doing today.
3. Radio stations push into online video as GAP Broadcasting launches with VMIX - Lacking its own video, the radio industry has been a little bit of the odd man out in the online video revolution. Some of the industry's bigger players like Clear Channel have jumped in, but there hasn't been a lot of momentum, especially with the ad downturn. But this week GAP Broadcasting, owner of 116 stations in mostly smaller markets announced a partnership with video platform and content provider VMIX. I talked to VMIX CEO Mike Glickenhaus who reported that radio stations are starting to get on board. For GAP, VMIX is providing an online video platform, premium content from hundreds of licensed partners, user-generated video tools and sales training, among other things. GAP's goal is to be a "total audience engagement platform" not just a radio station. Sounds right, but there's lots of hard work ahead.
4. So is there a "Long Tail" or isn't there? Ever since Chris Anderson's book "The Long Tail" appeared in 2006 there have been researchers challenging his theory which asserts that infinite shelf space drives customer demand into the niches. The latest attempt is by 2 Wharton professors, who, using Netflix data, observe that the Long Tail effect is not ironclad. Sometimes it's present, sometimes it's not. Anderson disputes their findings. The argument boils down to the definitions of the "head" and "tail" of the markets being studied. Anderson defines them in absolute terms (say the top 100 products), whereas the Wharton team defines them in terms of percentages (the top 1 %).
I've been fascinated with the Long Tail concept since the beginning, as it potentially represents a continued evolution of video choice; over-the-air broadcasting allowed for 3 channels originally, cable then allowed for 30, 50, 500, now broadband creates infinite shelf space. Independent online video producers and their investors have bet on the Long Tail effect working for them to drive viewership beyond broadcast and cable. With Nielsen reporting hours of TV viewership holding steady, we haven't yet seen cannibalization. However, with Nielsen, comScore and others reporting online video consumption surging, audiences may be carving out time from other activities to go online and watch.
Enjoy your weekends! There will be no VideoNuze on Monday as I'll be observing Yom Kippur.
Categories: Advertising, Aggregators, Broadcasters, Indie Video, Radio
Topics: AMC, GAP Broadcasting, Hulu, Long Tail, Netflix, VMIX
-
4 Items Worth Noting from the Week of September 14th
Following are 4 news items worth noting from the week of Sept. 14th:
1. Ad spending slowdown continues - TNS Media Intelligence reported that 1st half '09 U.S. ad spending declined 14.3% vs. a year ago, to $60.87 billion. Spending in Q2 '09 alone was down 13.9% vs. a year ago, the 5th straight declining quarter. The only bright spots TNS reported were Internet display ads (up 6.5%) and Free Standing Inserts (up 4.6%).
Rupert Murdoch and others in the industry have lately been suggesting that advertising is starting to improve and that the worst is behind us. But TNS SVP Research Jon Swallen was less sanguine, saying only that "Early data from third quarter hint at possible improvements for some media due to easy comparisons against distressed levels of year ago expenditures." While the online video ad sector has held up far better than most, the ad spending crash has caused many in the industry to re-evaluate whether ad-only models are viable, particularly for long-form premium content online. Subscription-oriented initiatives will only intensify the longer the ad slowdown lasts.
2. Veoh's court victory is important for all in the industry - I'd be remiss not to note the significance of U.S. District Judge A. Howard Matz's granting of Veoh's motion for summary judgment, effectively throwing out Universal Music's suit alleging Veoh had infringed UMG's copyrights. Judge Matz articulated the specific reasons he believed Veoh operated within the "safe harbor" provisions of the DMCA.
As a content producer myself (albeit at a completely different level than a music publisher or film studio!), I've generally been a huge advocate of copyright protection. But the fact is that DMCA - for better or worse - set out the rules for digital copyright use and they must be enforced clearly and forcefully. Anything less leaves the market in a state of confusion, with industry participants wary of inviting costly, time-consuming legal action (Veoh has said the UMG suit cost it millions of dollars in legal fees). For online video to thrive the rules of the road need to be well-understood; Judge Matz's ruling made an important contribution toward that goal.
3. Digitalsmiths announces new senior level hires - This week Digitalsmiths announced that it has brought on board Josh Wiggins as its new VP, Business Development, West Coast and two others, who will collectively be the company's first L.A.-based presence. They'll report in to Bob Bryson, SVP of Sales and Business Development.
I caught up with Digitalsmiths' CEO Ben Weinberger briefly, who explained that with tier 1 film/TV studios and other content owners (news, sports, etc.) the company's major focus, it was essential to have a full-time presence there staffed with people who know the industry cold. Ben reported that the company has honed in on target customers who have very large files, have video as their core business/revenue center, require sophisticated metadata management and often need a rapid video capture, processing and playout workflow. Digitalsmiths is proving a solid example of how to effectively differentiate through product and customer focus in a very crowded space. Announced customers include Warner Bros., Telepictures and TMZ.com, others are in the hopper (note Digitalsmiths is a VideoNuze sponsor).
4. New EmmyTVLegends.org site is a worth its weight in gold - On a somewhat lighter note, this week the Academy of Television Arts & Sciences Foundation unveiled EmmyTVLegends.org, which offers thoughtful, introspective video interviews with a wide range of TV's most influential personalities. If you have nostalgia for the classic TV shows from your youth, or just appreciate the amazing talent that has made the medium what it is, this site is for you. It is remarkably well-organized and accessible and brilliant proof of online video's power in presenting invaluable material that was previously available only to a lucky few.
I happily got lost in the site listening to Alan Alda talk about the fabulous writers of M*A*S*H and Steven Bochco describing the magic of "Hill Street Blues." I searched by "Happy Days" and quickly found the exact clips of Ron Howard talking about the role of his "Richie Cunningham" character in the show's arc and Henry Winkler revealing the influence of Sylvester Stallone on how he developed the voice of "Fonzie." Mary Tyler Moore is irresistible discussing specific scenes of the Mary Tyler Moore show and her poignant memories of Mary Richards navigating the working world. Kudos to the Academy, the site is a gem.
Enjoy the weekend and L'shanah tova (Happy New Year) to those of you, who like me, will be observing Rosh Hashanah this weekend!
Categories: Advertising, Aggregators, Music, People, Technology
Topics: Academy of Television Arts & Sciences Foundation, Digitalsmiths, EmmyTVLegends.org, TNS, UMG, Veoh
-
VideoNuze Report Podcast #32 - September 18, 2009
Daisy Whitney and I are pleased to present the 32nd edition of the VideoNuze Report podcast, for September 18, 2009.
This week Daisy and I first discuss my post from earlier this week, "How TV Everywhere Could Turn Cable Operators and Telcos Into Over-the-Top's Biggest Players," which has become one of the most popular posts I've written in the past 2 years.
In the post I asserted that if certain cable operators and telcos were to unbundle their TV Everywhere ("TVE") offering from their video subscription requirement, they could offer a "TVE 2.0" service outside their current geographic areas. In effect they'd be going over the top of their industry counterparts, invading new service territories.
It would be a bold move, but one that I suggested might be irresistible. Between slowing growth in their existing markets and new competitors rolling out OTT services nationwide, big cable operators and telcos could face the prospect of being turned into marginalized, geographically-bound players. I've heard from lots of folks this week about the TVE 2.0 concept - some who think it's inevitable; some who think it's inconceivable. I explain more in the post and on the podcast. You decide.
Meanwhile, Daisy provides an update from this week's iMedia Brand Summit, where marketers and agencies spent a lot of time discussing the effectiveness of traditional TV advertising vs. online video advertising. Daisy shares some very interesting statistics she gathered at the conference concerning how some industries are overspending in TV and getting underperformance. As Daisy explains, the key to advertising is no longer reach, but targeting. Listen in to learn more.
Click here to listen to the podcast (15 minutes, 9 seconds)Click here for previous podcasts
The VideoNuze Report is available in iTunes...subscribe today!
Categories: Advertising, Cable TV Operators, Podcasts
-
4 Items Worth Noting from the Week of September 7th
Following are 4 news items worth noting from the week of Sept. 7th:
1. Hulu's boss says it needs to charge for content - Bloomberg ran a story this week quoting Chase Carey, deputy chairman of News Corp (Fox's owner, and therefore a part-owner of Hulu) as saying at a BofA investor conference, "Ad-supported only is going to be a tough place in a fractured world....You want a mix of pay and free."
VideoNuze readers know that while I've admired Hulu's user experience from the start, I've long been critical of its thin ad model, which falls well short of generating revenue/program/viewer parity with traditional on-air program delivery. That lack of parity has caused Hulu's owners to cordon off access to Hulu on TVs for most viewers. But the networks' fear of cannibalizing their own P&Ls only frustrates loyal Hulu users, who neither understand nor care about such legacy concerns. All of this and more led me months ago to conclude a subscription offering is inevitable from Hulu. The impending TV Everywhere launches, which further marginalize ad-only business models, and now Carey's public remarks, solidify my thinking. We'll soon see some type of Hulu subscription tier.
2. Move Networks notches a win with Cable and Wireless deal - Score one for Move Networks, which this week announced Cable and its first tier 1 telco customer. Move enables C&W to deliver an HD, linear multichannel video service, plus on-demand and broadband content to its broadband customers, all through existing DSL connections. Move's repositioning, which I wrote about recently, obviates telcos' need to invest billions in upgrading their networks to get into the IPTV business. Indeed, Roxanne Austin, Move's CEO told me yesterday that C&W has for years considered all the various options for getting into video, but has never pulled the trigger until now. The deal covers up to 7 million homes and interestingly, rather than getting a license fee, Move will be paid a share of subscriber revenue. Roxanne says another big deal will be announced shortly.
3. iPod Nano gets video, battle with Cisco's Flip escalates - As you likely know, Steve Jobs unveiled the new iPod Nano this week, which incorporates an SD video camera. Following the iPhone 3GS adding video recording capability, I think it's pretty clear that Apple has decided video is the next big thing for its devices. As I suggested recently, Apple's embrace is going to drive user-generated video - and YouTube, as the undisputed home for it - to a whole new level.
But one wonders what this all means for Cisco's recently-acquired Flip video camera, and others from Creative, Sony, Kodak, etc? Cisco in particular has a lot on the line since it just shelled out almost $600M for Flip's parent Pure Digital. Granted Apple's devices are still SD, while Flip now emphasizes HD, but still, getting video recording "for free" as Jobs put it at the launch is pretty compelling for consumers. Even if the Flip deal doesn't work out as planned, Cisco will still be selling a whole lot more routers to handle all of this newly-generated broadband video, so it's a winner either way.
4. AT&T Wireless adding 3G capacity - In last Friday's "4 Items" post, I noted a great story the NY Times ran showcasing the frustrations that AT&T Wireless customers are experiencing due to the millions of data-intensive iPhones clogging up the network. AT&T has been hearing complaints from all sides, and this week announced 3G network upgrades in 6 cities this year, with plans to cover 25 of the top 30 U.S. cities by the end of next year, and 90% of its current 3G footprint by the end of 2011. These upgrades can't come soon enough for iPhone users. Meanwhile the company's YouTube video, featuring "Seth the blogger guy" explaining how AT&T is addressing network issues itself came under attack, as AdAge reported. There's no pleasing everyone.
Enjoy the weekend!
Categories: Advertising, Aggregators, International, Mobile Video, Technology, Telcos
Topics: Apple, AT&T, Cable and Wireless, Cisco, Hulu, iPod Nano, Move Networks, News Corp.
-
YouTube Movie Rentals: An Intriguing But Dubious Idea
Last week the WSJ broke the news that YouTube is in talks with Lionsgate, Sony, MGM and Warner Bros. about launching streaming movie rentals. On the surface this is an intriguing proposition: the 800 pound gorilla of the online video world tantalizing Hollywood with its massive audience and promotional reach. However, when you dig a little deeper, I believe it's a dubious distraction for YouTube, which is still trying to prove that it can make its ad model work.
I appreciate all the possible reasons YouTube is eyeing movie rentals. To evolve from its UGC roots, the company has been anxious for more premium content to monetize. But with Hulu locking up exclusive access
 to ABC, Fox and NBC shows for at least the next year and a half or longer, full-length broadcast TV shows are largely unavailable. And now TV Everywhere threatens to foreclose access to cable TV programs. All this makes movies even more attractive.
to ABC, Fox and NBC shows for at least the next year and a half or longer, full-length broadcast TV shows are largely unavailable. And now TV Everywhere threatens to foreclose access to cable TV programs. All this makes movies even more attractive. Then there's Google's uber mission to organize the world's information. YouTube executives are savvy enough to know that not all content can be delivered solely on an ad-supported basis - not yet nor possibly ever (for more about the challenges of effectively monetizing broadcast TV shows, let alone movies, see my prior posts on Hulu). To succeed in gaining access to certain content, offering a commerce model is ultimately essential. Since YouTube has already put in place some key commerce-oriented infrastructure pieces like download-to-own and click-to-buy, rolling out a rental option is less of a stretch. Lastly, YouTube can position itself to Hollywood as a more flexible partner and viable alternative to Apple's iTunes.
Regardless, YouTube movie rentals are still a dubious idea for at least 3 reasons: they're a distraction from YouTube's as yet unproven ad model, there are too many competitors and too little opportunity to differentiate itself and the revenue opportunity is relatively small.
Focus on getting the ad model working right - Given its market-leading 40% share of all online video streams, I've long believed that YouTube is the best-positioned company to make the online video ad model work. YouTube has made solid progress adding premium content to the site that it can monetize, but it still has a lot of work ahead to make its ads profitable. As I wrote in June, Google's own senior management cannot yet clearly articulate YouTube's financial performance, causing many in the industry to worry about YouTube's sustainability. Some might assert that YouTube can keep tweaking the ad model while also rolling out rentals but I disagree. With the ongoing ad spending depression, YouTube must stay laser-focused on making its ad model work, and also on communicating its success.
Too many competitors, too little differentiation - It's hard to believe the world really needs another online option for accessing movies, and mainly older ones at that. There's Hulu, iTunes, Netflix, Amazon, Xbox and soon cable, satellite and telcos rolling out movies on TV Everywhere, just to name a few. Maybe YouTube has some secret differentiator up its sleeve, but I doubt it. Rather, it will be just one more comparably-priced option for consumers. And in some ways it will actually be inferior. For example, unlike Netflix and Amazon, YouTube's browser-centric approach means watching movies on YouTube will remain a suboptimal, computer-based experience. Unless YouTube is willing to pay up big-time, there's also no reason to believe it will get Hollywood product any earlier than proven services like Netflix and iTunes.
Revenue upside is small - It's hard to estimate how many movie rentals YouTube could generate, but here's one swag, which shows how limited the revenue opportunity likely is. Let's say YouTube ramped up to .5% of its 120M+ monthly U.S. viewers (assuming it had U.S. rights only to start) renting 1 movie per week (not a trivial assumption considering virtually none of YouTube's users have ever spent a dime on the site and there are plenty of existing online movie alternatives). YouTube's revenue would be 600K rentals/week x $4/movie (assumed price) x 30% (YouTube's likely revenue share) = $720K/week. For the full year it would be $37.4M. With YouTube's 2009 revenue estimates in the $300M range, that's about 12% of revenue. Nothing to sneeze at, but not world-beating either, especially as compared to YouTube's massive advertising opportunity.
Given these considerations, I contend that YouTube would be far better off trying to become the dominant player in online video advertising, replicating Google's success in online advertising. Like all other companies, YouTube has finite resources and corporate attention - it should focus where it can become a true leader. There's enough quality content and brands willing to partner with YouTube on an ad-supported basis to keep the company plenty busy, and on the road to eventual financial success.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Advertising, Aggregators, FIlms, Studios
Topics: Hulu, Lionsgate, MGM, Sony, Warner Bros., YouTube
-
First Look at comScore's July '09 Video Ad Networks' Rankings
Below is a first look at comScore's rankings for video ad networks' "potential" reach for July '09. The rankings, which have not yet been publicly shared, reveal a relatively tight clustering of 5 video ad networks - ScanScout, Tremor Media, YuMe, Broadband Enterprises and BrightRoll - with ScanScout capturing the number 1 spot in its first month being fully measured by comScore.
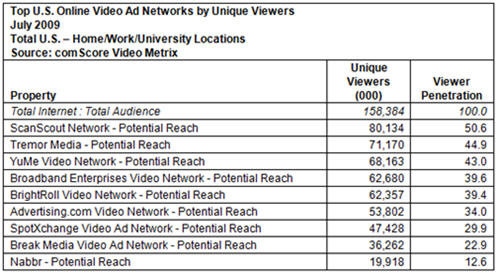
The "potential reach" aspect of these rankings is important to understand. As I explained in June in "Unraveling comScore's Monthly Viewership Data for Online Video Ad Networks," the potential reach numbers account for the aggregate number of viewers of all the sites that the ad network has the right to place ads on. However, as I discussed with Tania Yuki, comScore's director of product management, it's not a perfect measure, though comScore is continually trying to improve it.
The rankings are determined through a combination of the ad networks' self-reported publisher list and comScore's own tracking. If a video network reports that any one publisher accounts for 2% or more of its viewers, comScore requires a letter proving the business relationship. There is also a self-policing mechanism as comScore provides a "dictionary" of all publishers that each ad network reports. Competitors can review the dictionary and appeal to comScore if something appears amiss. Still, there's some looseness in the methodology, and having spoken to a number of industry executives, also a fair amount of concern that it is accurately portraying the industry's true performance.
comScore recognizes the limitations of the potential reach approach and that it is just one way of understanding a video ad network's value. Actual monthly performance is equally important, and comScore has been working with ad networks to implement this reporting as well. As I wrote in June, the "hybrid" approach requires ad networks to insert a 1x1 beacon in their video players. Though this approach also has its limitations, many of the biggest video ad networks are now implementing the beacon, and soon comScore will likely begin reporting actual as well as potential reach.
Video ad networks are a very important part of the online video ecosystem, responsible for placing millions of dollars of ads each month. Importantly they allow a level of targeting and reach that brands seek, but are often unable to attain on their own with a handful of direct site relationships. With the online video medium still relatively new, buyers require data helping them understand their options. However, the comScore data is just a first filter, diligent buyers still must dig in to understand how each network, or individual site meets their needs.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Advertising
Topics: BrightRoll, Broadband Enterprises, ScanScout, Tremor Media, YuMe
-
VideoNuze Report Podcast #27 - August 14, 2009
Daisy Whitney and I are pleased to present the 27th edition of the VideoNuze Report podcast, for August 14, 2009.
In this week's podcast, Daisy and I discuss "The Future of Internet Video," a new research report released this week by eMarketer. Coincidentally, we had each read the press release about the report and found ourselves disagreeing with its conclusions.
As Daisy explains, the report essentially asserts that for online video advertising to continue to grow, the viewing experience between the computer and TV must converge. The logic is that TV's "lean-back" viewing mode is a preferred context for advertisers, and therefore for advertising against online video to grow, the video must be accessible on TVs.
Daisy takes issue with this, arguing that while convergence is great, there are indeed times when watching on a computer is preferred by consumers. A "new norm" has emerged with the computer as a parallel viewing platform. Rather than looking at this as an obstacle, advertisers should embrace consumers' behavior, and capitalize on it.
My main disagreement is that eMarketer believes that a "lean-back" TV viewing mode is preferred by advertisers over the "lean-forward" computer viewing mode. While eMarketer argues the computer mode creates viewer distraction and incents clicking away from ads, I see it the other way around: when watching video on computers, ads cannot be skipped, calls to action can be easily implemented (e.g. "click here to receive....) and everything of course can be measured. Contrast this with the rampant ad-skipping that now occurs in DVR-enabled homes.
Listen in and draw your own conclusions.
Separately, I can't resist touching on the topic of "authenticity" of broadband video I wrote about earlier this week in "How I Got Punked by the Megawoosh Waterslide Video." I received lots of feedback on this post, with plenty of people 'fessing up that they got punked too, while others called me the "poster child for gullibility!" Either way, authenticity of broadband video is a fascinating topic.
Click here to listen to the podcast (13 minutes, 58 seconds)
Click here for previous podcasts
The VideoNuze Report is available in iTunes...subscribe today!
Categories: Advertising, Podcasts
-
4 News Items Worth Noting from the Week of July 27th
Following are 4 news items worth noting from the week of July 27th:
New Pew research confirms online video's growth - Pew was the latest to offer statistics confirming that online video usage continues to soar. Among the noteworthy findings: Long-form consumption is growing as 35% of respondents say they have viewed a TV show or movie online (up from 16% in '07); watching video is widely popular, draw more people (62%) than social networking (46%), downloading a podcast (19%) or using Twitter (11%); usage is up across all age groups, but still skews young with 90% of 18-29 year olds reporting they watch online vs. 27% of 65+ year olds; and convergence is happening with 23% of people who have watched online reporting they have connected their computers to their TVs.
FreeWheel has a very good week - FreeWheel, the syndicated video ad management company I most recently wrote about here, had a very good week. On Monday, AdAge reported that YouTube has begun a test allowing select premium partners to bring their own ads into YouTube, served by FreeWheel. Then on Wednesday, blip.tv announced that it too had integrated with FreeWheel, so ads could be served for blip's producers across their entire syndication network. I caught up with FreeWheel's co-CEO Doug Knopper yesterday who added that more deals, especially with major content producers, are on the way. FreeWheel is riding the syndication wave in a big way.
Plenty of action with CDNs - CDNs were in the news this week, as Vusion (formerly Jittr Networks) bit the dust, after going through $11 million in VC money. Elsewhere CDN Velocix (formerly CacheLogic) was acquired by Alcatel-Lucent. ALU positioned the deal as fitting with its "Application Enablement" strategy, supporting customers' needs in a "video-centric world." Limelight announced its LimelightREACH and LimelightADS services for mobile media delivery and monetization (both are based on Kiptronic, which it acquired recently). Last but not least, bellwether Akamai reported Q2 '09 earnings, that while up 5% vs. year ago, were down sequentially from Q1. Coupled with a cautious Q3 outlook, the company's stock dropped 20%.
IAC is making big moves into online video - IAC is making no bones about its interest in online video. Last week the company unveiled Notional, a spin-out of CollegeHumor.com, to be headed by that site's former editor-in-chief Ricky Van Veen. Then this week it announced another new video venture, with NBCU's former co-entertainment head Ben Silverman. IAC chief Barry Diller seems determined to push the edge of the envelope, as IAC talks up things like multi-platform distribution and brand integration. With convergence and mobile consumption starting to take hold, the timing may finally be right for these sorts of plays. At a minimum IAC will keep things interesting for industry watchers like me.
Click here to see an aggregation of all of the week's broadband video news
Categories: Advertising, CDNs, Indie Video, Syndicated Video Economy
Topics: Akamai, Alcatel-Lucent, blip.TV, FreeWheel, IAC, Limelight, Pew, Velocix, Vusion, YouTube
-
Blip.TV's New Deals Give Broadband Producers a Boost
Broadband-only producers got a boost yesterday as blip.tv, which provides technology, ad sales and
 distribution for thousands of online shows, announced a variety of new deals as well as product improvements. The deals offer blip's producers new distribution, new monetization and new access to TVs. In order:
distribution for thousands of online shows, announced a variety of new deals as well as product improvements. The deals offer blip's producers new distribution, new monetization and new access to TVs. In order:Distribution: blip's new deal with YouTube means that producers using blip can deliver their episodes directly to their YouTube accounts, eliminating the two step process. With YouTube's massive traffic, getting in front of this audience is critical to any independent producer. Since my first conversation with blip's co-founder Mike Hudack several years ago, the company's mantra has been widespread syndication. Blip already distributed its producers' shows to iTunes, AOL Video, MSN Video, Facebook, Twitter, and others. Vimeo is another new distribution partner announced yesterday.
Monetization: A new integration with FreeWheel means that ads blip sells can follow the programs it distributes wherever they may be viewed. I've written about FreeWheel in the past, which offers essential monetization capability for the Syndicated Video Economy. With the blip deal, FreeWheel delivered ads can be inserted on YouTube. This follows news earlier this week that YouTube and FreeWheel had struck an agreement which allows content providers that use FreeWheel and distribute their video on YouTube can have FreeWheel insert their ads on YouTube (slowly but surely YouTube is opening itself up to 3rd parties).
Access to TVs - Last but not least is blip's integration with the Roku player which will help bring blip's shows directly to TVs (adding to deals blip already had with TiVo, Sony Bravia, Verizon FiOS, Boxee and Apple TV). While Roku's footprint is still modest, it is positioned for major growth given current deals with Netflix and Amazon, and others no doubt pending. At $100, Roku is an inexpensive and easy-to-operate convergence device that is a great option for consumers trying to gain broadband access on their TVs. Gaining parity access to TV audiences for its broadband producers is a key value proposition for blip.
In addition to the above, blip also redesigned its dashboard and work flow, making it easier for producers to manage their shows along with their distribution and monetization. An additional deal with TubeMogul announced yesterday allows second by second viewer tracking, providing more insight on engagement.
Taken together the new deals help blip further realize its vision of being a "next generation TV network" and provide much-needed services to broadband-only producers. This group has taken a hit this year, given the tough ad sales and funding environments, so they need every advantage they can get.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Advertising, Aggregators, Analytics, Devices, Indie Video, Syndicated Video Economy
Topics: blip.TV, FreeWheel, Roku, TubeMogul, Vimeo, YouTube
-
Subscription Overload is on the Horizon
One might think that the depths of the worst economic recession in decades would be a lousy time to begin asking penny-pinching consumers for additional payments to access content. Yet this is exactly what many video providers plan to do, as a variety of broadband-delivered video subscription plans are beginning to take shape. Based on conversations I've been having with industry executives and what I've been reading, various subscription plans are now underway. This leads me to think that "subscription overload" is on the horizon.
Interest in getting consumers to pay has several sources. Many executives have concluded that advertising alone is an insufficient model, even as the cost of delivering broadband video is actually plummeting. Some of this concern relates to the widespread advertising slowdown, where even established players like the big broadcast networks are being forced to accept rate cuts. These declines cannot be made up with greater ad quantity as there's prevailing worry about just how many ads can be loaded into a broadband-delivered program before the viewer gets turned off.
There is also significant fear of not learning from the demise of the U.S. newspaper industry, which largely adopted an ad-only online business model that hasn't worked (causing some like the NY Times to now consider reinstituting subscription services). Newspapers' woes have become a touchstone in practically every conversation I've participated in recently. Last, but not least, there's no small amount of envy toward cable networks, whose dual subscription/advertising revenue model has allowed them to weather the recession better than most.
Subscription plans seek some combination of differentiators: offering premium video in better windows, at better-quality, with deeper selection, across multiple devices and with some degree of exclusivity. The thinking is that these enhancements will allow subscription services to be distinguished from and co-exist with free ad-supported services. The implicit bet is that these differences will be understood and valued by consumers.
Subscription plans are beginning to leak out, as happened last week in remarks by Disney CEO Bob Iger. Many in the industry (including me) anticipate that Hulu will launch a subscription service soon, particularly as it seeks to become a part of cable operators' TV Everywhere initiatives (which themselves seek to enhance the value of current cable subscriptions).
Other plans are on the drawing board. When I read yesterday, for example, about NBC's Ben Silverman jumping to IAC to form a new video venture, I suspect it's almost a given that the venture will consider some type of premium model. The growth of mobile video is another factor fueling subscriptions. This is what MLB is doing with its new At Bat 2009 subscription app for the iPhone, which builds on its highly successful MLB.TV broadband subscription service.
With so many subscription services underway, it's inevitable that many of them won't get traction. I mean, is it likely that consumers will pay extra so they can see a program online just hours after it airs, instead of a day later? Or so they can receive 1080-equivalent HD quality online, when 720-equivalent HD is available for free? I'm skeptical, even before factoring in the recession-driven belt-tightening many consumers have adopted. The bar for a subscription service to succeed is very high.
Still, with broadband allowing video providers direct access to their target audiences, their well-known brands as powerful enablers, and the crummy advertising climate showing no letup, it is no surprise that the pendulum is swinging heavily toward subscriptions.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Advertising, Newspapers, Sports
-
MTV Unveils Research on Short-Form Video Advertising
MTV Networks released some interesting research yesterday on the optimal way to present advertising in short-form online video. Its "Project Inform" looked at how multiple ad presentations from 3 blue chip
 advertisers performed and were liked by users across 50 million video streams on MTV.com, ComedyCentral.com, VH1.com, NickJr.com and CMT.com. The research was conducted in partnership with InsightExpress using Panache's video ad platform.
advertisers performed and were liked by users across 50 million video streams on MTV.com, ComedyCentral.com, VH1.com, NickJr.com and CMT.com. The research was conducted in partnership with InsightExpress using Panache's video ad platform. The research found that the most effective ad product was a "lower 1/3 product suite" consisting of a 5 second pre-roll combined with a 10 second lower 1/3 semi-transparent Flash overlay that began about 10 seconds after the video itself began. Effectiveness was defined as brand lift, measured by metrics like unaided awareness, aided awareness and purchase intent. The research also measured consumers' likeability of each ad product. This finding provides support for why overlays seem to keep popping up; for example I now see overlays on most of the video clips I watch on YouTube.
In second place was a conventional 30 second pre-roll which did well on both effectiveness and consumer likeability. That surprises me somewhat because I've believed for a while that 30 seconds is way too long for an ad where the content itself may only be 1-3 minutes in length. Granted it's a subjective judgment, but my personal experience has been that 30 seconds feels like an eternity when I know the content I'm accessing is going to be pretty brief. In fact I've noticed a clear trend toward 15 second pre-rolls accompanying short video clips, which I assumed suggested content providers had thankfully come to a similar conclusion.
In third place in the MTV research was a "sideloader product suite", which included a 5 second pre-roll with a 10 second custom unit that slides out of the right side of the video window 10 seconds after the video itself began (so it sounds like the lower 1/3 product suite except the overlay is on the right instead of the bottom). I've never seen a unit like this, but to the extent that it may block valuable content in the right side of the window I could see users feeling it was intrusive.
There's lots of research underway about different ad formats' effectiveness, and the MTV research adds to the industry's collective knowledge about best practices. There's still a ways to go though as industry participants launch and test new types of ad formats in search of the ultimate ad presentation.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Advertising, Cable Networks
Topics: InsightExpress, MTV, Panache
-
Catching Up on Last Week's Industry News
I'm back in the saddle after an amazing 10 day trip to Israel with my family. On the assumption that I wasn't the only one who's been out of the office around the recent July 4th holiday, I've collected a batch of industry news links below so you can quickly get caught up (caveat, I'm sure I've missed some). Daily publication of VideoNuze begins again today.
Hulu plans September bow in U.K.
Rise of Web Video, Beyond 2-Minute Clips
Nielsen Online: Kids Flocking to the Web
Amid Upfronts, Brands Experiment Online
Clippz Launches Mobile Channel for White House Videos
Prepare Yourself for iPod Video
Study: Web Video "Protail" As Entertaining As TV
In-Stat: 15% of Video Downloads are Legal
Kazaa still kicking, bringing HD video to the Pre?
Office Depot's Circuitous Route: Takes "Circular" Online, Launches "Specials" on Hulu
Upload Videos From Your iPhone to Facebook Right Now with VideoUp
Some Claims in YouTube lawsuit dismissed
Concurrent, Clearleap Team on VOD, Advanced Ads
Generating CG Video Submissions
MJ Funeral Drives Live Video Views Online
Why Hulu Succeeded as Other Video Sites Failed
Invodo Secures Series B Funding
Comcast, USOC Eye Dedicated Olympic Service in 2010
Consumer Groups Push FTC For Broader Broadband Oversight
Crackle to Roll Out "Peacock" Promotion
Earlier Tests Hot Trend with "Kideos" Launch
Mobile entertainment seeking players, payment
Netflix Streams Into Sony Bravia HDTVs
Akamai Announces First Quarter 2009 State of the Internet Report
Starz to Join Comcast's On-Demand Online Test
For ManiaTV, a Second Attempt to be the Next Viacom
Feeling Tweety in "Web Side Story"
Most Online Videos Found Via Blogs, Industry Report
Categories: Advertising, Aggregators, Broadcasters, Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators, CDNs, Deals & Financings, Devices, Indie Video, International, Mobile Video, Technology, UGC
Topics: ABC, C, Clearleap, Clippz, Comcast, Concurrent, Hulu, In-Stat, Invodo, iPod, Kazaa, Nielsen, Office Depot, Qik, VideoUp, YouTube
-
VideoNuze Report Podcast #23 - July 2, 2009
Below is the 23rd edition of the VideoNuze Report podcast, for July 2, 2009.
This week Daisy shares additional information about ESPN's Ad Lab for emerging media. The Ad Lab, which was first disclosed by ESPN last year, is intended to various ad formats in the ESPN video player. It is one of many different tests and research projects in the market. As Daisy and I say, everyone's trying to learn how best to monetize the nascent online video; this creates a lot of valuable data, which market participants then need to parse through to fully understand.
I get into further details on my post yesterday, "Video Companies Raised $64M in Q2 '09, Notching Another Stellar Quarter." Despite the recession and the slowdown in venture capital investments, at least 26 industry companies have raised at least $219M over the last 3 quarters, which is impressive by any measure. Still, it hasn't been easy, and one indicator of what investors prefer is that not one of the 26 investments is in a content provider or video aggregator.
Click here to listen to the podcast (14 minutes, 24 seconds)
(Note, with vacations planned, our next podcast will be July 24th)
Click here for previous podcasts
The VideoNuze Report is available in iTunes...subscribe today!
Categories: Advertising, Cable Networks, Deals & Financings
-
Rhett and Link Are Another Example of YouTube's Franchise Value
If you haven't heard of Rhett and Link, you need to check them out to understand another of the myriad ways that video is being democratized, advertising is being reimagined and value is being built in YouTube. My wife brought Rhett and Link to my attention after hearing a report about them on National Public Radio last night.
Rhett and Link are two engineers and lifelong friends who operate out of a North Carolina basement writing and performing short comedic songs. Emboldened by family and friends they've created over 200 videos that have generated 16 million views and a loyal following on YouTube and their own site rhettandlink.com. No doubt you'll agree their songs and videos are funny, clever and very memorable.
Calling themselves "internetainers" and having generated a signature style, they are now being contracted by advertisers to turn their talent toward developing promotion songs. Their folk song drive-through order for Taco Bell has generated almost 1 million views on YouTube. And their hilarious spot for Red House furniture store in Highpoint, NC, which spoofs race relations, has generated almost 1.5 million views. There will certainly be more of these promotional songs in the hopper. That's because given what these advertisers are probably paying for these spots, their ROIs must be off the charts, especially compared to traditional advertising tactics. And with Rhett and Link's following, all new promotional songs now have a built in viral tailwind.
Rhett and Link remind me of Lee and Sachi LeFever of Common Craft, who I recently wrote about. They are all part of an emerging group of talent who would be considered "non-professionals" by the traditional standards of entertainment, advertising and communications. But with their own authentic and engaging approaches and direct access to audiences, they have been able to break through and attract large followings.
A key linchpin to all of their success is YouTube, whose massive audience and viral sharing is unmatched. Even as it strives for partnerships with premium quality video providers, YouTube's value to the Common Crafts and Rhett and Links of the world is undeniable. If leveraged properly, as it has been by these creators (and by others like Demand Media), it can also lead to genuine businesses opportunities.
When I repeatedly say that YouTube has massive franchise value - even though it is currently unprofitable - it's these kinds of examples, which put YouTube in the center of an emerging grassroots video ecosystem, that I'm thinking of. There's no other site that comes close to YouTube's reach, brand awareness or viral sharing potential.
If you have other examples along these lines, please send them along!
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Advertising, Indie Video
Topics: Common Craft, Rhett and Link, YouTube
-
VideoNuze Report Podcast #21 - June 19, 2009
Below is the 21st edition of the VideoNuze Report podcast, for June 19, 2009.
Daisy discusses highlights from the OMMA Video conference that she organized in NYC this week. Daisy recaps the keynote from Eileen Naughton, Google's director of media platforms in which she said that child YouTube sensation "Fred" is pulling down a six-figure income. She also reviews comments by Andy Markovitz, Kraft's digital marketing and media director who recommended the online video ad industry needs more scale, better targeting and more format choices. Those sentiments were echoed by other speakers. Daisy has more details here.
This week I discuss my post from yesterday, "Does It Actually Matter How Much Money YouTube is Losing?" I recognize I took a somewhat contrarian standpoint here, and admit it feels a bit irresponsible to suggest that YouTube's losses don't matter much (except to Google of course). It's always been great sport to debate how much money YouTube is losing. But the fact is, as long as Google has the financial wherewithal to sustain YouTube's losses (whatever they actually are), and deems the site strategic in the long run (which I strongly believe it is), then the size of its losses is really pretty much irrelevant. I know lots of you disagree with my assessment; feel free to post a comment and explain why!
Click here to listen to the podcast (15 minutes, 40 seconds)
Click here for previous podcasts
The VideoNuze Report is available in iTunes...subscribe today!
Categories: Advertising, Aggregators, Podcasts
Topics: Google, Podcast, YouTube
-
Unraveling comScore's Monthly Viewership Data for Online Video Ad Networks
A monthly reminder that online video remains a work in progress is comScore's viewership data for online video ad networks. Even as someone who follows the industry closely, I find these reports confusing. The press
 releases often distributed by various online video ad networks touting their progress only adds to the confusion. I touched on this last month, and to clear away some of the fog, last week I spoke to Tania Yuki, comScore's product manager for its Video Metrix measurement service.
releases often distributed by various online video ad networks touting their progress only adds to the confusion. I touched on this last month, and to clear away some of the fog, last week I spoke to Tania Yuki, comScore's product manager for its Video Metrix measurement service. comScore's traffic reports are extremely important for the online video industry's growth because they are a key source of data for advertisers, media buyers, agencies and others looking to tap into this new medium. Ad networks in particular are an important part of the online video ecosystem because they provide significant reach, targeting and delivery technology, all of which are required by prospective advertisers.
A key part of the current confusion is that each month comScore's Video Metrix Ad Focus report - which details the total audience of unique viewers for online properties and ad networks - combines both the actual audience of destination properties with the potential reach of video ad networks. For example, here's the top 10 for April:
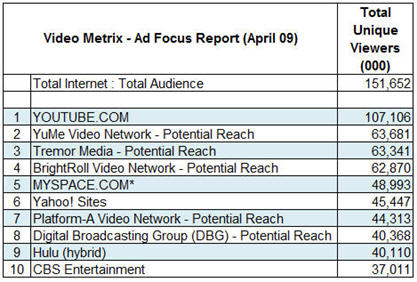
As you can see, 5 of the top 10 listed are ad networks, whose measurement is potential, while the other 5 are actuals. "Potential" is supposed to represent the aggregate number of viewers of all the sites that the ad network has the right to place ads on. However even the validity of this number is amorphous, because networks are only required to provide comScore proof of their relationships if the site accounts for more than 2% of all streaming or web activity.
Recognizing the need to provide more clarity, comScore has recently made available the option for networks to participate in a "hybrid" measurement approach, meant to track networks' actual viewership. To participate, networks need to place a 1x1 pixel, or "beacon" inside any video player where their ads appear. comScore takes the data reported by the beacons and combines it with its 2 million member panel of users whose behavior it tracks. It reconciles differences between the two through a "scaling" process that looks at the intensity of users' non-video behaviors.
To give a sense of the difference between potential and actual, comScore reports BrightRoll - which along with Nabbr are the only video ad networks to have implemented the beacons by April - as having 26M actual viewers vs. the 62M potential reported.
comScore's hybrid approach, which fits with its recently-announced "Media Metrix 360" service, is an important step forward in providing more clarity on how video ad networks are actually performing. Still, as Tania explained, even the hybrid approach has its own idiosyncrasies. For example, some publishers resist having a network's beacon incorporated into their video player, because they want to receive traffic credit themselves. Further, it is a voluntary program. Tania said that in addition to BrightRoll and Nabbr, other networks like BBE, YuMe and Tremor are all working through the implementation currently.
The actual numbers are important for buyers, so that ad networks' viewership can be assessed on an "apple to apples" basis with online properties, as well as non-video options. Tania said that media buyers tell comScore they value both potential and actual numbers. Though that sounds right to me, I think that for the online video medium to mature, buyers are going to put increasing emphasis on actual performance, particularly as it relates to existing media. That's why recent efforts from YuMe and Tremor to translate online video's impact into TV's gross rating points (GRP) paradigm are also important.
In short, comScore seems to be doing its part to improve reporting clarity. However, this isn't going to resolve itself overnight; the market will continue to experience reporting confusion for some time to come.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Advertising
Topics: BBE, BrightRoll, comScore, Nabbr, Tremor Media, YuMe
-
4 Industry News Items Worth Noting
Looking back over the past week's news, there are at least 4 industry items worth noting. Here are brief thoughts on each:
Time Warner starts to acknowledge execution realities of "TV Everywhere" - I was intrigued to read this piece in Multichannel News covering comments that Time Warner Cable COO Landel Hobbs made about its TV Everywhere's plans being slowed by "business rules." Though I love TV Everywhere's vision, I've been skeptical of it because it's overly ambitious from technical and business standpoints. This was the first time I've seen anyone from TW begin to acknowledge these realities (though Hobbs insists "the hard part is not the technology"). I fully expect we'll see further tempered comments from TW executives in the months to come as it realizes how hard TV Everywhere is to execute.
VOD and broadband video vie for ad dollars - I've been saying for a while that broadband can be viewed as another video-on-demand platform, which inevitably means that it's in competition with VOD initiatives from cable operators. For both content providers and advertisers, a key driver of their decision to put resources into one or the other of the two platforms is monetization. And with VOD advertising still such a hairball, broadband has gained a decisive advantage. As a result, I wasn't surprised to read in this B&C article that ad professionals are imploring cable operators to get on the stick and improve VOD's ad insertion processes. Cablevision took an important step in this direction, announcing this week 24 hour ad insertion. Still, much more needs to be done if VOD is going to effectively compete with broadband video for ad dollars.Cisco sees an exabyte future - Cisco released an updated version of its "Visual Networking Index" which I most recently wrote about in February. Once again, Cisco sees video as the big driver of IP traffic growth, accounting for 91% of global consumer IP traffic by 2013. The fastest growing category is "Internet video to the TV" (basically the convergence play), while the biggest chunk of video usage will still be "Internet video to the PC" (today's primary model). Speaking to Cisco market intelligence people recently, it's clear that from CEO John Chambers on down, the company believes that video is THE growth engine in the years to come.
iPhone's new video capabilities - Daisy reviews this in her podcast comments today. It's hard to underestimate the impact of the iPhone on the mobile video market, and the forthcoming iPhone 3G S's video capabilities (adaptive live streaming, video capture/edit and direct video downloads for rental or own) mean the iPhone will continue to raise the mobile video bar even as new smartphone competitors emerge. Nielsen has a good profile of iPhone users here. It notes that 37% of iPhone users watch video on their phone, which 6 times more likely than regular mobile subscribers.
Categories: Advertising, Cable TV Operators, Mobile Video, Video On Demand, Worth Noting
Topics: Apple, Cablevision, Cisco, iPhone, Time Warner Cable, TV Everywhere
-
A New Old Model for Making Money with Original Online Entertainment Video
Today I'm pleased to introduce "VideoNuze Forums," a periodic opportunity for online video industry experts to contribute their thoughts and ideas to the VideoNuze community. I'm a firm believer that only through the industry's collective ideas and energy will online video reach its ultimate potential.
In this kickoff post, David Graves shares his thoughts on how advertisers can collaborate with online video producers to fund original online entertainment, while leveraging the syndication model. David is a veteran media executive who I've known for years; he's served in executive roles at Yahoo and Reuters, and more recently founded PermissionTV. He's now consulting with Global Capital Strategic Group.
Please contact me if you're interested in contributing. I can't guarantee I'll run everything, but I welcome your ideas.
A New Old Model for Making Money with Original Online Entertainment Video
by David Graves
In the very beginning of television, advertising agencies worked directly with creative people to produce the dramatic programs they wanted to put their ads in. Now, 60 years later, it's time for them to do so again, on the Web.
Between then and now, distributors such as TV networks have become the ones who financed and controlled video programming and acted as the middleman between creatives and advertisers. But today there aren't enough distributors with both the will and the resources to speculatively fund large volumes of online entertainment video.
There are many creative people who would like to produce for the new online medium, particularly now that it can be done for historically low costs. But it's hard to make money. Even so, some dramatic video like Strike.TV is getting produced on the hopes that it will attract an audience that might get sold to advertisers. This is nice but inefficient and usually unprofitable.
In order for the Internet to develop as a substantial platform for original entertainment video, a new model has to form that gives producers some additional upfront confidence. There needs to be a better chance of generating a profit in order to encourage Internet producers to produce and people with money to fund them. Since the paid model is still highly challenged, even for well-known, branded fare (e.g. broadcast network programs), advertising is the most likely source of revenue.
Advertisers are clearly open to the potential benefits of online video advertising. To begin with, they love TV commercials over every other form of advertising. Online, their ads can't be skipped, can be better targeted and offer the possibility of an immediate response or interaction on top of the branding value. What's not to like?
But experiments with advertiser-created programming have by and large been disappointing. That's because it doesn't make sense for advertisers to be the ones financing, creating or distributing video. It's not what they do. On the other hand, partnerships like that of Alloy Entertainment and Johnson & Johnson, to create the "Private" Web series for teen girls, which debuts next month, exemplifies the potential. Brands like Neutrogena will be subtly integrated into the shows.
The model that will work is one where advertisers hook up directly with creative programmers to help encourage show ideas they like. Some call this "branded entertainment" and it can take many forms. For example, it could be an advertising commitment at an agreed-upon CPM, contingent on seeing the finished product. Or a pre-buy that helps fund the production in return for a lower CPM. Even a smile and a wink would have value.
If a producer had an embedded advertiser at a decent CPM, they could arrange for distribution both on their own sites and through syndication. Given the state of ad sales today, offering syndicated sites free, high-quality video content with a built-in CPM split would be like offering the proverbial candy to a baby. Further, there will be syndicators like Pixsy and others who would no doubt be happy to take on the job of arranging distribution for a slice of the CPM.
This model is very similar to the way TV stations have been getting their first run syndicated content (like Oprah and Wheel of Fortune) for years. The programs come with a certain number of embedded commercials along with slots that the stations can sell themselves. It's called "syndicated barter." There are many advertisers who have used this method to ensure that their ads run in the right editorial environment. What they end up paying is the aggregate rating that the individual stations generate.
For original online video entertainment to flourish it seems inevitable that producers and advertisers will need closer partnerships to address the vacuum created by the lack of distribution funding.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Advertising, Indie Video, Syndicated Video Economy, VideoNuze Forums
Topics: Alloy, Johnson & Johnson, Pixsy
-
VideoNuze Report Podcast #19 - June 5, 2009
Below is the 19th edition of the VideoNuze Report podcast, for June 5, 2009.
Daisy was in New York this week for the "NewFronts," a day-long meeting that Digitas sponsored, mainly for independent online video creators and media buyers/agencies. The goals were to educate the market and fuel advertiser interest. Daisy reports that despite the mixed news coming out of the independent video world this year, it was an upbeat gathering.
I provide additional detail on Microsoft's announcement this year of new entertainment-oriented features for XBox 360. The gaming console continues to take on more of a convergence positioning, with new instant-on 1080p video, live streams, Zune integration, etc. With an installed base of 30 million users, Microsoft has a prime opportunity to drive convergence and get a video foothold. The new Xbox 360 features coincide with last week's Hulu Desktop announcement and this week's YouTube XL unveiling.
Click here to listen to the podcast (14 minutes, 47 seconds)
Click here for previous podcasts
The VideoNuze Report is available in iTunes...subscribe today!
Categories: Advertising, Aggregators, Devices, Indie Video, Podcasts
Topics: Digitas, Hulu, Microsoft, NewFronts, Podcast, XBox, YouTube



