-
Hubris Cursed AOL But Broadband Crushed It
I highly recommend reading Saul Hansell's piece in last Friday's NY Times, recapping the ridiculously optimistic quotes senior executives at AOL and Time Warner have made over the years (and be sure to peruse readers' consistently vitriolic comments). For anyone who's watched AOL's rise and fall, the quotes are a stroll down memory lane. But while the picture that emerges is that hubris cursed AOL and contributed mightily to its downfall, in reality it was broadband, and AOL's colossal mismanagement in transitioning to it, that crushed the company.
The chart below shows that AOL's dial-up subscribers topped out in Q3 '02 at 26.7 million, and have been in a free-fall ever since, sitting at just 6.3 million at the end of Q1 '09, a drop-off of 20.4 million or 76%. Where did those 20.4 million dial-up subs go, along with tens of millions of other dial-up and new Internet users? To broadband Internet access, supplied by cable companies and telcos. These companies have grown their U.S. broadband subs from 15.2 million in Q3 '02 to 69.2 million in Q1 '09, an astonishing increase of 54 million subscribers in just 7 years.
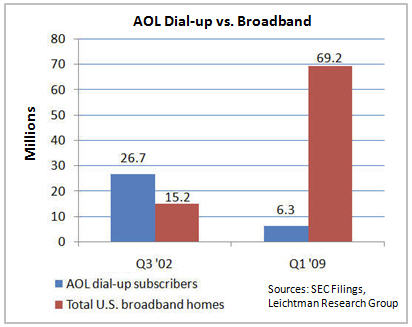
Cable and telco broadband providers have feasted on the carcasses of AOL and other dial-up services like MSN and Earthlink. But, here's what's both incredible and really sad: had AOL management been less arrogant and more strategic in its approach to broadband, it's quite possible that things could have turned out quite differently.
Back in the mid-to-late '90s, I had a front-row seat at AOL's initial reactions to broadband. In that period I was VP Business Development at Continental Cablevision, then the 3rd largest cable operator in the U.S. with over 5 million video subscribers. We were one of the pioneers in testing and rolling out "high-speed" Internet service. While we thought our speedy and always-on broadband connections were a better mousetrap vs. dial-up, we were very concerned about our lack of online content, video-centric branding and ability to effectively market this exciting new service.
In the pre-@Home days, I pushed to explore how we could partner with AOL to help us get our service off to a faster start. A deal with AOL would have had significant advantages to them as well. AOL at the time had a huge capex burden building out more modem banks to keep up with its swelling subscriber ranks. Even still, there was already plenty of AOL subscriber frustration with the slowness of the AOL network, and often you couldn't even get connected on your first or second tries. At least in our geographic footprint we could unburden them of their network build-out, offer better-quality connections and allow them to focus on content and brand-building. As the 3rd largest cable operator, we also offered them a valuable proof-point that they could use to build industry-wide relationships.
After much preparation and scheduling, we met with one of AOL's most senior executives. After articulating our broadband vision and opportunity to work together, he arrogantly dismissed us as if we were precocious children. To him the opportunity we were describing was far too small, and to illustrate his point he asserted that AOL would have 10 million subscribers before we had our first 100,000 (a prediction that was probably correct!).
Needless to say, no meaningful deal with us - or any other cable operator - every materialized. AOL went on to flounder around with various incarnations of AOL Broadband, none of which ever got any traction. AOL continued to grow its subscribers for a number of years and capitalized on its reach by extracting hundreds of millions of dollars from VC-backed startups eager for access to its massive captive audience (some of those deals would later come under scrutiny, as would AOL's accounting treatment for its subscriber business). AOL then bought Time Warner, and the rest as we know is history.
But what if things had gone differently? What if that AOL executive and others had seen the handwriting on the wall - that broadband would eventually render dial-up obsolete - and decided that AOL needed to figure out how to transition to it, instead of dismissing it? Had that happened, it could have forged partnerships throughout the cable and telco industries that would have let it focus on content and services in an open, broadband environment. In fact, I think it's quite possible that AOL could have pre-empted @Home and the RoadRunner venture that Continental eventually joined from getting traction (why start over when AOL, the 800 pound gorilla is in your corner?).
Instead AOL fell victim to its own arrogance and limited strategic vision. Broadband went on to become the single most powerful enabler of the Internet as we know it today (e.g. billions of spontaneous Google searches, Tweets, Amazon purchases, and more recently video views). AOL is now a crippled mish-mash of mostly second-rate properties, on its umpteenth management team, led by new CEO Tim Armstrong.
In retrospect, those fateful decisions AOL made about broadband 10-15 years ago set the stage for the company's eventual demise.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Broadband ISPs, Cable TV Operators, Portals, Telcos
-
4 News Items Worth Noting from the Week of July 20th
Following are 4 news items worth noting from the week of July 20th:
Apple reports blowout iPhone sales in Q2, continuing to drive market - It was another record quarter, as Apple reported selling 5.2 million iPhones, bringing to 21.4 the total sold to date. This despite acknowledging temporary shortages during the quarter. The iPhone continues to revolutionize the mobile market, and from my standpoint is the key catalyst for both recording and consumption of mobile video. This market is poised for significant growth as new smartphones hit the market along with fixed monthly data plans. Apps like MLB.com At Bat 2009, which offers live streams of games, are certain to be hits and emulated widely.
8 minute video of Amazon's Jeff Bezos discussing lessons learned and Zappos acquisition - You couldn't miss news this week of Amazon acquiring Zappos for around $900M, its largest deal ever. Interestingly, Amazon posted a video on YouTube of Bezos discussing the deal, but not until he walked through several maxims of Amazon's success (obsess over customers, think long term, etc.). The video is extremely informal, with Bezos flipping hand-scrawled notes on an easel and improvising funny anecdotes. It has a slightly random feel (until he gets to the Zappos part, you start to wonder, what's the point of all this?), but I give Amazon and Bezos lots of credit for using video in a totally new way to communicate with stakeholders. I'd love to see more CEOs do the same.
Is Disney CEO Bob Iger serious about creating a subscription site for its online video? This week at Fortune's Brainstorm conference, Iger floated the idea that Disney will offer movies, TV shows and games for paying subscribers. The timing seems more than coincidental as Comcast gears up for its On Demand Online trial. Is Iger serious about this, or is it a head fake from Disney so it can try to negotiate incremental payments from Comcast and others seeking to distribute Disney content online? It's hard to tell, but I'd be curious to see what Disney has in mind for its possible subscription service. Consumers hate the idea of paying twice for anything (even paying once is not so popular), so if Disney is somehow going to create another window where they charge for access to content that's still on, or was recently on cable, that would be an awkward model.
"Mad Men" coming to Comcast's On Demand Online trial - Speaking of the Comcast trial, I was thrilled to hear from David Evans, SVP of Broadband at Rainbow Media (owners of AMC, the network behind Mad Men) at yesterday's CTAM Teleseminar that the show will be included in Comcast's trial and presumably in rollout. David is very bullish on online distribution and the larger TV Everywhere concept, though cautioned that there are many rights-related issues still hanging out there. I'm a huge Mad Men fan (whose new season starts on Aug 16th) and the idea that I don't have to worry about recording each episode or managing space on my DVR, and that I can watch remotely when I'm on the road, all underscore TV Everywhere's value.
Categories: Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators
Topics: Amazon, AMC, Apple, Comcast, Disney, iPhone, MLB, Rainbow Media, YouTube, Zappos
-
VideoNuze Report Podcast #24 - July 24, 2009
After several weeks of holidays and vacations, Daisy Whitney and I are back on track this week with our 24th podcast of the year, for July 24, 2009.
This week Daisy and I dig into YouTube from two different angles. Daisy picks up on a piece she wrote that explains the success YouTube is having attracting brands to set up their own channels within the site. These channels can cost up to $200K or more per year. However, there are lots of less expensive ways to work with YouTube, and as Daisy explains, with video helping drive purchase intent, it's a prerequisite that every brand should now have some type of a video presence there.
Despite this, as I wrote earlier this week in "Google is Being Clumsy in Explaining YouTube's Performance," I think YouTube's progress isn't being messaged very well to the market. In its recent Q2 earnings call, a supplementary analyst call and a blog post earlier this week, Google executives sent confusing and sometimes unsupported messages about how far along they are in figuring out to monetize YouTube's premium content-oriented traffic. Given YouTube's bellwether status in the industry, it is being closely watched by many for signs of success or failure.
Click here to listen to the podcast (14 minutes, 6 seconds)
Click here for previous podcasts
The VideoNuze Report is available in iTunes...subscribe today!
Categories: Aggregators, Brand Marketing, Podcasts
-
Video Syndicator 5Min Raises $7.5 Million Series B Round
5Min, a video syndication company specializing in "how-to" content, is announcing this morning that it has raised a $7.5 million series B round, led by new investor Globespan Capital Partners with participation from prior investor Spark Capital. The new round comes on top of the $5 million first round the company raised in January '08. I spoke with CEO Ran Harnevo yesterday to learn more about the company's progress.
5Min, which I last wrote about in Dec. '08, is a textbook Syndicated Video Economy company. As Ran
 explained, its key value proposition is an automated, comprehensive solution for sites seeking to incorporate high-quality relevant video that also offers content providers viewership reach and awareness beyond their own destination sites. There is no cost to either distributors or content providers to participate and resulting ad revenues are split among the parties.
explained, its key value proposition is an automated, comprehensive solution for sites seeking to incorporate high-quality relevant video that also offers content providers viewership reach and awareness beyond their own destination sites. There is no cost to either distributors or content providers to participate and resulting ad revenues are split among the parties. The model is enabled by 5Min's VideoSeed syndication platform, which matches video from 5Min's 100,000+ title catalog to pages that its distribution network's sites specify. The matching is based on the video's metadata which 5Min has assigned and a semantic understanding of the pages themselves. 5Min's video player is embedded on these pages, providing content and ads. The network now consists of hundreds of horizontal (e.g. Answers.com, Wikia, etc.) and vertical sites that reach over 200 million unique visitors/mp generating 14 million unique viewers/mo. This is in addition to the 3.5 million unique visitors to its 5Min.com site. Ran wouldn't specify how many actual video views the network is driving, but said it's in the "tens of millions per month."
5Min focuses on key categories in lifestyle, knowledge and instructional and has built critical mass important for advertisers seeking to contextually target these viewers. 5Min has its own sales team and also uses 3rd party ad networks. Primary units are pre-rolls and overlays. Ran says the company has sold out 100% of its inventory, but would only say CPMs are on the "high end of the market."
5Min continues to aggressively grow its content library, but without producing any of its own content. Ran believes strongly that there's plenty of great content out there already, the challenge producers have is getting it more widely distributed, viewed and monetized (all the things 5Min focuses on).
Historically the company has sourced mainly from DVDs, small-to-medium sized video producers and semi-professionals (all with agreements). 5Min is also starting to offer branded content from partners like UGO Entertainment, Motor Trend, Ford Models, Kiplinger's and others. Ran also alluded to upcoming deals with tier 1 video brands. The how-to category itself is chock full of competitors like Demand Media, Howcast and VideoJug that are producing their own video, but at this point the only how-to specific provider 5Min has a deal with is MonkeySee.com.
I'm not surprised by 5Min's success. It is playing to many of the most important trends in the online video space I've written about repeatedly: fragmentation of audiences, the importance of search and SEO for discovery, higher CPMs through targeted advertising, technology to drive distribution scale and the superior value to consumers in certain categories (especially how-to) of video-based content over traditional text-based alternatives. As more and more sites recognize they need video to stay competitive, but that producing it themselves is an expensive and uneconomic proposition, syndicators like 5Min will enjoy ongoing success.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Deals & Financings, Syndicated Video Economy
Topics: 5Min, Globespan Capital Partners, Spark Capital
-
Will Kaltura's Open Source Video Platform Disrupt the Industry?
This morning Kaltura takes the wraps off its "Community Edition" open source video platform, available as a free download, thereby threatening to disrupt its established proprietary competitors (e.g. Brightcove, thePlatform, Ooyala, Digitalsmiths, Fliqz, Delve, VMIX, etc.). Yesterday Kaltura's CEO Ron Yekutiel explained open source and Community Edition's opportunity. Later in the day I spoke to executives at many of its competitors to get their take what impact open source will have on the video platform market.
As a quick primer, open source isn't a novelty; it's a standard way that certain kinds of software are now developed. Successful companies like Red Hat have been built around open source. In fact many of today's web sites run on the open source software stack commonly known as "LAMP" - Linux (OS), Apache (web server), MySQL (database) and Perl/PHP/Python (scripts). Kaltura has been pioneering open source in the video platform industry which has been dominated by proprietary competitors. Ron believes the video platform industry is ripe for open source success because it has too many proprietary companies offering minor feature differences, all using a SaaS model only and competing too heavily on price.
Kaltura Community Edition's three big differentiators are that it's free for the base platform and offers greater control through self-hosting which can be behind the customer's firewall. Ron also believes that by tapping
 into the open source community, CE can offer more flexibility and extensibility than its competitors.
into the open source community, CE can offer more flexibility and extensibility than its competitors. As with all open source options though, free isn't "free," because if you're interested in support and maintenance, professional services for customization and certain features like syndication, advertising, SEO and content delivery, these all cost extra. And you can't forget about the costs of the internal staff you'd need to run the video platform or the costs of the infrastructure itself (servers, bandwidth, storage, etc.). In the SaaS world, many of these costs are borne by the provider and then reflected in the monthly fee. Determining which approach is more cost-effective depends on your particular circumstances and needs.
All of this is why, as one competitor's CEO told me yesterday, the choice to go open source more often than not isn't primarily price-based; rather it's features-based. In fact, given the range of low cost proprietary alternatives (e.g. $100-$200/mo packages from companies like Fliqz and Delve), even free doesn't represent really significant savings.
When it comes to features, clearly the ability to download CE and self-host is a big differentiator, and will be valued by segments of the market. As Ron pointed out, there are government agencies, universities and others who have mandates to self-host. He also noted that by customers' gaining access to CE's code, their ability to integrate with other applications and customize is enhanced (though again, not without an additional cost).
Other industry executives countered that unless you have to self-host, these advantages are diminished by the fact that in this capex and opex budget constraints make SaaS more appealing than ever, especially for smaller customers with less in-house technical expertise. They added that they're rarely asked about self-hosting options (though that could well be due to self-selection).
Further, many of the leading video platform companies offer a slew of APIs, which open their platforms to 3rd party developers without needing to be open source per se (examples include Brightcove's and thePlatform's robust partner programs). Another industry CEO noted that while there's a gigantic and highly active open source community in the LAMP world, it remains to be seen just how vibrant it is in the video space. And it's important to remember that the intense competition among today's video platforms have already driven the feature bar quite high.
So the question remains: will Kaltura's CE open source approach truly disrupt the video platform industry, causing rampant customer switching and gutting today's pricing models? My sense is no, or at least not immediately. Instead, Kaltura will definitely grow the market, creating new video customers from those who have been dissatisfied with current choices or have not yet jumped into video, but inevitably will. CE will likely peel away some percentage of existing proprietary customers who have been eager for a self-hosted, open source alternative. For many others though, they'll be keeping an eye on open source and will successfully push their existing providers to adopt similar capabilities if they're valued.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Technology
Topics: Brightcove, Delve, Digitalsmiths, Fliqz, Kaltura, Ooyala, thePlatform, VMIX
-
Google is Being Clumsy in Explaining YouTube's Performance
Yesterday's "YouTube myth busting" post on its YouTube Biz Blog had the opposite of its intended effect: rather than providing more transparency about YouTube's performance as it hoped to do, it only set off
 another round of frustrated posts in the blogosphere imploring Google to release actual YouTube numbers.
another round of frustrated posts in the blogosphere imploring Google to release actual YouTube numbers. The post came on the heels of last week's Q2 '09 earnings call and supplementary briefing call (transcripts here and here) which were full of optimistic, yet confusing comments about YouTube's "trajectory" from a handful of Google's senior executives.
Here's what CFO Patrick Pichette said on the supplementary call: "I think that it is true that we are pleased with YouTube's trajectory. And in part the reason why we're communicating it to the Street is there's been so much press over the last quarter with all of these documentations of, you know, massive cost and no business models and all kind of negative press that we've read a lot about. And we just wanted to kind of reaffirm to the Street that this is a very credible business model and it's one that's got trajectory. So in that sense it's just to kind of tell everybody that we're on progress on the plan that we had made for it."
But what plan is he referring to? In almost 3 years of owning YouTube, Google has never publicly disclosed a specific plan for YouTube or laid out its business model, so attempts at reaffirming it fall flat because there's nothing against which progress can be judged. Here are other comments, with my reactions in parentheses.
Pichette on the earnings call: "We are really pleased both in terms of its (YouTube's) revenue growth, which is really material to YouTube and in the not long, too long distance future, we actually see a very profitable and good business for us, so from that perspective, we are really pleased with the trajectory." (WR: that sounds pretty bullish)
Jonathan Rosenberg, SVP of Product Management on the earnings call: "I think what I said - or what I meant to say was that monetizable views have tripled in the last year and that we are monetizing billions of views every month." (WR: that sounds bullish too, but wouldn't some actual numbers really bolster this point?)
Rosenberg on the supplementary call: "And that's part of why I think it's taken us time to kind of triangulate toward what works, and I think some of the things that we have now are still in the pretty nascent stages..." (WR: nonetheless, per earlier comment, profitability can already be forecast in the not too distant future?)
Nikesh Arora, President of Global Sales Operations and Business Development on the earnings call: "So we are seeing significant sell-through in most of our major markets where we have YouTube homepage for sale." (WR: of what ad unit - pre-rolls or display?)
Arora on the earnings call: "So I think the next phase of YouTube is going to be toward pre-roll video on short clips and long form video (which we are in the process of doing) various deals in, which we've announced in the past." (WR: that's new news, YouTube's spoken primarily of overlays in the past)
Rosenberg on the supplementary call: "I would not say our overall optimism that we expressed with respect to YouTube is primarily a function of one specific format. We've actually been testing pre-rolls, I think, for quite a while. So if you interpret that one single comment to pre-rolls to imply the broad conclusion with respect to optimism on YouTube, I think that's probably a mistake." (WR: so maybe pre-rolls aren't actually the next big thing?)
Yesterday's post: "Myth 5 YouTube is only monetizing 3-5% of the site. This oft-cited statistic is old and wrong, and continues to raise much speculation." (WR: what is the percentage then?)
CEO Eric Schmidt on the earnings call: "The majority of YouTube views are not professional content. They are user generated content because that's the majority of what people are watching." In response to whether YouTube is able to monetize user-generated content: "Has not been our focus." (WR: again, letting us know what percentage is professional and the focus of monetization would be very helpful)
These comments raise lots of questions about how far along Google actually is in understanding YouTube's traffic and its ability/plan to monetize it. I think Google is being clumsy in explaining YouTube's performance because it got nervous about the eye-popping estimates that have been floating around lately about how much money YouTube is losing and rushed to try to mitigate this perception, but without being ready to present real numbers as backup. Further, I don't think it rehearsed its executives very well about what to say or how to say it, so the improvised comments did not convey a clear consistent message.
As someone who believes YouTube has enormous long-term value for Google, my advice is that its executives should just stay mum on YouTube until they're ready to make a logical case backed by facts and data. That may take longer than Google or the market hoped, allowing the rumor mill to continue to churn. But continuing to make unsupported statements will only rile YouTube followers further, and eventually sap Google's credibility.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Aggregators, UGC
-
Cable's Emmy Nominations Illustrate Cord-Cutting's Challenge
Last week when the primetime Emmy award nominees were announced, cable programs turned in another strong performance, garnering 272 of the 487 nominations. The Emmys and other awards illustrate one of the key challenges for would-be cord-cutters: outside of per-program download options (e.g. iTunes) that will persist, in the coming TV Everywhere world, virtually none of cable's award-winning programming will be accessible online unless you subscribe to a cable/satellite/telco service provider. This is a critical fact in understanding how the broadband video world is going to unfold.
One of the reasons TV Everywhere is so compelling is that it offers cable networks an on-ramp to online distribution while preserving their existing - and increasingly valuable - dual revenue (monthly affiliate fees and advertising) business model. As more content executives are concluding that advertising alone will not be sufficient for profitable long-form program distribution online, the payments cable networks receive from cable/satellite/telco providers is more valuable than ever. TV Everywhere's online access will inevitably lead to heavier viewership and enhanced loyalty.
The Emmy nominations show the expanding breadth of cable's quality. As the below chart depicts, this year 26 different cable networks' programs were nominated, with HBO, the perennial leader picking up 99 nominations (it should be noted that last week HBO signed on to Comcast's On Demand Online technical trial, further entrenching HBO in the cable world, therefore dimming the notion that HBO will ever be available outside the traditional premium subscription model).
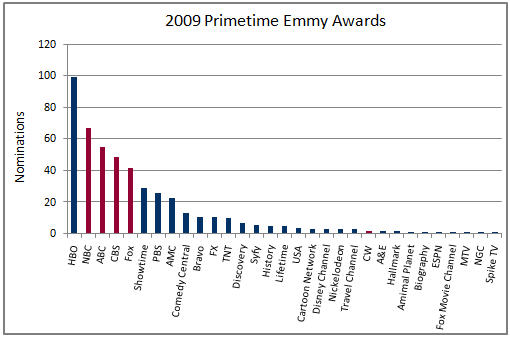
Cable's strength is even better understood by looking at the major Emmy award categories. For example, in the outstanding drama series category, cable got 5 of 7 nominations (AMC-2, FX, HBO, Showtime). In the outstanding children's program category, cable got all 3 nominations (Disney Channel-2 and Nickelodeon). In the outstanding reality program series category, cable got 5 of 6 nominations (A&E, Bravo, Discovery-2, NGC). Even in outstanding comedy series, cable got 3 of 7 nominations (HBO-2, Showtime).
When TV Everywhere gets fully rolled out, cable networks will have little-to-no incentive to make much of their programming available to non-paying video subscribers. That means that the Hulus of the world will have to content themselves with a catalog of broadcast programs, older movies and made-for-broadband series. As broadcast's Emmy nominations show, that still means there's plenty of popular content to drive online audience. But until Hulu figures out a subscription model, it (and its content suppliers) will be economically disadvantaged to cable both on-air and online. This is no small issue given each TV program episode now costs $2-3 million to produce.
Meanwhile, consumers will make their own video choices. If they choose to cut the cord they won't have subscription-based online access to programs like Entourage, Weeds, MythBusters, Hannah Montana, Mad Men or Dexter, not to mention top-shelf sports from ESPN, TNT and others. For some people eager to cut the cord, that will be just fine. But I'm betting that for the majority of viewers that would be unacceptable and they'll continue to choose to subscribe. TV Everywhere can use cable programs' popularity to blunt cord-cutting before it ever takes off and cement cable's appeal in the broadband era.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Broadcasters, Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators
Topics: Comcast, HBO, TV Everywhere
-
4 News Items Worth Noting from the Week of July 13th
Following are 4 news items worth noting from the week of July 13th:TV Everywhere survey should have cable industry clicking their heels - I wasn't at all surprised to read results of a new Solutions Research Group survey fielded to 500 Comcast and Time Warner Cable subscribers giving the concept of TV Everywhere positive reviews. As Multichannel News reported, in the overall survey 28% of respondents said the idea was "excellent" and 45% said it was "good." Digging in further though, among those 18-49 the "excellent" score surged to 80%, while 87% of Hulu and Fancast users approved of the idea. Unprompted, respondents cited benefits like convenience, remote viewing, getting better value from their cable subscriptions, watching on PCs in rooms without TVs and catching up on missed programs. My take: consumers "get" what TV Everywhere is all about and already have positive initial reactions, meaning there's very significant upside for the cable industry.Paid video forecast to surpass free - A Strategy Analytics forecast that got attention this week says that the global paid online video market will be worth $3.8B in 2009, exceeding the global free online video segment which will total $3.5B. I haven't seen the details of the forecast, but I'm very curious what's being included in each of these numbers as both seem way too high to me. The firm forecasts the two segments to grow at comparable rates (37% and 39%), suggesting that their size will remain relatively even. I suspect we're going to be seeing a lot of other research suggesting the paid market is going to be far larger than the ad-supported market as sentiment seems to be shifting toward subscriptions and paid downloads.
Consumer generated video contests remain popular - VideoNuze readers know I've been intrigued for a while now about contests that brands are regularly running which incent consumers to create and submit their own videos. Just this week I read about two more brands jumping on the bandwagon: Levi's and Daffy's retail stores. NewTeeVee had a good write-up on the subject, citing new research from Forrester which reviewed 102 different contests and found the average prize valued at $4,505. I see no end in sight for these campaigns as the YouTube generation realizes it's more lucrative to pour their time into these contests than training their cats to skateboard. Brands too are recognizing the wealth of amateur (read cheap!) talent out there and are moving to harness it.
MySpace has lots of work ahead to become a meaningful entertainment portal - The WSJ ran a piece on Monday based on an interview with Rupert Murdoch in which he was quoted as saying MySpace will be refocused "as an entertainment portal." That may be the winning ticket for MySpace, but I'm not totally convinced. MySpace has been in a downward spiral lately, with a 5% decline in audience over the past year, a 30% headcount reduction and an executive suite housecleaning. While always strong in music, according to comScore, its 48 million video viewers in April '09 were less than half YouTube's 108 million, while its 387 million video views were about 5% of YouTube's 6.8 billion. Clearly MySpace has a very long way to go to give YouTube serious competition. It will be interesting to see if the new management team Murdoch has installed at MySpace can pull off this transition.
Categories: Aggregators, Brand Marketing, Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators, UGC
Topics: Comcast, Forrester, MySpace, Strategy Analytics, Time Warner


