-
New York Magazine Relaunches Video; Curation is Key
New York magazine, the go-to-source for in-the-know New Yorkers, has relaunched the video section of its web site using the Magnify.net platform. What separates the magazine's effort from others is its plan to actively augment video it produces itself with other video sources, including users. By "curating" others' video, New York is looking to beef up the video section of its site by tapping into others' energy. Michael Silberman, the magazine's GM, Digital Media, explained more to me last week.
Michael said that as a print publication, New York was unlikely to ever have a large staff devoted to video production (it currently has just one dedicated person). However, the New York team has been watching broadband video's surging popularity and wanted to capitalize on this by making video an integral part of its web site. A key goal was to cost-effectively bulk up the volume of video it offered. That led the team to focus on how to aggregate and intelligently curate video from other sources so that the magazine's sensibility would be maintained. And all of this needed to be done in a "Hulu-like" user experience with accurately tagged videos presented in a logical flow.
In a prior post about Taste of Home magazine, I wrote about curation and how it can be a powerful editorial lever for print publishers' sites that have lean video budgets. The reality is that there is a lot of really interesting video being created that would be quite valuable to mainstream publications. In the Internet era, timeliness and omnipresence are important calling cards. Tapping into video-enabled readers, who often find themselves at the right place at the right time with their cellphones, digital cameras and Flips on hand, can produce real value if incorporated the right way.
Curation has been a mantra of Steve Rosenbaum, CEO and founder of Magnify.net, which I originally profiled here. The company has been continuously augmenting its video platform features while maintaining a focus on curation as a differentiator. This clearly paid off with the New York win; Michael said that of all the video platform companies it investigated, Magnify was the only one that could fully support its curation objectives. He also cited Magnify's robust customization tools using mainly CSS and Javascript that allowed his team to migrate the entire video section over in just 5 weeks.
New York plans to bring on a producer who will, among other things, run the curation process. No doubt there will be plenty of trial-and-error in the hunts for and includes appropriate 3rd party video, including users' submissions. But as I explained in the Taste of Home post, curation's potential suggests the emergence of a new editorial model for video that is particularly relevant in these penny-pinching economic times. It's the kind of break-from-tradition that may be jolting to editorial purists, but which reflects pragmatic - and strategic - thinking about how print publications can evolve and succeed in the broadband video era.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Magazines
Topics: Magnify.net, New York, Taste of Home
-
What the Broadcast TV Networks Can Learn from the Boston Globe's - and Other Newspapers' - Demise
Those of us who live in New England and still actually subscribe to Boston Globe woke up Saturday morning to a banner headline on page 1: "Times Co. threatens to shut Globe, seeks $20m in cuts from unions." With newspapers around the country declaring bankruptcy or going out of print, the news really shouldn't have come as a surprise.
The Globe's and other newspapers' struggles have been widely reported. They are on the wrong end of a double-barreled shotgun: the years-long shift in consumer behavior toward the Internet and more recently,
 the devastating recession. To me there's a strong analogy here: the Internet (an "electronic printing press") is to newspapers what broadband (a new video delivery platform) is to broadcast TV networks. So what can the broadcast TV networks learn from the newspapers' travails so they avoid a similar fate? Here are 5 thoughts:
the devastating recession. To me there's a strong analogy here: the Internet (an "electronic printing press") is to newspapers what broadband (a new video delivery platform) is to broadcast TV networks. So what can the broadcast TV networks learn from the newspapers' travails so they avoid a similar fate? Here are 5 thoughts:Keep the product in synch with the customer - it's cliche to say this, but at the root of every successful business is an ability to keep the product in synch with the customer's behavior. But as the world changes, staying in synch is often at odds with traditions, deeply-ingrained cultures and management's skills. The harsh reality is that there can be no sacred cows when it comes to the product. Just because something's always been done a certain way does not make it right.
For TV networks, I think the key lesson here is around program length. By tradition, programs have been 30 or 60 minutes. But online is about short-form content. Broadband delivery provides an opportunity to expand the networks' mission and capture new market share (as some are already doing). That doesn't mean giving up on 30 and 60 minute programs, but it does mean more actively diversifying their attention and resources.
Focus on monetization - If keeping the product right is job #1, then getting paid for it is certainly job #2. Newspapers have experimented widely with ad-supported and paid models, yet they've suffered their own "analog dollars, digital pennies" conundrum, with online users not generating comparable revenues per eyeball as the print edition. There are various explanations for why they've fallen short.
When I look at networks' current online efforts, I am increasingly concerned they're not going to succeed either. Their ad strategy for online programs is not aggressive enough (yes, as a viewer it hurts to say that) to make the online delivery model work. And on the execution side, as NBC.com recently showed, they're often not even capitalizing on what's readily available to them. Both need to change fast.
Partner effectively - Newspapers have grappled for years with how to defend classified categories like help wanted through industry partnerships. Now broadcast networks are rallying around Hulu (and possibly TV.com) as their own partnership vehicles. But these entities mustn't be forced to compete with one hand behind their back. They need rights to choice ad inventory to sell. They need to be free to pursue their own partnerships and not be curtailed as Hulu currently is with Boxee. And they need to be supported financially and strategically for the long run. Even then, none of this guarantees success.
Restructure costs aggressively - There's simply no escaping the fact that businesses with troubled top lines need to restructure their costs aggressively to stay viable. The key is getting ahead of this process, rather than waiting until the last possible minute. This isn't easy with unions and guaranteed jobs and managements that are well-paid. Broadcast TV networks face similar issues: strong guilds rightfully protective of their members' interests and executives who are perceived as overly compensated. Many in the industry have called out the fact that all of Hollywood needs to focus more on aligning costs with market realities. The day of reckoning is at hand.
Prepare to be radical - Painful as it is, sometimes there's no avoiding doing the radical. The free market can be quite ruthless. If Craig Newmark chooses to run Craigslist as a virtual non-profit, then anyone looking to make money out of classifieds is going to get hit. If the Huffington Post can make a business out of repackaging others' content under its own headlines and excelling at SEO then original newsgathering is threatened. And if Google can support YouTube's operating losses, then it will be around to continue to take video market share and attention away from incumbents. These are game-changing forces; the responses to them need to be equally radical.
While Americans have never watched more TV than they do today, there are storm clouds all around the broadcast networks. Hopefully they're studying the newspapers' demise and taking away the right lessons.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Broadcasters, Newspapers
Topics: The Boston Globe
-
Time Warner's Jeff Bewkes is Hurting the Cable Industry by Hyping "TV Everywhere"
Leading up to and during this week's Cable Show (the cable TV industry's big once-per-year conference), Time Warner CEO Jeff Bewkes continued to hype his company's "TV Everywhere" vision. Observing the media coverage of this initiative since the WSJ broke the news about it over a month ago, following how industry executives are responding to it, and listening to Mr. Bewkes's further comments, I've concluded that TV Everywhere - and Mr. Bewkes's hyping of it - is actually hurting the cable industry, not helping it. I don't think this was his intent, but I do believe it's the reality.
Let me say upfront, I think the idea that cable TV network programs being made available online, to paying multichannel video subscribers, but without an extra fee, is terrific. But it is a very long-term idea, requiring that lots of divergent constituent business models come into alignment. It also requires significant - and coordinated - technology development and implementation by numerous parties that have widely varying willingness and readiness to participate. And not least, someone has to actually pay for all this cross-industry technology development and testing to preclude it from becoming a hacker's paradise. It's a very tall order indeed.
Yet when I read Mr. Bewkes's comments about TV Everywhere and its implementation, he inevitably points to what Time Warner Cable (btw, not the company he runs any longer with the spinoff now almost complete) is doing with HBO in Milwaukee. By continuing to do so, I believe he is trivializing how complicated implementing something like TV Everywhere would be across the industry and across the country.
Mr. Bewkes's sketchiness with the details of how TV Everywhere would work is obvious in his interview with PaidContent's Staci Kramer here and here. There are plenty of generalizations and descriptions of the
 end-state, but little offered about how this would all be accomplished. One example: "...all of the video providers would have a link in their software where they could be pinged to see if the person is a video subscriber. That's not a complicated thing. It's simply a software program that asks does anybody have Staci as a sub and then Charter says, yes, I've got her and bang."
end-state, but little offered about how this would all be accomplished. One example: "...all of the video providers would have a link in their software where they could be pinged to see if the person is a video subscriber. That's not a complicated thing. It's simply a software program that asks does anybody have Staci as a sub and then Charter says, yes, I've got her and bang." Yeah, right! And if things were only that easy then maybe the cable and satellite industry wouldn't also have the 2nd lowest customer satisfaction score out of 43 industries measured by the American Customer Satisfaction Index (ahead of only airlines).
Meanwhile because the details have been so sparse, the media has been left to come to its own confusing and often conspiratorial conclusions about what TV Everywhere really means to consumers. Here's a sample of the recent headlines: "TV Everywhere - As Long As You Pay for It," "Time Warner Goes Over the Top," "Some Online Shows Could Go Subscription-Only" and "Pay Cable Tests Online Delivery." Talk about message mismanagement...
The cable industry - both operators and programmers - are getting hurt most by the hype and confusion around TV Everywhere. Consumers' expectations are being raised without any sense of timing or what will actually result. Many consumers already have no love lost for their cable operator and would jump at the chance to cut the cord. The flowery-sounding "TV Everywhere" suggests that day may be coming at exactly the moment when the industry should be collectively driving home a positive story that cable operators are investing in broadband - yet again - to provide more value to subscribers.
Meanwhile cable networks are also being hurt by TV Everywhere's hype. They are being forced to respond in public (as Disney's Bob Iger did in his keynote yesterday) to these vague ideas. But it is a PR nightmare-in-the-making for them, as they need to defend why consumers will have to continue paying subscription fees to watch their programs online, while broadcast TV network programs are freely available. That's a thankless job for them, and reading through Mr. Iger's speech yesterday, you could almost sense his resentment at being forced into this position.
Why Mr. Bewkes isn't modulating his comments about TV Everywhere in light of all this eludes me. Anyone who's ever created a product knows about "roadmaps," where product features are added over time, and customers are methodically messaged about enhancements to come. With TV Everywhere, it's as if all that matters to Mr. Bewkes is talking about the glorious end state, thereby erasing meaningful online benefits that can be delivered along the way. Contrast this with Comcast's OnDemand Online plan that offers the simple, but still highly-valuable near-term proposition of online cable programs on its own sites, and possibly the networks' as well.
Ironically, nobody should know the perils of hype better than Time Warner executives, since this was the company that brought us the ill-fated "boil-the-ocean" Full Service Network back in 1994. A reminder: those who ignore history are doomed to repeat it.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators
Topics: Comcast, Disney, Time Warner
-
VideoNuze Report Podcast #12 - April 3, 2009
Below is the 12th edition of the VideoNuze Report podcast, for April 3, 2009.
After a week off, Daisy Whitney and I are back. This week we discuss new comScore data Daisy learned about while attending the OMMA Video conference, which supports the idea of TV ad spending shifting from TV to broadband video. Then we dig deeper into the significance of Disney's deal to bring promotional clips to YouTube, which the companies announced earlier this week. More detail on the deal is also in this post I wrote on Tuesday.
Click the play button to listen to the podcast (13 minutes, 49 seconds):
Click here for previous podcasts
The VideoNuze Report is available in iTunes...subscribe today!
Categories: Podcasts
Topics: comScore, Disney, Podcast, YouTube
-
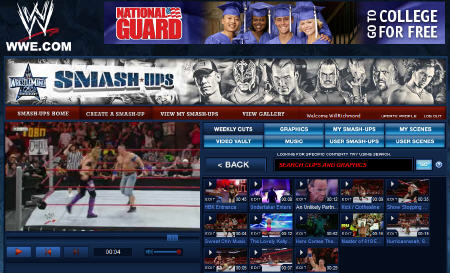
WWE's "Smash-Ups" Drives Excitement for WrestleMania 25th Anniversary
World Wrestling Entertainment (WWE) has created an innovative user-edited video application called "Smash-Ups" to engage its fans and drive excitement for this Sunday night's "WrestleMania 25th Anniversary" event. It's a great example of how long-form video can be segmented and made available to users to exercise their creativity in support of the brand. In this case, WWE is also offering a $5,000 prize to the user who creates the best clip.
I've been a fan of these kinds of mashup or re-mix apps, going back to a post I did in August '07 about the one that Universal Pictures and Metacafe created for "The Bourne Ultimatum." More recently, NFL has had success with its NFL "Replay Re-Cutter" launched last fall. I continue to believe they offer a clever way for fans to engage with the brand and potentially tapping into archive content that likely isn't creating any current value. The clips create new video views and incremental ad inventory. And as the clips are shared by users they also become a cheap source of viral marketing.
WWE gets all this. Brian Kalinowski, WWE's EVP, Digital Media said, "The WWE is renowned for its passionate fans and compelling content, and WrestleMania Smash-Ups allows us to bring both together in an innovative, engaging broadband video experience....unleashing the full value of our library of tens of thousands of video clips to drive greater engagement from our viewers and enhanced content monetization." In addition to the video clips, Smash-Up lets users edit the segments provided, and insert audio tracks and title cards. If there's one downside, it's that the maximum clip length is 2 minutes, which is not a lot of time for hard-core fans to create a meaningful montage out of 25 years of classic footage.
The Smash-Ups are powered by Gotuit, a company I've written about which has also recently announced it is powering Major League Soccer's "QuickKicks" video portal and remix and Lifetime's "Movie Mash-up" feature. As CEO Mark Pascarella and VP &GM Patrick Donovan, explained, a key Gotuit advantage for all these initiatives is that no new video clips are actually being created. Rather, by using Gotuit's metadata and indexing capabilities, the content provider can tag particular scenes and present them as clips. When users create their mixes, they're actually just combining a series of "virtual clips" - time-coded in and out points in the underlying long-form video files. This makes managing these activities a lot simpler and cost-effective. The Smash-Ups also showcase how the Gotuit UI can be fully customized and integrated with WWE's look-and-feel.
WWE is monetizing the clips through both sponsorships (THQ) and ads. A pre-roll or mid-roll is inserted up to a maximum frequency of 1 ad per 2 minutes of content (a Gotuit setting the content provider can adjust). Users can share their creations with embed code or via email. WWE has also done a great job promoting the Smash-Ups, enlisting its superstars to make their own videos which are posted on YouTube.
These user-edited applications (especially if they're part of contests with meaningful incentives) are a pretty compelling tactic for content providers to drive viewership and monetization. I expect we'll continue to see more of them launched.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: UGC
Topics: Lifetime, MetaCafe, NFL, WrestleMania, WWE
-
YouTube to Merge with Hulu, Entity to be Renamed Either "YouLu" or "HuTube"
In a surprising turn-of-events, VideoNuze has learned that Google will acquire Hulu and merge it with YouTube. The resulting entity will be named either 'YouLu' or 'HuTube.' The merger brings together the two most-trafficked video sites into a powerful new player.
In an interesting twist, the final acquisition price has not yet been determined. Instead, the price will be based on a new algorithm Google is creating to accurately measure just how effective Hulu is at turning its
 users' brains into 'creamy giggity-goo' as Seth MacFarlane asserts it will in the latest of Hulu's alien-inspired ads. The algorithm will actually be able to count how many more of users' brain cells die as a result of watching shows on Hulu beyond the cells that already died due to regular on-air network TV viewership.
users' brains into 'creamy giggity-goo' as Seth MacFarlane asserts it will in the latest of Hulu's alien-inspired ads. The algorithm will actually be able to count how many more of users' brain cells die as a result of watching shows on Hulu beyond the cells that already died due to regular on-air network TV viewership. It turns out that Hulu's positioning as an 'evil plot to destroy the world' was considered highly synergistic with Google's longstanding mantra to 'do no evil.' Google CEO Eric Schmidt revealed that the company decided some time ago to move beyond its good-guy image, saying, "Look, we got a lot of mileage out of that 'doing no evil' malarkey, but it's time to get real. We're an avaricious multi-billion company now, and all these wacky tree-hugging green initiatives our engineers keep dreaming up can't hide that." He added, "We really admire the traction Hulu is getting by turning 'evil' into a virtue and want to tap into that concept further. Those Hollywood guys beat us hands-down when it comes to creativity."
For its part, Hulu's owners' decision to merge with YouTube, for a price not yet quantifiable, can only be seen as waiving the white flag of surrender. In an email exchange between Jeff Zucker, NBCU's CEO and Peter Chernin, Fox's former CEO (who made the original Hulu deal), obtained by VideoNuze, Zucker's frustration with Hulu's distant second place status is palpable. Among other things he says, "I thought we had dumbed down our shows as much as possible, but YouTube has clearly tapped into audiences' insatiable appetite for the inane. Who would have thought that skateboard-riding cats crashing into walls would have more audience appeal than our $2 million/episode scripted dramas. There really is no accounting for taste."
In response Chernin is quoted as saying, "Rupert always thought Hulu was a small potatoes deal, not really
 capable of losing a large, exciting amount of money. On the other hand, YouTube has been a gigantic black hole for Google, so the opportunity to join forces and achieve scale at losing money together was just incredibly compelling." He added, "Plus, you have to remember, Rupert's heart is really in newspapers. He continues to think this whole Internet thing is a fad that will eventually blow over, with people returning to newspapers as their trusted source of news and propaganda. So the company is logically positioning itself to have sizable video losses to offset expected massive gains in newspaper profitability."
capable of losing a large, exciting amount of money. On the other hand, YouTube has been a gigantic black hole for Google, so the opportunity to join forces and achieve scale at losing money together was just incredibly compelling." He added, "Plus, you have to remember, Rupert's heart is really in newspapers. He continues to think this whole Internet thing is a fad that will eventually blow over, with people returning to newspapers as their trusted source of news and propaganda. So the company is logically positioning itself to have sizable video losses to offset expected massive gains in newspaper profitability."Meanwhile, in a meeting with employees, Hulu CEO Jason Kilar reportedly sought to put a positive spin on the merger. Employees who have Twittered the meeting say that to pump up employee enthusiasm he re-told stories of how much fun it was to originally come up with the name 'Hulu,' reportedly saying, "Look how much mileage we got of one ridiculous-sounding made-up name, just imagine the branding possibilities of the even more-ridiculous sounding names YouLu or HuTube..." Negotiations are already underway with the Chinese portal and domain parking company that own the respective URLs.
The merger left many industry analysts scratching their heads. Representative of their reaction, VideoNuze's Will Richmond said, "Geez, I never thought we'd see a more nonsensical media merger than the one between Time Warner and AOL, but I think this YouLu/HuTube thing might just be it. Let's hope it's not for real, and is just some kind of April Fool's Day joke cooked up by an industry analyst to provide some once-per-year, cheap laughs."
Categories: Aggregators, Deals & Financings
Topics: FOX, Hulu, NBCU, YouTube
-
6 Reasons Why the Disney-YouTube Deal Matters
Late yesterday's announcement that Disney-ABC and ESPN would launch a number of ad-supported channels focused on short-form content was yet another meaningful step in broadband video's maturation process. Here are 6 reasons why I think the deal matters:
1. It validates YouTube as a must-have promotional and distribution partner
For many content providers it's long since become standard practice to distribute clips, and often full-length content, on YouTube. Yet aside from CBS, no broadcast TV network has seriously leveraged YouTube.
 That's been a key missed opportunity, as YouTube is simply too big to ignore. It's not just that YouTube notched 100M unique viewers in Feb. '09 according to comScore, it's that the site has achieved dramatically more market share momentum over the past 2 years than anyone else, increasing from 16.2% of all streams to 41% of all streams.
That's been a key missed opportunity, as YouTube is simply too big to ignore. It's not just that YouTube notched 100M unique viewers in Feb. '09 according to comScore, it's that the site has achieved dramatically more market share momentum over the past 2 years than anyone else, increasing from 16.2% of all streams to 41% of all streams. Increasingly, YouTube is not the 800 pound gorilla of the broadband video market; it's the 8,000 pound gorilla. Disney has acknowledged what has long been tacitly understood - as a video content provider, it's impossible to succeed fully without a YouTube relationship.
2. It creates a path for full-length Disney-ABC programming to appear on YouTube and elsewhere
While this deal only contemplates short-form video, and more than likely, mostly promotional clips, it almost certainly creates a path for full-length episodes to appear as well, as the partners build trust in each other and learn how to monetize. Full-length content is most likely to come from ABC, not ESPN (the release
 pointedly states no long-form content from ESPN's linear networks is included) as part of a newly expanded distribution approach.
pointedly states no long-form content from ESPN's linear networks is included) as part of a newly expanded distribution approach.For YouTube, which has been aggressively evolving from its UGC roots in its quest to generate revenues, the current clip deal alone is a big win; gaining distribution rights to full-length programs would be an even more significant step. Underscoring YouTube's flexibility, the current deal allows ESPN's player to be embedded, and for Disney-ABC to retain ad sales. YouTube's reported redesign, which places more emphasis on premium content, is yet another way it is getting its house in order for premium content deals.
3. It opens up a new opportunity for original short-form video to flourish
When you think about broadcast TV networks and studios, you immediately think of conventional long-form content. Yet all of these companies have been producing short-form content that either augments their broadcast programs, or is originally produced for broadband, as Disney's own Stage 9 is pursuing. The levels of success of this content have been all over the board.
With YouTube as a formal partner, Disney can aggressively leverage it as its primary distribution platform, gaining more direct access to this vast audience. Facing unremitting market pressures on many fronts, broadcast TV networks themselves need to reinvent their business models. Short-form original content married to strong distribution from YouTube would be a whole new strategic opportunity.
4. It puts pressure on Hulu and other aggregators
It's hard not to see YouTube's gain as Hulu's - and other aggregators' - loss. For sure nothing's exclusive here, and as PaidContent has reported, discussions about Disney distributing full-length programs on Hulu (as well as YouTube) are also underway. But the Disney deal underscores something important that differentiates YouTube from Hulu: YouTube is both a massive promotional vehicle and a potential long-form distributor, while Hulu is really only the latter.
YouTube's benefit derives from its first-mover status. Hulu has done a tremendous job building traffic and credibility in its short life, but it is still distant to YouTube in terms of reach. I continue to believe it is far easier for YouTube to evolve from its UGC roots to become also become a premium outlet than it is for Hulu - or anyone else - to ever compete with YouTube's reach.
5. It raises threat warning to incumbent service providers by another notch
It's also hard not to see the Disney deal moving YouTube's threat level to incumbent video service providers (cable/satellite/telco) up another notch. We discussed YouTube's importance to these companies at the Broadband Video Leadership Evening 2 weeks ago (video here), and I thought the panelists generally did not give YouTube much credit as it deserves.
I continue to believe that of all the various "over-the-top" threats to the current world-order, YouTube is the most meaningful ad-supported one. It has massive audience, a potent monetization engine in Google's AdWords, and with the Disney deal, increased credibility with premium content providers. Especially for younger audiences, the YouTube brand means a lot more than any incumbent service provider's. If I were at Comcast, Verizon or DirecTV, I'd be keeping very close tabs on YouTube's evolution.
6. It exposes the absurdity of the ongoing Viacom-Google litigation
Two weeks ago at the Media Summit I listened to Viacom CEO Philippe Dauman describe the status of his company's $1 billion lawsuit against Google and YouTube. As he talked of mounds of data and reams of documentation being collected and reviewed, I found myself slumping in my chair, thinking about how well all the lawyers involved in the case must be doing, and yet how pointless it all seems.
The old adage "2 wrongs don't make a right" fits this situation perfectly. There is no question that in the past YouTube was lax about enforcing copyright protection on its site and cavalier about how it responded publicly to the concerns of rights-holders. But it has made much progress with its Content ID system and a good faith effort to become a trusted partner. All of this is evidenced by the fact that Disney wouldn't even be talking to YouTube, much less cutting a deal, if it didn't view YouTube as reformed. While the media world is moving on, adapting itself to the new rules of video creation, promotion and distribution, Viacom continues to waste resources and executive attention pursuing this case. To be sure, Viacom has been plenty active on the digital front, but it is long overdue that these companies figure out how to resolve their differences and instead focus on how to work together to generate profits for themselves, not their lawyers.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Advertising, Aggregators, Broadcasters, Cable Networks, Partnerships, UGC
Topics: Disney, ESPN, Google, Viacom, YouTube
-
Interview with Tom MacIsaac, New CEO, ExtendMedia
This morning ExtendMedia is announcing that one of its board members, Tom MacIsaac has been named CEO. Tom is a long-time technology executive and venture capitalist. He and I got to know each other when he was running Lightningcast, one of the earliest broadband video advertising companies, which was sold to AOL in 2006. Tom went on to run strategy and M&A at AOL, where he led a $1B in acquisitions and more recently has been a venture partner at BlueRun Ventures and run Cove Street Partners, his own investment and advisory firm.
Tom's addition is a big step forward for the company, which has established a strong, yet relatively low-key position in the market. In my view that's been for two reasons: first, because Extend has emphasized pay media models, whereas a lot of the attention has been on ad-supported ones, and second, because while
 Extend has had a very strong team, the CEO role itself has been vacant for some time. For better or worse, one of the lessons I've learned over the years is that a high-profile, well-known CEO, who spends a significant portion of his/her time on externally-oriented visibility-building activities is a key success factor for young companies. I'm not a fan of the "rock star" CEO model, but I do believe in the "CEO as #1 company salesman" approach. Without such a person in place, a young company's whole team has to work that much harder to succeed.
Extend has had a very strong team, the CEO role itself has been vacant for some time. For better or worse, one of the lessons I've learned over the years is that a high-profile, well-known CEO, who spends a significant portion of his/her time on externally-oriented visibility-building activities is a key success factor for young companies. I'm not a fan of the "rock star" CEO model, but I do believe in the "CEO as #1 company salesman" approach. Without such a person in place, a young company's whole team has to work that much harder to succeed.Tom and I talked about his new role, ExtendMedia's opportunities and the broadband market in general. An edited transcript follows:
VN: Congratulations on joining ExtendMedia. What attracted you to the role?
TM: Extend is in an extremely exciting space as IP video changes the entire media and communications landscape. It has a great team with deep domain expertise, is very well-funded with great investors in Atlas Venture, Venrock and TVM Capital and has an enviable competitive position being the leading independent carrier-grade multi-screen video platform.
VN: Describe ExtendMedia's key product and technology differentiators and who its primary competitors are.
TM: We provide an enterprise class, multi-screen video platform that content owners and distributors use as a foundational asset in building video services. We manage video content across the lifecycle from ingest to monetization and across IPTV, web and mobile services in both ad-supported and pay media business models.
Our primary competitor is thePlatform, a division of Comcast. We don't really run into the Flash-based web video publishing companies like Brightcove, Ooyala, PermissionTV, etc. because we are usually deeper in the our customers' infrastructure trying to solve more complex problems that span the set-top box, PC and/or mobile devices, using multiple business models.
VN: ExtendMedia has always been strong with pay media business models, but has focused less on ad-supported ones. Given your background at Lightningcast, do you think that will change?
TM: Extend has always supported both ad-based streaming business models as well as pay media, but you're certainly right that we have been particularly strong in pay media. That said, we have new additional capabilities to help our customers in their ad-supported streaming media businesses in our next release and later this year will have yet another set of interesting enhancements targeted on maximizing video CPMs for our customers. We aren't going to get into the ad serving business but we are going to extend the boundaries of our product in that direction so that we can help the ad monetization engines we partner with leverage everything at our customers' and our disposal to maximize CPMs. We have some specific ideas on how we can really add value here.
VN: What kind of company is an ideal ExtendMedia customer?
TM: A telco, cable MSO or mobile carrier that is building a multi-screen video platform or a large diversified media company that has built several stove-piped digital video services over the last few years and is now trying to pull everything together on a single infrastructure.
VN: What areas of your background and experience do you think will be most valuable to the company?
TM: I've been in the technology business for 20 years, as a lawyer to tech companies, as a venture capitalist, as a board member, as a founder/entrepreneur and as an executive in large technology companies. I've sold three companies that I've run to public companies and acquired five venture-backed companies as an executive at AOL. That's a pretty good array of perspectives to bring to the table.
But my video advertising expertise in particular will definitely come into play at Extend. At Lightningcast we built the first advertising technology platform designed to monetize IP video and were at the table at the inception of some of the most successful video services out there - Comcast's Fancast and Hulu, for example. Despite all the activity and investment in the area, with possibly one or two exceptions, in the three years since I left Lightningcast no one's doing anything we didn't think of and do first.
VN: What do you think your top 2-3 priorities will be?
TM: We're on the right track, so it's all about execution.
VN: What's your perspective on the broadband video market today? And what would you say about incumbent service providers' evolving role in delivering broadband video services?
TM: I think the incumbent service providers are getting much smarter about IP video. They are leveraging their advantages much more effectively. When the web video phenomenon took off it was initially about user-generated content and giving the little guy content creator a direct-to-consumer path. The problem is that that hasn't paid off - the business model doesn't work yet - the dollars just aren't there.
The trend today is back to professional content and that plays to service providers' strengths. Initially it was all about advertising, and now the trend is toward dual offerings of both ad-supported and pay media business models, which is also good for incumbents. Many service providers, like our customers AT&T and Bell Canada for example, have set-top box, web and mobile sand boxes to play with and if folks like Extend can help them deliver video across and between those platforms and help manage the environments and entitlements from a single platform that will provide real value to their consumers and will drive loyalty. Comcast's On-Demand Online and Time Warner's TV Anywhere initiatives are good examples of service providers figuring out how to leverage their strengths in ways that benefit them, their content partners and consumers.
VN: You've been a venture capitalist, have raised venture financing and have successfully sold companies. What advice do you have for broadband video entrepreneurs given the state of the economy?
TM: The space is clearly overbuilt in many segments. There will be a lot of fallout. Investors are gun-shy. So do your research and make sure you have something unique. That said, it is going to be one of the most interesting and lucrative areas in all of technology over the next decade. So if you've got something truly innovative - go for it.
VN: Thanks Tom, and good luck.
(note: ExtendMedia is a VideoNuze sponsor)
Categories: People, Technology
Topics: ExtendMedia