-
Net Neutrality in 2008? Let's Hope Not.
Network or "net" neutrality, a confusing legislative concept being promoted by large online and content players, may be the hottest broadband video topic in 2008, at least according to Jeff Richards, VP of VeriSign's Digital Content Services, who makes his case at his blog Demand Insights.
I had the pleasure of informally debating net neutrality's merits with Jeff (who's officially neutral on the subject by the way) over cocktails at a VeriSign customer event I just spoke at. Jeff is persuasive about why net neutrality is such a hot button issue, and that its resolution - one way or another - has broad repercussions across the technology, content and Internet industries.
First, a primer for those not familiar with net neutrality. To date the Internet has functioned as a level playing field of sorts. Anyone putting up a web site could be confident in the knowledge that broadband ISPs would neither favor nor disadvantage one player's access to users over another's.
Big online content and technology companies now want to codify this tradition in legislation commonly referred to as net neutrality. Big broadband ISPs (i.e. cable operators and telcos) regard this as needless regulatory meddling, a classic "solution in search of a problem" that would unnecessarily limit their future business dealings and influence their investment decisions.
Interest in net neutrality legislation has waxed and waned, as lobbyists for the pro-net neutrality side (content and technology firms) try to convince legislators that this really is an important issue for constituents and that this isn't just a "rich vs. richer" debate that should be left to the industry's participants to figure out, while anti-net neutrality lobbyists (cable and telco firms) argue the opposite point of view.
So what might precipitate the resurgence of interest in passing net neutrality legislation? In two words, broadband video.
As Jeff points out, the massive adoption of broadband video, which still disproportionately comes from illegal video file-sharing networks, is motivating ISPs to reevaluate current policies. Stoking this reevaluation is the awakening that the really big money is now being made by legitimate companies like Google (current market cap $200+ billion) which ride freely over ISPs' networks. As such, ISPs are wondering whether the balance of economics has gotten out of whack and if they can get a bigger share of the pie.
Some ISPs are now blocking or "shaping" certain types of traffic. The most recent example that came to light was Comcast, who the AP recently found is blocking BitTorrent's traffic in the Bay Area. Comcast's vague response, coupled with ill-thought out earlier remarks from telco executives about their own business intentions, have inflamed conspiracy theorists' worst fears about what kind of world could result absent immediate net neutrality action.
Yet for me, preemptive net neutrality legislation can only be justified if you buy into one or both of the following two assumptions.
First, that any new premium tier of service ISPs may want to sell to certain preferred providers (e.g. Google is search engine of choice, so its results somehow load faster) must, by definition, mean that some other provider is disadvantaged as a result. But this presupposes a zero-sum ISP network, which is not true. To enable a high quality-of-service ("QOS") tier for preferred partners does not technically necessitate a degrading other non-preferred services. Not to mention degrading other services would be a foolish, provocative thing for ISPs to do.
The second assumption is that regardless of whether ISPs create QOS-enabled premium tiers, they cannot be trusted not to block or harmfully shape traffic, whether it's legitimate or not. While there have been random acts of blocking by smaller ISPs, this does not seem to be a rampant problem right now. And it's important to distinguish between blocking legitimate vs. illegitimate traffic. For instance, when Comcast blocks illegitimate P2P file-sharing traffic then to me that's a good thing. It frees up network resources for the rest of us who are paying to use the network for legitimate purposes. I'm not going to cry for some 15 year-old kid who can't speedily download a pirated copy of the latest Hollywood thriller, nor should you.
While the pro-net neutrality folks obviously believe ISPs will be bad actors, to my mind, even if you make the above assumptions, this does not form the basis for preemptive net neutrality action now. Sure it's tempting to believe that cable and telco companies, still with plenty of monopolistic DNA flowing through their corporate veins, would indeed act unfairly, for now it is most appropriate to give them the benefit of the doubt.
Washington's laissez-faire attitude toward Internet regulation has been one of the key reasons for the Internet's continued innovation and growth. Attacking broadband video and the Internet, which are among the last few bastions of economic growth left in America is unwise, particularly given the fact that the "law of unintended consequences" is virtually synonymous with all recent telecommunications regulation. Preemptively impose network neutrality and who knows what the actual result will be.
So for now net neutrality regulation should stay on the backburner. When and if it's appropriate, it can be re-prioritized. Instead, I'd prefer keeping Washington's focus on cleaning up a separate, larger and far more pressing problem caused by another rush to preemptive government action (hint, it starts with an "I" and ends with a "Q").
Categories: Broadband ISPs, P2P, Regulation
Topics: BitTorrent, Comcast, VeriSign
-
Google's Android: Striving for Broadband's Openness
Google's announcement on Monday of its "Android" mobile operating platform is another example of open platforms' appeal and underscores why broadband video has grown so quickly and is so compelling.

For those who missed the news, on Monday Google announced its Android mobile platform and the Open Handset Alliance, with 33 other companies, aiming to accelerate innovation and application development for mobile devices. In essence the goal is to develop a widely-deployed open platform,
 comparable to the Internet itself. Mobile video would certainly be a key beneficiary if Android succeeds.
comparable to the Internet itself. Mobile video would certainly be a key beneficiary if Android succeeds.This push to openness in mobile can be seen as an attempt to emulate what's unfolded in the broadband video industry over the last 5 years. The result of broadband's openness has been nothing short of staggering, Whether it's video found at YouTube, iTunes, Hulu, NYTimes.com, MLB.com, Cosmopolitan.com or countless others, the torrent of video that's been unleashed, the shift in consumer behavior that's ensued and the capital that's been invested in this sector are all the direct result of broadband's open pipe.
In fact, as I have said innumerable times, the reason why broadband video delivery is the single most disruptive influence on the traditional video industry is precisely BECAUSE it offers an open platform for producers to send video directly to their target audiences. As such, it eliminates the requirement for video producers to land a deal with a traditional gatekeeper to the home such as a broadcast or cable TV network, or a cable TV, satellite or telco service provider.
In short, the ability for producers to connect directly with their audiences strikes at the heart of the traditional video distribution value chain, threatening a permanent re-ordering of the economics of the video business. It enables all kinds of players who have been shut out of the video game to now jump in.
And while broadband video is admittedly still in its embryonic stage from a revenue standpoint, its long-term appeal portends vulnerability for those who cling too long to the traditional closed, walled-garden model. The Internet has shown us all the power of open over closed models, of interoperability over proprietary approaches, and of often chaotic, but user-centric growth over top-down control.
Broadband's ecosystem is experiencing a rapid "layer-cake" effect where new technologies and applications are being built on top of preceding ones. The result is a vibrant, entrepreneurial culture in the broadband sector. If Android succeeds the same will be true in the mobile video sector as well.
Categories: Mobile Video, Partnerships
Topics: Android, Cosmopolitan, Google, Hulu, iTunes, MLB.com, NYTimes.com, Open Handset Alliance, YouTube
-
HD Broadband Video Rollouts Will Be Driven by Advertising Model Growth and ROI
Last week's unveiling of HDWeb from Akamai (disclaimer: a VideoNuze sponsor), coupled with Limelight's recent announcement of its LimelightHD service offering, further raise the visibility and near-term prospect of higher-quality video streaming.

Underlining this was the impressive array of support in the two press releases from customers willing to be quoted expressing their interest in HD. I read all this as putting to rest any doubts about whether content providers are interested in offering HD. Supporting Akamai's release were MTV, NBA, Gannett, while supporting Limelight's release were Fox
 Interactive, Brightcove, Adobe, Silverlight and Rajshri.com (India's #1 broadband portal).
Interactive, Brightcove, Adobe, Silverlight and Rajshri.com (India's #1 broadband portal). Content providers I talk to are enthusiastic about pushing the quality bar, though a key issue is cost of delivery and potential ROI. Obviously to push out HD-quality streams means higher bandwidth and storage needs, the 2 key drivers of CDN charges. To support higher costs, improved revenue potential is required. And this is why HD rollouts are dependent on broadband video advertising prospects.
With ad support the primary business model for broadband video, I think a chicken-and-egg dynamic between ads and HD is going to play out. The better the ad revenue prospects, the more willing content providers will be to invest in HD. This is a reminder of why further maturing of broadband video ad models and supporting technologies are so important. So while the paid download model will also continue to grow, if you really want to get a handle on HD's prospects, keep an eye on the broadband video ad business. Continued traction will govern how much HD we'll all be seeing.
In the mean time, HDWeb from Akamai provides an enticing glimpse of an online HD future. I had no problem accessing its content over my standard Comcast broadband connection. The video quality is unlike anything I've yet seen online. If you get a chance, take a look at the NBA highlights clip (screen shot below). The clarity is mind-boggling.
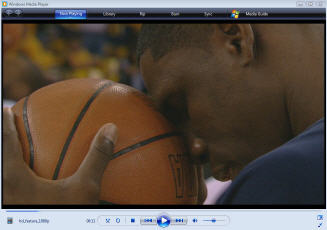
Can Akamai actually deliver this at scale? At the recent Akamai analyst day I attended, Chief Scientist/co-founder Tom Leighton said their network roadmap is to have 100TB of capacity by 2010, which could theoretically support 50 million concurrent 2MB streams. We're a long way from that usage level, but Akamai seems to be squarely focused on making HD a reality. And they're not alone, along with Limelight there are numerous other HD CDN initiatives underway. All this means that the video quality bar will inevitably rise.
Categories: Advertising, CDNs, HD
Topics: Akamai, HDWeb, Limelight
-
UGC Video Ads Becoming More Viable
Announcements from both ScanScout and Digitalsmiths continue to show that ads against UGC video may become more viable. There has been much skepticism about whether the vast trove of UGC video will be monetizable. Concerns about UGC monetization have been partly behind the recent emphasis by traditionally UGC-centric sites like YouTube, Metacafe, Veoh and others to move up the video quality food chain by offering branded or independent video.
Last week ScanScout announced trademark approval for its "Brand Protector" technology which is aimed at
 allowing advertisers to have their messages accompany only content that is deemed appropriate. And today Digitalsmiths (disclaimer: VideoNuze sponsor) has announced "AdSafe", which has the same basic intent and may also functional at a more granular levels of acceptability. Both of these initiatives are should be read as good news in helping the UGC ad market get its footing. Brands looking to harness the power and popularity of UGC video should definitely be investigating these kinds of solutions.
allowing advertisers to have their messages accompany only content that is deemed appropriate. And today Digitalsmiths (disclaimer: VideoNuze sponsor) has announced "AdSafe", which has the same basic intent and may also functional at a more granular levels of acceptability. Both of these initiatives are should be read as good news in helping the UGC ad market get its footing. Brands looking to harness the power and popularity of UGC video should definitely be investigating these kinds of solutions. 
Today Digitalsmiths also introduced "AdIQ", which brings the concept of "conquest ads" to the broadband video advertising world. For those unfamiliar with conquest ads, this is when a brand in the same category as a competitor buys inventory where a competitor is somehow mentioned or identified in the content itself. Here's a pretty good explanation from iMedia.
So for example, say Reebok is mentioned or identified in a video scene and say Nike wants to buy an overlay ad to play at that moment. Conversely, AdIQ allows Nike to ensure that its ad never runs against Reebok (or other competitors') content mentions. This is pretty cool stuff. But how about the media buyer who gets the responsibility to administer all this? I haven't seen the implementation, but I hope Digitalsmiths has made it simple to set up and monitor these campaigns!
Categories: Advertising, Technology, UGC
Topics: Digitalsmiths, ScanScout
-
NFL Demonstrates Syndication is Not Right for Everyone
As many of you know, in general I'm a big-time advocate of syndication as a strategy to permeate broadband video into all the "nooks and crannies" of the Internet. Many content providers have embraced this path, most recently Hulu and CBS (with its Audience Network). The purpose of syndication is to ensure that content reaches users where they currently visit, as opposed to requiring them to come to a new destination. That "destination-centric" approach was of course the way the traditional media industry worked.
But the NFL shows that syndication isn't right for everyone. In instances where there is genuinely unique content, it can make sense to pursue a pure destination strategy.

To illustrate, yesterday I missed part of the Patriots-Colts game. Though I did catch the end, I was eager to see the big plays. During the parts of the game I saw there were several promos for video available at NFL.com. So post-game I started pinging the NFL's site and it turned out that within about 1 1/2 hours of the end of the game, there was a 5:13 edited montage posted. It included most of the big plays and was available exclusively at NFL.com.
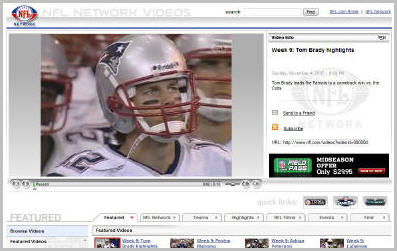
The NFL caused a kerfuffle earlier this year when it issued highly restrictive rules governing use of and monetization of its game video. But having had this experience, I think they made the right call. When you have must-see content and own all the rights, I think it is indeed better to pursue a destination strategy. You get all the views. You get all the monetization. You get all the site loyalty and cross-promotion opportunities. You get everyone linking to you. And you have the exclusive archive.
It's rare to own something as valuable as NFL game video. But if your video does have similar attributes, then I would encourage considering destination over syndication. If you go this route though, being highly proactive to serve users' interests, as the NFL is doing, is essential to success.
Categories: Sports
-
Hulu 1.0 Gets a Solid B+
I'm now back from Digital Hollywood and I've had an opportunity to give Hulu 1.0 a spin as part of its private beta. I've also looked the Hulu offering at AOL which is not yet comparable (less content, fewer features) to the one at Hulu.com. So I think that for now using Hulu through the private beta is the only way to get the full 1.0 experience.

My initial reactions are positive and I give Hulu 1.0 a solid B+, with many of the fundamentals well done, but with certain features needing improvement, as to be expected from a beta launch. All in all, considering the short development window in which Hulu was created, the Hulu team deserves much credit.
Hulu 1.0 should more than silence those who snarkily pre-labeled it "Clown Co" and misunderstood it to be a "YouTube killer", which it is not. Hulu has not embarrassed its primary investors (and content providers) NBC and News Corp in any way, and in fact, has set the stage for taking back control of how its full-length content and clips are distributed online. This was of course the investors' main motivation - creating a legitimate platform for them to control their online destiny and capture the lion's share of the economics.
Design and Video QualityHulu sports a clean, open design format, heavy on thumbnail images. It's easy to find your way around, and there's little risk of getting lost in the process. The home page, seen below, offers 3 main branches, Popular Episodes (will number 1 on the list ever be anything but an episode from The Office though?), Most Popular Clips (looks like all provided by Hulu, none by users) and Recently Added (a nice addition here would be to expose the original air date without actually having to click through).Once clicking into a clip or full length video, the video player experience was excellent. Not only is the player consistent for all videos, but the quality was as well. I never experienced any delays, re-buffering, pixelation, audio/video out of synch or other typical video issues. In full screen mode there was a little degradation, but was certainly above the acceptable-quality bar.
 ContentCurrently there are 34 individual content providers (though many under common parentage) contributing a broad range of current and older TV programming and films. While the other 2 big broadcasters CBS and ABC are missing, there's plenty of cable network and studio fare available. All is easily navigable through the browse function.
ContentCurrently there are 34 individual content providers (though many under common parentage) contributing a broad range of current and older TV programming and films. While the other 2 big broadcasters CBS and ABC are missing, there's plenty of cable network and studio fare available. All is easily navigable through the browse function.The biggest knock on the content is its inconsistency. For example, click on "24" and you can choose from 3 episodes from Season 1 and one from Season 6. Battlestar Galactica gives all of Season 1, but nothing else. Same for a classic like The Mary Tyler Moore Show. Huh? All of this makes it confusing for the user to know what to expect. If all this is due to rights or other limitations, it would be good for Hulu to signal or explain this somehow.
AdvertisingCertainly one of the best decisions Hulu made is how it's initially implementing ads, though the implementation doesn't appear consistent across all video, or at least the ones I watched. There are no pre-rolls, though there are 5 second sponsor messages up front, but only for certain shows it seems, not all of them. There are mid-rolls, typically 15-30 seconds, and fortunately these are show only one at a time, not in pods. And there's a countdown so it's clear when video will resume.Of course, the bigger question is whether this limited amount of advertising is sufficient to make Hulu's economic model work, especially if sometime down the road, online consumption cannibalizes on-air consumption.
FeaturesMany of the expected features are offered - embed, share, full screen, create a playlist and user reviews. One feature that has great potential is the "create a custom clip". This allows users to manipulate a timebar to create their own favorite clips. I could see this being very popular, especially for passionate fans. And it allows a whole new range of short form video inventory to be created with no incremental effort by Hulu staff.Yet for now the create a clip capability is buried in the "Share" feature, which seemingly only allows the custom clip to be emailed. And pinning down your desired start and stop points is very tough. Since custom clips are the only UGC-like opportunity in Hulu, these should be given more prominence. Ideas could include showcasing a users' gallery of favorites, allowing them to be saved to playlists, syndicating them to partners' sites and allowing them to be mashed up.
Wrap-upIn general, while I think Hulu1.0 is an admirable starting point, the custom clip situation underlines the one major disconnect I have with Hulu: I sense that in its zeal to become a site focused on premium, non-UGC content, it managed to miss out on emphasizing a community-building, social-networking focus that would help make it feel more interactive and inviting.These are exactly the types of things that have helped make YouTube such a hit. Offering some of these features doesn't mean Hulu becomes a YouTube competitor, vying for UGC supremacy. Rather, it means giving users some of the social tools they love, which they can now use with premium content only Hulu has to offer. If and when Hulu embraces these opportunities as well, an "A" grade will be attainable.UPDATE: Reed Price, MSN Entertainment's Editor-in-Chief emailed me to remind me that MSN (an initial Hulu distribution partner) has already rolled out a relatively extensive integration of Hulu video. He provided a number of links including these 4:
Thanks for the heads-up Reed. When I see that other distribution partners have integrated Hulu I intend to write another post comparing/contrasting the distributors' various approaches. I have a hunch they'll vary widely.Categories: Broadcasters, Startups
Topics: Hulu, NBC, News Corp.
-
5 Observations from My Digital Hollywood Panel
 Yesterday I moderated a spirited panel at Digital Hollywood. Panelists included:Rebecca Baldwin -GM, Zap2it, Tribune Media ServicesJonathan Bokor - VP, Business Development, Tandberg TelevisionDave Brown - Senior Product Marketing Manager, CiscoRich Cusick - SVP, Digital Media, TV GuideBob Leverone - VP, Television, Dow JonesRex Wong - CEO, DAVE Networks
Yesterday I moderated a spirited panel at Digital Hollywood. Panelists included:Rebecca Baldwin -GM, Zap2it, Tribune Media ServicesJonathan Bokor - VP, Business Development, Tandberg TelevisionDave Brown - Senior Product Marketing Manager, CiscoRich Cusick - SVP, Digital Media, TV GuideBob Leverone - VP, Television, Dow JonesRex Wong - CEO, DAVE NetworksI had 5 observations from the discussion:
1. Broadband video is making its mark - From the panelists' intros, it was clear that these companies are all being impacted by broadband. For example, Cisco used to be all about IP, now "video networking" is driving growth, Dow Jones used to be all about print, now it's creating high-quality original video for multimedia experiences, TV Guide used to be about print and cable, now it has significant online video guide. Broadband's impact is poised to grow further.2. With video proliferation, navigation is key challenge - panelists agreed that users' ability to find what they're looking for in the sea of broadband video is a huge issue. Both TV Guide and Zap2it are focused mainly on TV/entertainment content for now, question arises, will there be a one-stop guide destination for all broadband video (TV, films, short form, UGC, news, etc.)? Nobody owns that position right now, so who is best-positioned to fill that role?
3. Broadband video must be more than just TV - Jonathan made the point most strongly, and others agreed. For broadband to succeed it must do more than just be another medium for delivering existing TV programs. Sure, there's a rush to get broadcast TV shows online, but only real innovation will distinguish broadband from me-too TV delivery. Here, here. I've been preaching that for ages. Broadband offers a whole new creative palette to harness.
4. Cable operators wary of broadband video - no big surprise here, but Dave made it clear that major cable operators are wary of broadband and are focused on retaining as much control of the video experience as possible. For example, I asked what the roadmap looked like for cable operators to enable users to watch YouTube videos (and other broadband-only fare) on their TVs through cable set-top boxes, and if I understood Dave's response correctly, it sounds like no time soon. Quality, liability, and of course control are key limitations. If cable's not going to bring broadband to the TV anytime soon, might that open the door for third-party boxes?
5. WGA strike could drive more broadband projects - Rich speculated that a byproduct of a potential WGA strike and writers sitting around would be that maybe more broadband projects would be undertaken. Hard to predict, but there's certainly plenty of interest in broadband-only production, so my guess is writers wouldn't have a problem finding opportunities. Wouldn't it be ironic if the potential strike, which has new media compensation at its core, actually spurred more broadband video?
Categories: Events
Topics: Cisco, DAVE Networks, Digital Hollywood, Dow Jones, Tandberg, Tribune, TV Guide, Zap2it
-
At Digital Hollywood, Updates Later
I'll have more updates from Digital Hollywood later today. My new Dell Windows Vista laptop has chosen an unfortunate time to have a complete crash, so I'm trying my best to restore and get back online (in Business Center now). Ah technology...Categories: Miscellaneous


