-
R.I.P. Maven Networks
Well, it looks as though it's official: as reported by TechCrunch and others, Yahoo is discontinuing Maven Networks's third party video publishing activities though Yahoo's statement says it will use Maven technology for internal video efforts. As I've mentioned periodically, I was an early consultant to Maven, which was a pioneer in the video platform space.
Way back then (!) in 2003 most people in the media business still had a difficult time imagining why broadband video was so strategic and game-changing. Maven's team did a lot of the early spadework in evangelizing broadband's potential and building market momentum. Its reward was being acquired for $160M by Yahoo in February, 2008 in what I believe is still the largest pure play broadband deal.
However, the Yahoo acquisition was never a perfect strategic fit, even before factoring in the well-documented chaotic mess that Yahoo has become in recent years. The problem was that Yahoo is a media company, deriving the majority of its revenue from advertising. On the other hand, Maven was a technology/products company (though some in the industry always questioned the true proprietary value of Maven's technology). The most strategic deal for Maven would have been with a larger technology/products company, where it would have become part of broader suite of video products and services. Yahoo was never really well-suited to support Maven's third party video customers (and in reality it hasn't for a while now), and with all its other troubles, this move was widely expected.
For Maven's founders and investors, the company's acquisition marked a successful exit that others in the industry envy, particularly in this crummy M&A market. Still, the Yahoo-Maven deal is yet another example that when selling a company, price isn't the sole criteria for longer-term success.
Categories: Deals & Financings, Portals, Technology
-
Digitalsmiths Launches VideoSense 2.0 Including New "Free Form" Video Search Capability
This morning Digitalsmiths, a leading video platform company, is launching VideoSense 2.0, a suite of content management, publishing, presentation and search products. In particular, the new release includes an innovative "free form" video search box that leverages Digitalsmiths' metadata creation capability. Last week I spoke to Ben Weinberger, Digitalsmiths' CEO to learn more.
A key Digitalsmiths' strength has always been its metadata tools, which use a broader, proprietary set of algorithms such as facial recognition, scene classification and object identification. With this release the metadata tags are being organized into what Digitalsmiths' calls a "MetaFrame" - a frame-by--frame analysis of the video file(s) that are all based on time stamps. A MetaFrame in turn enables more accurate video search, content organization and monetization both within a video and across a library of videos.
With respect to video search specifically, Ben explained that VideoSense's search technology matches the submitted term against a video library to return results based on criteria like names, locations, dialogue, objects within a scene or other criteria the content owner specifies. The content owner can also tweak the rules so that specific criteria receive higher weighting. Results are typically returned in half a second or less, providing a video search experience close to what we've come to expect in web search. There's also a "Did you mean?" prompt for more refined results. The free form search box can be integrated onto any web page via an API.
The below example shows the results of a search Ben ran in the demo against a customer's library (unfortunately blurriness is added here due to customer confidentiality).
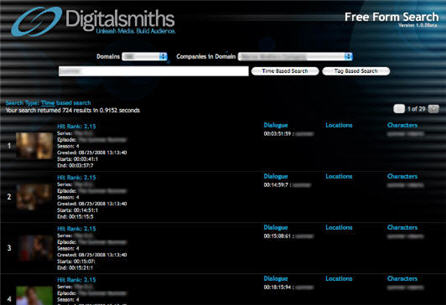
Of course the more valuable the experience is, the more video is likely to be consumed, generating more streams and ad inventory. Ads too can gain better targeting through MetaFrame processing (and VideoSense is integrated with all the major video ad servers and networks). Deeper, richer search can also power B2B use of video clips, such as when a specific scene from one video is to be incorporated into another (think of a movie like "Forest Gump" that has myriad historical scenes interspersed).
From my perspective metadata is going to become more and more important as the sheer number of videos available explodes with both long-form and derivative short clips. Content owners' key challenge will be to manage these ever-larger libraries (Ben uses the notion of "metadata as the glue" holding libraries together; I think that's an apt description). Others like EveryZing, Grab Networks and Gotuit have also recognized the importance of metadata and have their own approaches. For Digitalsmiths, a differentiator is its focus on extremely large files and its focus on studio customers. It aims to function as a full-blown video platform provider for all forms of digital distribution.
Ben said Digitalsmiths has a slew of customers it will be unveiling in the coming weeks that are using MetaFrame and the VideoSense 2.0 suite.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
(Note Digitalsmiths is a VideoNuze sponsor)
Categories: Technology
Topics: Digitalsmiths, EveryZing, Gotuit, Grab Networks
-
4 Industry Items from this Week Worth Noting
YouTube mobile video uploads exploding; iPhones are a key contributor - The folks at YouTube revealed that in the last 6 months, uploads from mobile phones to YouTube have jumped 1,700%, while in the last week, since the new iPhone GS was released, uploads increased by 400% per day. I didn't have access to these stats when I wrote on Monday "iPhone 3GS Poised to Drive User-Generated Mobile Video," but I was glad to see some validation. The iPhone 3GS - and other smartphone devices - will further solidify YouTube as the world's central video hub. I stirred some controversy last week with my "Does It Actually Matter How Much Money YouTube is Losing?" post, yet I think the mobile video upload explosion reinforces the power of the YouTube franchise. Google will figure out how to monetize this over time; meanwhile YouTube's pervasiveness in society continues to grow.
Nielsen study debunks mythology around teens' media usage - Nielsen released a new report this week "How Teens Use Media" which tries to correct misperceptions about teens' use of online and offline media. The report is available here. On the one hand, the report underscores prior research from Nielsen, but on the other it reveals some surprising data. For example, more than a quarter of teens read a daily newspaper? Also, 77% of teens use just one form of media at one time (note, data from 2007)? I'm not questioning the Nielsen numbers, but they do seem out of synch with everything I hear from parents of teens.
Paid business models resurfacing - There's been a lot of talk from media executives about the revival of paid business models in the wake of the recession's ad spending slowdown and also the newspaper industry's financial calamity. For those who have been offering their content for free for so long, putting the genie back in the bottle is going to be tough. Conversely for others, like those in the cable TV industry, who have resisted releasing much content for free, their durable paid models now look even more attractive.
Broadcast TV networks diverge on strategy - Ad Age had a good piece this week on the divergence of strategy between NBC and CBS. The former is breaking industry norms by putting Leno on at 10pm, emphasizing cable and avidly pursuing new technologies. Meanwhile CBS is focused on traditional broadcast network objectives like launching hit shows and amassing audience (though to be fair it is pursuing online distribution as well with TV.com). Both strategies make sense in the context of their respective ratings' situations. Regardless, broadcasters need to eventually figure out how to successfully transition to online distribution, something that is still unproven (as I wrote here).
Categories: Aggregators, Broadcasters, Mobile Video, UGC
Topics: Apple, CBS, iPhone, NBC, Nielsen, YouTube
-
VideoNuze Report Podcast #22 - June 26, 2009
Below is the 22nd edition of the VideoNuze Report podcast, for June 26, 2009.
This week Daisy and I discuss the TV Everywhere and OnDemand Online initiative that Comcast and Time Warner unveiled this week. As I wrote in this post on Wednesday, the companies are beginning a trial in July for 5,000 Comcast subscribers, who will gain online access to a selection of TNT and TBS programs. The primary purpose of the trial is to test security of the content. The companies anticipate that other cable networks will join the trial too, and that other video service providers will begin their own trials in the near future.
In the podcast we explore further why granting cable subscribers online access is an important step forward in the evolution of the broadband video medium, and what it means to the overall ecosystem. There are a lot of unknowns about how TV Everywhere/OnDemand Online will work; Time Warner's and Comcast's CEO were candid about that. For now they released a set of "principles" to guide their pursuits. There will be much more to come on this story.
Click here to listen to the podcast (15 minutes, 27 seconds)
Click here for previous podcasts
The VideoNuze Report is available in iTunes...subscribe today!
Categories: Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators, Podcasts
Topics: Comcast, Podcast, Time Warner, TV Everywhere
-
Unveiling Move Networks's New Strategy
Move Networks, the well-funded Internet television technology company which has been virtually silent for the last 60 days since acquiring Inuk Networks and bumping former CEO John Edwards to Executive Chairman, is pursuing a major repositioning. Earlier this week I met with Marcus Liassides, Inuk's former CEO and founder who joined Move's management team, who previewed the company's new strategy to be a wholesale provider of IPTV video services delivered over open broadband networks.
Broadband video industry participants know Move best for its proprietary adaptive bit rate (ABR) technology and player, which power super-high quality live and on-demand video streams for broadcasters
 like ABC and Fox. Move gained a lot of attention by raising over $67M, including a $46M Series C round in April '08 from blue chip investors.
like ABC and Fox. Move gained a lot of attention by raising over $67M, including a $46M Series C round in April '08 from blue chip investors.Despite all this, Marcus explained that coming into 2009 Move had at least 3 significant problems, symbolic of how fluid the broadband video market remains.
First, its core business of charging content providers in the range of $.30/GB of video delivered was being pressured by the fact that advertising-only business models couldn't support this pricing. Content providers loved Move's quality; they just couldn't afford it, particularly given the alternative of plunging CDN delivery rates.
Second, Move's pricing and business model were being challenged by both Microsoft and Adobe entering the market with ABR streaming features of their own (I wrote about this here). But because both were enabled on the server side (IIS and FMS respectively), the cost of ABR moved from content providers to CDNs, who might or might not choose to charge extra for these features. Either way, Move's direct cost looked comparatively more expensive, especially as the recession pounded ad spending.
Last, but not least, Marcus explained that Move's product development approach was undisciplined, leading to resources being spread too thin in too many directions. That was reflected by the market's ongoing difficulty in categorizing which business Move was really in.
Meanwhile, U.K.-based Inuk, which had been on its own funding and product development roller-coaster, was delivering its Freewire IPTV service to about 200K university students in the UK, Ireland and Canada. Because Inuk needed to serve these students when they were off campus, it had developed a "virtual set-top box" application that duplicates on the PC the IPTV service that had traditionally been delivered via an expensive IPTV set-top box. Inuk was using Move's ABR technology to power video delivery to the PC. Recognizing potential synergies and trying to address its other issues, Move acquired Inuk in April.
Move's new positioning as a provider of IPTV video services delivered over open broadband networks essentially replicates what Inuk has been doing, except that going forward services will be offered wholesale, not retail like with Freewire. Move's strategy starts from the proposition that to get cable TV networks online requires that they be paid consistent with the norms, rather than expecting them to free and ad-supported only. It also anticipates that consumers demand not just VOD offerings, but a full linear lineup as well (as an aside, that aligns with Sezmi's thinking too). While Move will continue supporting existing customers like ABC and others, its new wholesale model is a major shift in that it uses the company's core technology to support packaged multichannel video services, instead of a la carte web-based video.
Marcus explained that Move is targeting 3 verticals: (1) telcos which haven't traditionally offered video services (or have through direct satellite partnerships), (2) broadband ISPs looking to get into the video business, and (3) existing video service providers looking for a lightweight capex approach for extending their service either for remote access (a la "TV Everywhere") or in other rooms in the house (a model which has traditionally required another set-top box and truck roll for installation).
Marcus demo'd the Freewire service to me using his PC and a large monitor, and it looks great. There's instant channel changing, HD (when available), a great looking guide and auto-DVR of every program, all in the cloud. Freewire also offers targeted advertising, and HTML-based apps like Twitter integration, etc. My caveat is that I have no idea how well the service would scale to millions of homes.
Move's new positioning puts it in the middle of tectonic video industry shifts. For example, what's the appetite of 3rd parties like telcos and ISPs for new video solutions? Will other, well-suited consumer brands like Google, Netflix, Yahoo enter the multichannel video business, and if so how? What approach will cable operators like Comcast use for emerging, "TV Everywhere" services that would benefit from Move's lightweight capex model (note Comcast said it was using Move in its 5,000 subscriber technical trial yesterday)? How will major cable TV networks expect to get compensated in the broadband era where individuals, not homes, are the new unit of measurement? How will local ISPs, over whose networks remotely-accessed video will run, expect to be compensated? It's way too early to know the answers, but if Move's technology works as intended, and its costs are reasonable, it will likely find itself in the middle of a lot of very strategic industry discussions.
Another big change is that Marcus said the company's messaging will be focused more around business cases and services than its specific technologies. That seems smart given giants like Microsoft and Adobe are closely circling these waters with lots of their own technology, which could easily swamp Move. If all this wasn't enough, Move is also in the midst of hiring a new CEO and implementing a new management team, all of which will be announced imminently. One thing Move isn't doing for now is raising additional capital, which Marcus said is not needed.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
(Note: Move Networks is a current sponsor of VideoNuze)
Categories: Broadcasters, Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators, Deals & Financings, IPTV, Technology, Telcos
Topics: ABC, Adobe, FOX, Microsoft, Move Networks
-
Nokeena Raises $6.5M from Mayfield
Nokeena Networks is announcing this morning that it has raised $6.5M from Mayfield Fund, bringing its total funding to $15M. The new funding will be used primarily for marketing and sales. Nokeena's Media Flow Director is a software appliance that combines storage, caching and network optimization to deliver high-quality video at lower cost. I noted Nokeena in my recent post about the robust ecosystem of technology companies enabling higher-quality broadband video delivery.
Categories: Deals & Financings, Technology
-
Video Syndication Webinar Today
Today at 1:30pm EDT / 10:30am PDT, I'll be participating in a free webinar, "Demystifying Online Video Syndication." Video syndication continues to be one of the key trends in the online video market. I'll be sharing thoughts on where syndication is heading and where the main opportunities and challenges lie. We have over 500 people registered and it promises to be an exciting and educational session.
The webinar is sponsored by Grab Networks, whose co-president Marcien Jenckes will present information about its grabMediaOS solution that enables a "Create Once, Publish Anywhere" business model. Grab works with hundreds of content providers and is one of the primary players in driving the video syndication market.
If you're trying to understand the syndication opportunity and identify the right solutions to fit your needs, this webinar is for you!
Categories: Events
Topics: Grab Networks
-
Comcast, Time Warner Partner for "TV Everywhere"
This morning I listened in on the press conference with Comcast CEO Brian Roberts and Time Warner Inc. CEO Jeff Bewkes where they announced a 5,000 subscriber technical trial of TV Everywhere/OnDemand Online starting in July along with a set of "principles" guiding their efforts. Primarily the trial will test the security of the authentication technology.
TW will make available TNT and TBS programs in the trial, and will offer additional programs over time. Comcast plans to bring in other networks too. Both executives emphatically stated that for cable subscribers
 there will be no additional charge for online access. The companies clearly hope to use the trial and the publicity that will surround it to galvanize interest from other cable operators and programmers.
there will be no additional charge for online access. The companies clearly hope to use the trial and the publicity that will surround it to galvanize interest from other cable operators and programmers.The partnership effectively unifies the companies' disparate initiatives so that paying video subscribers will be "authenticated" to receive certain cable network programming online. Up until now Comcast has been pursuing its own vision of online access under a plan it dubbed "OnDemand Online," while TW has been pursuing a plan it called "TV Everywhere." The essential difference between the two, as I wrote about here, was that Comcast planned to only make programs available on its owned sites (at least initially), which TW talked of multiple third parties gaining access as well, right off the bat.
I've been critical of TW's approach to date as I thought it was wildly ambitious and under-estimated the technical challenges involved in pulling off third party integration. On the other hand, Comcast's walk-before-you-run attitude seemed far more practical. On the call, Mr. Bewkes in particular continued to downplay the difficulty of authenticating third parties, a position I think is unrealistic.
Regardless, I've been supportive of the general idea that paying video subscribers gain online access to cable programs. While some decry this as antithetical to the open, free-flowing Internet ethos, and a plot by evil cable companies to control video on the 'net, I've seen it differently.
The key is finding a model that's attractive to cable programmers (e.g. MTV, USA, CNN, etc) and consumers.
 Programmers benefit because they'd be provided with a viable online extension of their proven hybrid (monthly affiliate fee + advertising) business model. Until now they've been largely shut out of online distribution. That's because doing so for free would antagonize their cable/satellite/telco distributors who pay them around $25B/year. And that's before the point that free, ad-supported premium sites like Hulu have not yet proven themselves economically viable. Meanwhile, aside from a la carte paid download sites like iTunes/Unbox/others there hasn't been an online subscription model available to programmers.
Programmers benefit because they'd be provided with a viable online extension of their proven hybrid (monthly affiliate fee + advertising) business model. Until now they've been largely shut out of online distribution. That's because doing so for free would antagonize their cable/satellite/telco distributors who pay them around $25B/year. And that's before the point that free, ad-supported premium sites like Hulu have not yet proven themselves economically viable. Meanwhile, aside from a la carte paid download sites like iTunes/Unbox/others there hasn't been an online subscription model available to programmers. These are some of the real, but often not well-understood business issues. Everyone wants something-for-nothing, and the Internet has too often set those expectations. But cable programmers need to get paid for their efforts so they can continue to deliver the quality programming consumers have grown accustomed to. The newspaper industry's woes offer tangible proof of what happens to an industry when its proven business model gets stripped away.
Despite what some skeptics say, consumers also stand to gain. All that great cable programming that's been locked to the set-top box in the home would now be available online. It sort of like cable's version of on demand Sling, but without any upfront or monthly charge (at least that's what we're hearing for now).
With TV Everywhere/OnDemand Online, Comcast and Time Warner are taking a solid step forward in delivering more value to their subscribers who increasingly live their lives online. Now they need to tamp down the hype and just focus on executing in a logical, user-friendly way.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators
Topics: Comcast, Time Warner


