-
HD Cloud Launches Video Encoding Platform, Capitalizing on "Cloud Computing"
Three significant trends are behind today's launch of HD Cloud, a new video transcoding service being announced today: the proliferation of video file formats and encoding rates, the increase in syndication activity to multiple distributors and the cost and scale benefits of "cloud computing." HD Cloud founder and CEO Nicholas Butterworth (who I have known since he ran MTV's digital operations 10 years ago) walked me through the company's plan yesterday and how it benefits content providers looking to cost-effectively capitalize on broadband video's surging popularity.
Anyone who spends a little time watching broadband video will notice variations in video formats and quality. Behind the scenes there are diverse encoding specs for how video is prepared from its source file before it is served to users. This video encoding work is multiplied significantly for content providers if they also want to distribute through 3rd parties like Hulu, Netflix, Fancast, TV.com, etc, all of which have their own encoding specs. Further, these 3rd parties all have their own ways of accepting video feeds and associated metadata from content partners. Yet another driver of complexity are adaptive bit rate players like Move Networks which automatically hop between multiple files encoded at different bit rates depending on the user's available bandwidth. Combine it all and it means encoding has become a labor-intensive, complicated, yet highly-necessary process.
Traditionally encoding has been done locally by content providers using encoding solutions from enterprise-class companies like Anystream, Telestream, Digital Rapids and others. By offering encoding as a service, HD Cloud gives certain content providers an alternative to spending capex and running their own encoding farms. Content providers choose which source files are to be encoded into which formats and bit rates. They also provide HD Cloud with their credentials for distributing to authorized 3rd party sites. When a job is configured, HD Cloud performs the encoding and 3rd party distribution. HD Cloud doesn't store the files or keep a copy, mainly for security reasons.
The key to making all this work is so-called "cloud computing," whereby HD Cloud (and many others) essentially rent computing capacity from providers like Amazon's EC2. As new jobs come in, HD Cloud
 requests capacity, temporarily loads its encoding software (which is a combination of open source and its own custom code) and runs its jobs. When they're done, HD Cloud releases the capacity back to Amazon. It's all a little analogous to the old days of timesharing on mainframes, except with new efficiencies. HD Cloud's economics are based on Amazon buying the computing capacity and operating the facilities and utilizing them at a far higher rate than HD Cloud or any other customer would have on their own.
requests capacity, temporarily loads its encoding software (which is a combination of open source and its own custom code) and runs its jobs. When they're done, HD Cloud releases the capacity back to Amazon. It's all a little analogous to the old days of timesharing on mainframes, except with new efficiencies. HD Cloud's economics are based on Amazon buying the computing capacity and operating the facilities and utilizing them at a far higher rate than HD Cloud or any other customer would have on their own. The result is that HD Cloud prices its encoding at $2/gigabyte, which Nicholas thinks will only get cheaper as bandwidth prices continue to fall. A financial model he sent along suggests that the content provider's ROI given certain assumptions about the amount of content encoded and streamed could be 3-4 times higher than with traditional local encoding solutions. This also assumes the avoidance of upfront capex for local software and hardware encoding alternatives, an important cost-savings for many given the economy. HD Cloud is announcing Magnify.net as its first client today. Others in this space include mPoint, Encoding.com, ON2 and others.
Between encoding's growing complexity and syndication's appeal, content providers are going to need more extensive and cost-effective encoding solutions. Cloud computing in general, and HD Cloud (and others) seem well-positioned to address these needs.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Startups, Technology
Topics: Anystream, Digital Rapids, Encoding.com, HD Cloud, mPOINT, ON2, Telestream
-
September '08 VideoNuze Recap - 3 Key Themes
Welcome to October. Recapping another busy month, here are 3 key themes from September:
1. When established video providers use broadband, it must be to create new value
Broadband simultaneously threatens incumbent video businesses, while also opening up new opportunities. It's crucial that incumbents moving into broadband do so carefully and in ways that create distinct new value. However, in September I wrote several posts highlighting instances where broadband may either be hurting existing video franchises, or adding little new value.
Despite my admiration for Hulu, in these 2 posts, here and here, I questioned its current advertising implementations and asserted that these policies are hurting parent company NBC's on-air ad business. Worse yet, In "CNN is Undermining Its Own Advertisers with New AC360 Live Webcasts" I found an example where a network is using broadband to directly draw eyeballs away from its own on-air advertising. Lastly in "Palin Interview: ABC News Misses Many Broadband Opportunities" I described how the premier interview of the political season produced little more than an online VOD episode for ABC, leaving lots of new potential value untapped.
Meanwhile new entrants are innovating furiously, attempting to invade incumbents' turf. Earlier this week in "Presidential Debate Video on NYTimes.com is Classic Broadband Disruption," I explained how the Times's debate coverage positions it to steal prime audiences from the networks. And at the beginning of this month in "Taste of Home Forges New Model for Magazine Video," I outlined how a plucky UGC-oriented magazine is using new technology to elbow its way into space dominated by larger incumbents.
New entrants are using broadband to target incumbents' audiences; these companies need to bring A-game thinking to their broadband initiatives.
2. Purpose-driven user-generated video is YouTube 2.0
In September I further advanced a concept I've been developing for some time: that "purpose-driven" user-generated video can generate real business value. I think of these as YouTube 2.0 businesses. Exhibit A was a company called Unigo that's trying to disrupt the college guidebook industry through student-submitted video, photos and comments. While still early, I envision more purpose-driven UGV startups cropping up in the near future.
Meanwhile, brand marketers are also tapping the UGV phenomenon with ongoing contests. This trend marked a new milestone with Doritos new Super Bowl ad contest, which I explained in "Doritos Ups UGV Ante with $1 Million Price for Top-Rated 2009 Super Bowl Ad." There I also cataloged about 15 brand-sponsored UGV contests I've found in the last year. This is a growing trend and I expect much more to come.
3. Syndication is all around us
Just in case you weren't sick of hearing me talk about syndication, I'll make one more mention of it before September closes out. Syndication is the uber-trend of the broadband video market, and several announcements underscored its growing importance.
For example, in "Google Content Network Has Lots of Potential, Implications" I described how well-positioned Google is in syndication, as it ties AdSense to YouTube with its new Seth MacFarlane "Cavalcade of Cartoon Comedy" partnership. The month also marked the first syndication-driven merger, between Anystream and Voxant, a combination that threatens to upend the competitive dynamics in the broadband video platform space. Two other syndication milestones of note were AP's deal with thePlatform to power its 2,000+ private syndication network, and MTV's comprehensive deal with Visible Measure to track and analyze its 350+ sites' video efforts.
I know I'm a broken record on this, but regardless of what part of the market you're playing in, if you're not developing a syndication plan, you're going to be out of step in the very near future.
That's it for September, lots more planned in October. Stay tuned.
What do you think? Post a comment!
Categories: Aggregators, Analytics, Brand Marketing, Broadcasters, Magazines, Partnerships, Syndicated Video Economy, UGC
Topics: ABC, Anystream, AP, CNN, Doritos, Google, Hulu, MTV, NY Times, Taste of Home, thePlatform, Unigo, Visible Measu, Voxant, YouTube
-
Anystream and Voxant Merge, Making Big Bet on Syndicated Video Economy's Future
This morning Anystream, a leading digital media management and production company and Voxant, a content syndication network, have announced their merger. The deal marks an important milestone: it's the first M&A transaction that I'm aware of which is predicated on the Syndicated Video Economy dominating the future broadband video landscape.
NewCo's combined capabilities are noteworthy on many levels, one of which is its potential to disrupt the
 competitive dynamics of the video content management and publishing space by providing fundamental new value to content producers. There has been a lot of capital invested in this space, and by my recent count at least 18 companies are playing in or around it. With the broadband gold rush underway, there's been enough business to go around. Competition for new business has mainly focused on features and pricing/business models.
competitive dynamics of the video content management and publishing space by providing fundamental new value to content producers. There has been a lot of capital invested in this space, and by my recent count at least 18 companies are playing in or around it. With the broadband gold rush underway, there's been enough business to go around. Competition for new business has mainly focused on features and pricing/business models. Anystream has traditionally (and somewhat quietly) focused on digital media transcoding and workflow for more than 700 companies around the world. It too has moved up the stack into content management and publishing, lately handling the video management for NBC's Olympics on-demand distribution, and prior to that announcing deals with Hearst-Argyle Television and others. On the other hand, Voxant has been a mid/long tail syndicator, having built out a distribution network with 30,000 publishers gaining rights-cleared content from 400+ providers. These publishers generate 35 million video views per month, making the Voxant network #15 in video views according to comScore.
 NewCo's belief is that the bilateral syndication deals we've seen to date (e.g. CBS-Yahoo, ESPN-AOL, Next New Networks - Hulu, among many others) has whetted the market's appetite for this emerging business model, but that there is still far too much friction for syndication to really take off. That fits with what I hear from even the most aggressive content syndicators, one of whose CTOs said on a recent panel I moderated that his company is overwhelmed just trying to fully implement the handful of deals its already done.
NewCo's belief is that the bilateral syndication deals we've seen to date (e.g. CBS-Yahoo, ESPN-AOL, Next New Networks - Hulu, among many others) has whetted the market's appetite for this emerging business model, but that there is still far too much friction for syndication to really take off. That fits with what I hear from even the most aggressive content syndicators, one of whose CTOs said on a recent panel I moderated that his company is overwhelmed just trying to fully implement the handful of deals its already done.So, much as I've considered the Syndicated Video Economy solidly into its first phase of development, I've been sobered by the reality that the operational overhead of negotiating deals, implementing them through distributors' often heterogeneous sub-systems, and monitoring their performance requires so much human intervention that the whole syndication concept could end up collapsing under its own weight. (Side note, this is why the Google Content Network which I wrote about last week also has so much potential).
NewCo seeks to blend Anystream's and Voxant's capabilities, offering to content producers a seamless solution to manage, publish AND distribute clips and programs, at scale, to the Internet's widely dispersed audience. As I see it, NewCo is also a potential two-pronged market disrupter if - and for now this is still a big if - it can monetize premium video at scale through advertising.
First, these new revenues could put NewCo in a position to cross-subsidize its technology platform, thereby altering some of the fundamental economics in the platform space. This could trigger possible price-cutting by others solely dependent on platform revenue. Given the vast number of players in the space, and everyone's hunger for market share, this scenario isn't unreasonable to imagine. Second, NewCo could create steep switching barriers for its media customers. Upon getting a taste for turnkey NewCo-driven syndication revenues, content producers would almost certainly be less enticed by new platform-centric features that other competitors may offer. Combined, these disruptions would create a markedly new competitive dynamic.
Yet don't expect competitors to stand still; many of them are examining how to capitalize on their own distinct advantages to alter the dynamics still further. NewCo's abundantly strong management team must now execute on its vision and help its media customers realize syndication's real value. The Anystream-Voxant merger is a bold and possibly game-changing bet on the Syndicated Video Economy being fully realized over time. If that happens, NewCo will surely be among the industry's long-term winners.
What do you think? Click here to post a comment.
(Disclosures: Anystream is a VideoNuze sponsor and I also provided very brief "sounding-board" reactions to this merger prior to its closing.)
Categories: Advertising, Deals & Financings, Syndicated Video Economy, Technology
Topics: Anystream, Google, Voxant
-
Get Ready for the "Broadband Olympics"
At last, the 2008 Beijing Summer Olympics are upon us. In addition to the many extraordinary athletic performances we can expect, I believe this year's Games will be considered the first "Broadband Olympics." This potentially seminal event for the broadband medium was on my list of "6 Broadband Predictions for 2008."
Through NBC's massive investment in broadband coverage, consumers are going to enjoy a completely
 different Olympic experience, obsoleting many of our traditional responses around missing key Olympic moments: "I just couldn't stay up so late to see that one" or "Hopefully they'll replay that one, I'd really like to see it, or "My kids wanted to see that one but it was during school."
different Olympic experience, obsoleting many of our traditional responses around missing key Olympic moments: "I just couldn't stay up so late to see that one" or "Hopefully they'll replay that one, I'd really like to see it, or "My kids wanted to see that one but it was during school." It's hard to imagine a sporting event, or any other event for that matter, better suited to broadband coverage. The two key challenges of Olympic broadcast coverage have always been the limited shelf space that just one broadcast channel provides (leading to coverage of only the most popular sports, and even then mainly the final rounds) and the time zone differences, which have created an awkward scheduling mix for U.S. prime-time.
NBC, which has been touting its broadband Olympics coverage for months, has addressed these by offering a package of 2,200 hours of live streaming and 3,000 hours of on-demand highlights. The scale of NBC's broadband undertaking is unprecedented, and will easily create a new case study for future broadband event producers.
To get a little glimpse of how just the on-demand portion of coverage will work, yesterday I spoke with Anystream's CEO Fred Singer and COO Bill Holding. Anystream is a key media production and publishing partner of NBC's, essentially handling all of the work flows for the 10,000 video assets that will be available on-demand.
Fred and Bill gave me a sense of the massive complexity involved in ingesting video from the other side of the planet, processing it in a fraction of the customary time allowed, and then distributing it within minutes - according to an elaborate set of rights and business rules - to 16 partners in multiple formats. Often I speak of the complexity involved in the Syndicated Video Economy; there is no better example than the distribution of Olympics' video.
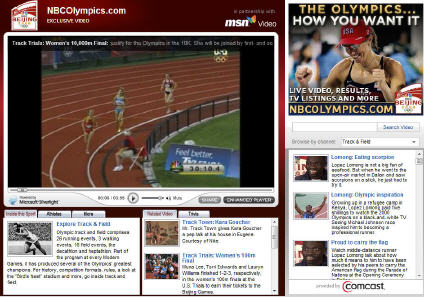 Meanwhile, the broadband Olympics will be a coming out party of sorts for Microsoft's Silverlight, the company's Flash-killer. Tens of millions of new downloads will be driven by the Olympics, and Silverlight's picture-in-picture, rewind and HD features will receive their initial real-world stress test.
Meanwhile, the broadband Olympics will be a coming out party of sorts for Microsoft's Silverlight, the company's Flash-killer. Tens of millions of new downloads will be driven by the Olympics, and Silverlight's picture-in-picture, rewind and HD features will receive their initial real-world stress test.Lastly of course, there are all of us consumers. While unprecedented coverage is available at NBCOlympics.com and elsewhere, to actually enjoy it entails getting down the learning curve of what, where, when and how individual sports will be offered. In short, massive choice requires consumer involvement. Nevertheless, I expect we'll be hearing about some very impressive broadband stats from NBC over the next two weeks and thereafter.
Let the Games begin!
Categories: Broadcasters, Sports
Topics: Anystream, NBC, Olympics
-
Anystream Lands Hearst-Argyle and Brings New Competition in Video Management Space
Anystream, a long-time player in video transcoding, is announcing that its Media Lifecycle Platform has been implemented by 11 of Hearst-Argyle's 29 owned and operated TV stations.
The move suggests even more vigorous competition is coming to the video management/publishing space where players like thePlatform, Brightcove, Maven, ExtendMedia, PermissionTV, Akamai (StreamOS), WorldNow and others have focused.
I sat down with Anystream (note, a periodic VideoNuze sponsor) president Bill Holding and founder/chairman Geoff Allen recently to learn more about their expansion strategy.
Anystream is well-known in the digital media space as it Agility transcoding platform is deployed in over 700 companies. Leveraging this base of relationships and its knowledge of customers' work flows, Anystream is
 now "moving north" by focusing on the video management layer. The core technology comes from Anystream's 2007 acquisition of Cauldron Solutions, which has been built out, renamed as Velocity and integrated with Agility.
now "moving north" by focusing on the video management layer. The core technology comes from Anystream's 2007 acquisition of Cauldron Solutions, which has been built out, renamed as Velocity and integrated with Agility. Anystream's new, broader positioning rests on its belief that the video "Produce-Manage-Monetize" lifecycle elements are deeply linked, and that ultimately a comprehensive, integrated solution will be prized by media companies serious about scaling their broadband video businesses. At the manage layer specifically, Velocity focuses on rights, scheduling, packaging, syndication and asset tracking.
Anystream believes metadata it gains access to, at the start of the video lifecycle through its transcoding role, is a unifying value driver in the video management and monetization phases.
Hearst-Argyle clearly saw the benefits of this approach, citing Anystream's metadata management as opening up new content re-use opportunities and creating competitive advantage. In the press release, Joe Addalia, H-A's director of technology projects, said H-A has cut its production and distribution to online channels "from 30 minutes to 3 1/2 minutes."
I continue to be impressed with how many companies are staking a claim in the broadband video management/publishing space. I'm constantly trying to discern the real competitive differentiators that separate industry players. Like many of you, I often find the landscape quite blurry, with overlapping capabilities. Each player tends to cite its traditional competencies as being the best building blocks from which to build a full scale management/publishing platform.
While it's tempting to say "they can't all be right," the fact that so many players are finding market success today indicates that content owners are not monolithic in their specific requirements and that a giant game of matchmaking seems to be occurring between content owners and video management providers. One day there may be a consensus on who truly has the "best" management platform, but for now that day seems to be far off.
What do you think? Post a comment and let us all know!
Categories: Broadcasters, Technology
Topics: Akamai, Anystream, Brightcove, ExtendMedia, Hearst-Argyle, Maven, PermissionTV, thePlatform, WorldNow
-
Welcome to the "Syndicated Video Economy"
I am ever mindful of the old adage about "missing the forest for the trees" as I try daily to understand the often minor feature differences between competing vendors or the nuances of startups' market positioning. As we all know, when you get too close to something, it's quite easy to lose the larger perspective. So periodically I think it's essential to take a huge step back to try to identify the larger patterns or trends that crystallize from the daily frenzy of deals and announcements.
As a result, I've come to believe that recent industry activity points to an emerging and significant trend: the early formation of what I would term the "syndicated video economy." By this I mean to suggest that I'm
 seeing more and more industry participants' strategies - in both media and technology - start from the proposition that the broadband video industry will only succeed if video assets are widely dispersed and revenue creatively apportioned.
seeing more and more industry participants' strategies - in both media and technology - start from the proposition that the broadband video industry will only succeed if video assets are widely dispersed and revenue creatively apportioned. For content providers the notion of widespread video syndication big change in their business approach. In the past year I think we've observed content providers of all stripes transition from "aggregating eyeballs", to "accessing eyeballs," wherever they may live now or in the future: portals, social networks, portable devices, game consoles, etc. Underlying this shift is the realization that advertising-based revenues are going to fuel the broadband video industry for the foreseeable future. The ad model requires scale and syndication is the best way to deliver it.
This shift by content providers has been accompanied by a loosening of traditional tightly-controlled, scarcity-driven distribution strategies, an acknowledgement that fighting newly-empowered consumers is a futile exercise. The evidence of this shift abounds. Consider the broadcasters like CBS, NBC and Fox, which through their affiliates (Hulu, CBS Audience Network) are syndicating programming to many portals/aggregators (e.g. Yahoo, MSN, AOL, YouTube), social networks (e.g. Facebook, MySpace, Bebo) and others. And Disney's Stage 9 digital studio, which premiered with YouTube and explicitly plans to tap into broadband video hubs. And cable networks like MTV Networks, which is pursuing a plethora of distribution deals. And traditional news-gatherers like local TV stations, newspapers and news services (e.g. Reuters, AP) which have stepped up their activity to scatter their video clips to the Internet's nooks and crannies. And the list goes on and on.
Taking their cue from the media companies' strategy shift, technology entrepreneurs and investors have ramped up their focus on this market opportunity. The prospect of the syndicated video economy blossoming drives news/information distributors such as Voxant, ClipSyndicate, Mochilla, TheNewsMarket and RedLasso, an ad manager such as FreeWheel, and a content accelerator such as Signiant, plus many others. Then there are more established companies guiding areas of their product development process by the prospect of the syndicated video economy's growth: Google, WorldNow, Akamai, thePlatform, Anystream, Maven Networks, Brightcove, PermissionTV and plenty of others (apologies to those I've left out!)
All of this suggests that the eventual "value chain" of the broadband video industry will look quite different than the traditional one (for more on this, I've posted some my slides from late '07 here.) As with all economies, in the nascent syndicated video economy there is vast interdependence among the various players, not to mention shifting market positions and degrees of pricing power and negotiating leverage. It is far too early to gauge who will emerge as the syndicated video economy's winners and losers. But make no mistake, lots of energy and investment will be expended trying to nurture its growth and exploit its opportunities.
Do you see the syndicated video economy forming as well? Post a comment and let us all know!
Categories: Advertising, Aggregators, Broadcasters, Cable Networks, Newspapers, Portals, Startups, Syndicated Video Economy
Topics: Akamai, Anystream, ClipSyndicate, FreeWheel, Google, Mochilla, RedLasso, Signiant, TheNewsMarket, thePlatform, Voxant, WorldNow
Posts for 'Anystream'
|


